

Rates of reaction
Required practical 5, core practicals.

Aims of Experiment
How does the concentration of an acid affect the rate of reaction?
In this experiment you will:
- react magnesium ribbon with different concentrations of hydrochloric acid
- measure the volume of gas produced for each concentration
- use your results to work out how the rate of reaction is affected by the concentration of the acid
How does the concentration of sodium thiosulphate affect the rate of reaction?
- react different concentrations of sodium thiosulfate with hydrochloric acid
- use a stop clock to time how long it takes for the mixture to become cloudy for each concentration
- use your results to work out how the rate of reaction changes as the concentration of the sodium thiosulfate changes
Risk Asessment
As a general rule, eye protection (goggles) must be worn for all practicals.
This risk assessment is provided as an example only, and you must perform your own risk assessment before doing this experiment.
Each group will need:
magnesium strips hydrochloric acid (3 concentrations) 250 ml conical flask 100 ml gas syringe
water bath sodium thiosulfate 50 ml measuring cylinder stop clock or stopwatch 10 ml measuring cylinder
Experiment Set-up
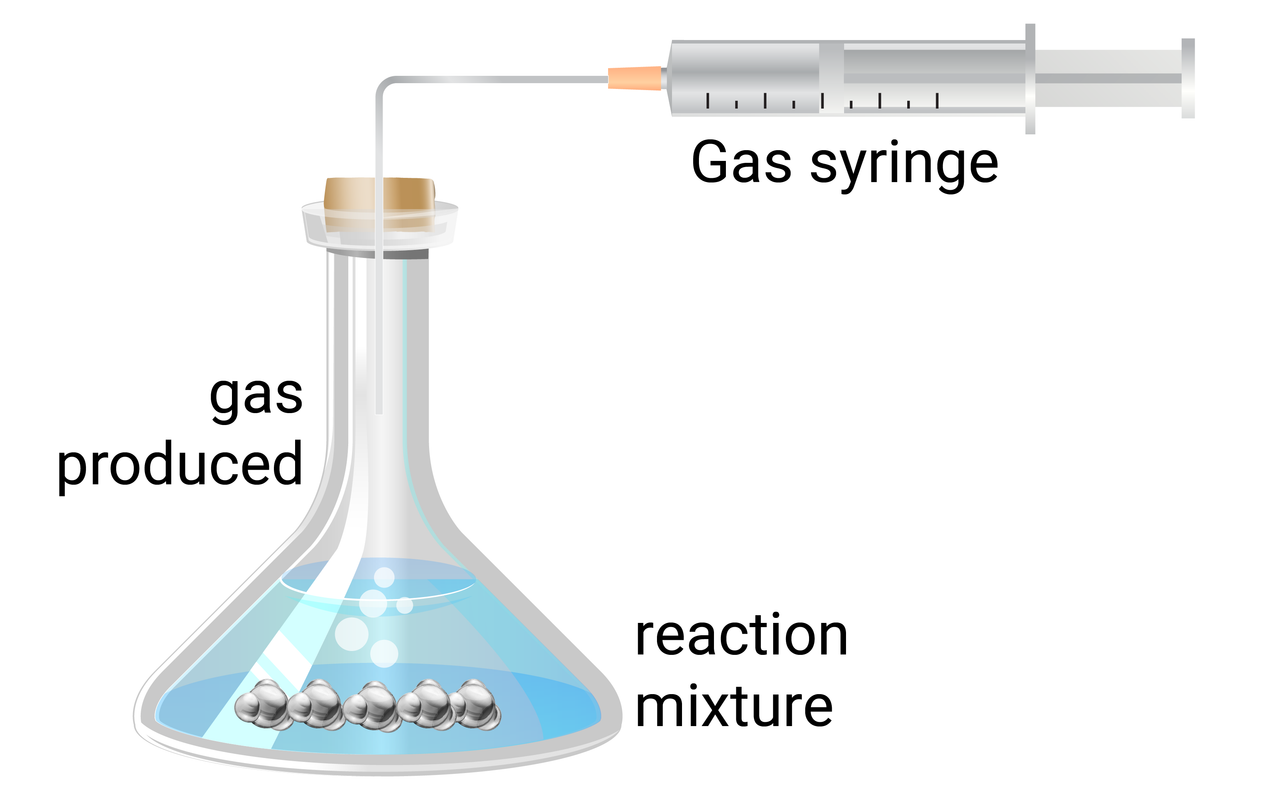
- use a measuring cylinder to add 50 ml of 0.5 mol/dm 3 hydrochloric acid to a conical flask
- add a single 3 cm strip of magnesium ribbon to the flask, and immediately connect the gas syringe and start a timer
- at every 20 seconds, record how much gas has been produced
- when the reaction is complete, clean the apparatus as instructed by your teacher
- repeat steps 1-4 with different concentrations (1.0 mol/dm 3 , and 1.5 mol/dm 3 ) of hydrochloric acid
- use a measuring cylinder to add 10 ml of sodium thiosulfate solution to a conical flask, then add 40 ml of water (concentration 8 g/dm 3 )
- measure and record the temperature of the solution
- place the conical flask on a piece of paper with a black cross drawn on it
- use another measuring cylinder to add 10 ml of hydrochloric acid to the flask, and immediately start a timer
- when the cross is no longer visible record the time taken, and then clean the apparatus as instructed by your teacher
- 20 ml sodium thiosulfate + 30 ml water (concentration 16 g/dm 3 )
- 30 ml sodium thiosulfate + 20 ml water (concentration 24 g/dm 3 )
- 40 ml sodium thiosulfate + 10 ml water (concentration 32 g/dm 3 )
- 50 ml sodium thiosulfate + no water (concentration 40 g/dm 3 ).

Results and Analysis
For each concentration plot a graph on the same set of axes to show:
- volume of gas (ml) on the Y axis (vertical)
- time (s) on the X axis (horizontal)
- a curve of best fit
Use your graph to compare the rates of reaction with different concentrations of hydrochloric acid with magnesium. Use collision theory to explain your findings.
Plot a graph to show:
- mean time (s) on the Y axis (vertical)
- concentration (g/dm 3 ) on the X axis (horizontal)
Describe the relationship between the independent variable and the dependent variable? What were your control variables? Evaluate the two methods that you have used to investigate the effect of concentration on rate of reaction.
Exam Question and Model Answer
A chemical company makes calcium chloride by reacting calcium carbonate and hydrochloric acid. They think they can increase the rate of reaction by increasing the concentration of the acid. Describe an experiment they could do in a laboratory to be able to test this idea.
Level 1 (1-2 marks)
Add calcium carbonate powder to a conical flask. Pour hydrochloric acid into the flask, mix, and immediately attach a gas syringe. Measure how much gas has been produced every 20 seconds, and record in a table. Compare the results to find out which reaction has a faster rate.
Level 2 (3-4 marks)
Add calcium carbonate powder to a conical flask. Pour hydrochloric acid into the flask, mix, and immediately attach a gas syringe. Measure how much gas has been produced every 20 seconds, and record in a table. Repeat these steps with other concentrations of hydrochloric acid as well (keep the volume the same). Compare the results to find out which reaction has a faster rate.
Level 3 (5-6 marks)
Add 5 g of calcium carbonate powder to a conical flask. Using a measuring cylinder, pour and mix 20 ml of 0.5 mol/dm 3 hydrochloric acid into the flask, and immediately attach a gas syringe. Measure how much gas has been produced every 20 seconds, and record in a table. Repeat these steps with 1.0 mol/dm 3 and 1.5 mol/dm 3 hydrochloric acid as well (keeping the temperature, volume of acid the same, and the mass of the calcium carbonate the same). Calculate the rate of each reaction (volume ÷ time), and compare the results to find out which reaction has a faster rate.

COMMENTS
Apparatus1. Eye protection 2. Conical flask (100 cm3) 3. Single-holed rubber bung and delivery tube to fit conical flask (note 1) 4. Troug…
When a gas is produced in a reaction it usually escapes from the reaction vessel, so the mass decreases. This can be used to measure the rate of reaction. For example, the reaction of calcium carbonate with hydrochloric …
Investigating the rate of a reaction. To measure the rate of a reaction, we need to be able to measure: How quickly the reactants are used up OR How quickly the products are …
How does the concentration of an acid affect the rate of reaction? In this experiment you will: react magnesium ribbon with different concentrations of hydrochloric acid; measure the volume of gas produced for each …
Watch the practical video to show learners how to monitor the rate of reaction and identify the effects of changing temperature and concentration, using both initial rate and continuous monitoring methods.
This experiment will alter the concentration in the reaction of hydrochloric acid and magnesium, and determine the effect of this change on the rate of reaction. The effect of concentration …
Students react sodium thiosulfate solution is reacted with acid – a sulfur precipitate forms. The time taken for a certain amount of sulfur to form can be used to indicate the rate of the reaction. Contains kit list and safety instructions.
The rate of reaction between magnesium and dilute hydrochloric acid can be measured using a gas syringe and stopwatch