- Privacy Policy

Home » Quantitative Research – Methods, Types and Analysis

Quantitative Research – Methods, Types and Analysis
Table of Contents
Quantitative research is a systematic investigation that primarily focuses on quantifying data, variables, and relationships. It involves the use of statistical, mathematical, and computational techniques to collect and analyze data. Quantitative research is often used to establish patterns, test hypotheses, and make predictions. It is widely applied in fields such as psychology, sociology, economics, health sciences, and education.

Quantitative Research
Quantitative research is a research approach that seeks to quantify data and generalize results from a sample to a larger population. It relies on structured data collection methods and employs statistical analysis to interpret results. This type of research is objective, and findings are typically presented in numerical form, allowing for comparison and generalization.
Key Characteristics of Quantitative Research :
- Objective : Focuses on numbers and measurable variables rather than subjective opinions.
- Structured : Employs well-defined research questions, hypotheses, and data collection methods.
- Statistical : Utilizes statistical tools to analyze data and validate findings.
- Replicable : Enables repetition of the study to verify results and increase reliability.
Example : A survey on the correlation between exercise frequency and stress levels among adults, using a Likert scale to measure responses.
Types of Quantitative Research
Quantitative research can be categorized into several types, each serving a specific purpose. The most common types include descriptive , correlational , experimental , and causal-comparative research.
1. Descriptive Research
Definition : Descriptive research describes characteristics or behaviors of a population without examining relationships or causes. It provides a snapshot of current conditions or attitudes.
Purpose : To gather information and create an overview of a particular phenomenon, population, or condition.
Example : A survey describing the demographics and academic performance of students at a university.
2. Correlational Research
Definition : Correlational research examines the relationship between two or more variables but does not imply causation. It analyzes patterns to determine if variables are associated or occur together.
Purpose : To identify associations or trends among variables without establishing cause and effect.
Example : Investigating the relationship between social media use and self-esteem among teenagers.
3. Experimental Research
Definition : Experimental research manipulates one or more independent variables to observe the effect on a dependent variable, establishing cause-and-effect relationships. This type of research involves control and experimental groups.
Purpose : To test hypotheses by isolating and controlling variables to establish causality.
Example : Testing the effect of a new medication on blood pressure by administering it to one group (experimental) and comparing it to a placebo group (control).
4. Causal-Comparative (Ex Post Facto) Research
Definition : Causal-comparative research investigates the cause-effect relationship between variables when experimental manipulation is not possible. It compares groups that differ on a particular variable to determine the effect of that variable.
Purpose : To explore cause-and-effect relationships retrospectively by comparing pre-existing groups.
Example : Studying the impact of different teaching methods on student performance by comparing classes taught with traditional versus technology-assisted instruction.
Quantitative Research Methods
Quantitative research methods focus on systematic data collection and analysis using structured techniques. Common methods include surveys , experiments , and observations .
Definition : Surveys are a popular quantitative method that involves asking participants standardized questions to collect data on their opinions, behaviors, or demographics. Surveys can be conducted via questionnaires, interviews, or online forms.
Purpose : To gather data from a large sample, allowing researchers to make inferences about the larger population.
Example : Conducting a survey to collect customer satisfaction data from a random sample of customers in a retail store.
Advantages :
- Cost-effective and time-efficient for large sample sizes.
- Provides structured data that is easy to analyze statistically.
Disadvantages :
- Limited depth, as responses are often restricted to specific options.
- Potential for response bias, where participants may not answer truthfully.
2. Experiments
Definition : Experiments involve manipulating one or more variables in a controlled environment to observe the effect on another variable. Experiments are often conducted in laboratories or controlled settings to maintain precision and limit external influences.
Purpose : To test hypotheses and establish cause-and-effect relationships.
Example : Conducting a laboratory experiment to test the effect of light exposure on sleep patterns.
- High level of control over variables.
- Establishes causality, which can support theory-building.
- Limited external validity, as findings may not always apply outside of the controlled setting.
- Ethical considerations may limit experimentation on certain subjects or groups.
3. Observations
Definition : Observational research involves systematically observing and recording behavior or events as they occur naturally, without interference. While often used in qualitative research, structured observational methods can yield quantitative data.
Purpose : To gather real-world data in a non-intrusive manner.
Example : Observing customer behavior in a store to track time spent in different areas and identify shopping patterns.
- Provides data on actual behaviors rather than self-reported responses.
- Useful for gathering data on situations where surveys or experiments may not be feasible.
- Observer bias may affect results.
- Can be time-consuming, especially if behaviors are infrequent or complex.
Data Collection Tools in Quantitative Research
Quantitative research relies on various tools to collect and quantify data, including:
- Questionnaires : Standardized forms with close-ended questions, often using scales (e.g., Likert scale) for responses.
- Tests and Assessments : Used to measure knowledge, skills, or other measurable attributes.
- Digital Tracking Tools : Software or digital applications that collect data, such as website traffic metrics or physiological monitoring devices.
Data Analysis in Quantitative Research
Data analysis in quantitative research involves statistical techniques to interpret numerical data and determine relationships or trends. Key techniques include descriptive statistics , inferential statistics , and correlation analysis .
1. Descriptive Statistics
Definition : Descriptive statistics summarize and organize data, providing basic information such as mean, median, mode, standard deviation, and range.
Purpose : To give an overview of the dataset, allowing researchers to understand general trends and distributions.
Example : Calculating the average test scores of students in a school to assess overall performance.
Common Measures :
- Mean : Average of all data points.
- Median : Middle value of an ordered dataset.
- Standard Deviation : Measure of variability around the mean.
2. Inferential Statistics
Definition : Inferential statistics allow researchers to make predictions or inferences about a population based on sample data. Techniques include hypothesis testing, t-tests, ANOVA, and regression analysis.
Purpose : To determine if observed results are statistically significant and can be generalized to a larger population.
Example : Using a t-test to compare average scores between two different teaching methods to see if one is significantly more effective.
Common Tests :
- t-Test : Compares the means of two groups to determine if they are statistically different.
- ANOVA (Analysis of Variance) : Compares means among three or more groups.
- Regression Analysis : Examines the relationship between independent and dependent variables.
3. Correlation Analysis
Definition : Correlation analysis measures the strength and direction of the relationship between two variables. It is used to determine if changes in one variable are associated with changes in another.
Purpose : To identify associations between variables without implying causation.
Example : Calculating the correlation coefficient between screen time and academic performance to determine if there is an association.
- Pearson Correlation Coefficient (r) : Measures linear correlation between two continuous variables.
- Spearman’s Rank Correlation : Measures correlation between two ranked variables.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Quantitative Research
- Objective : Minimizes researcher bias by focusing on numerical data.
- Generalizable : Findings from large, random samples can often be applied to a broader population.
- Replicable : Structured methods make it possible for other researchers to replicate studies and verify results.
Disadvantages
- Limited Depth : Quantitative research often lacks the depth of qualitative insights.
- Rigid Structure : Limited flexibility in data collection and analysis.
- Potential Bias : Response or sampling biases can affect results, especially in survey-based studies.
Tips for Conducting Effective Quantitative Research
- Define Clear Objectives : Develop specific research questions or hypotheses to guide the study.
- Choose the Right Method : Select a quantitative method that aligns with the research goals and type of data needed.
- Ensure Sample Representativeness : Use appropriate sampling techniques to ensure results can be generalized.
- Employ Proper Statistical Tools : Choose analysis techniques that match the nature of the data and research questions.
- Interpret Results Accurately : Avoid overgeneralizing findings and consider limitations when interpreting results.
Quantitative research provides a structured, objective approach to investigating research questions, allowing for statistical analysis, pattern recognition, and hypothesis testing. With methods like surveys, experiments, and observational studies, quantitative research offers valuable insights across diverse fields, from social sciences to healthcare. By applying rigorous statistical analysis, researchers can draw meaningful conclusions, contributing to the body of scientific knowledge and helping inform data-driven decisions.
- Creswell, J. W., & Creswell, J. D. (2018). Research Design: Qualitative, Quantitative, and Mixed Methods Approaches (5th ed.). SAGE Publications.
- Punch, K. F. (2014). Introduction to Social Research: Quantitative and Qualitative Approaches (3rd ed.). SAGE Publications.
- Field, A. (2013). Discovering Statistics Using IBM SPSS Statistics (4th ed.). SAGE Publications.
- Trochim, W. M., & Donnelly, J. P. (2008). The Research Methods Knowledge Base (3rd ed.). Cengage Learning.
- Babbie, E. R. (2021). The Practice of Social Research (15th ed.). Cengage Learning.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Questionnaire – Definition, Types, and Examples

Qualitative Research – Methods, Analysis Types...

Explanatory Research – Types, Methods, Guide

One-to-One Interview – Methods and Guide

Research Methods – Types, Examples and Guide

Textual Analysis – Types, Examples and Guide
Educational resources and simple solutions for your research journey

What is Quantitative Research? Definition, Methods, Types, and Examples

If you’re wondering what is quantitative research and whether this methodology works for your research study, you’re not alone. If you want a simple quantitative research definition , then it’s enough to say that this is a method undertaken by researchers based on their study requirements. However, to select the most appropriate research for their study type, researchers should know all the methods available.
Selecting the right research method depends on a few important criteria, such as the research question, study type, time, costs, data availability, and availability of respondents. There are two main types of research methods— quantitative research and qualitative research. The purpose of quantitative research is to validate or test a theory or hypothesis and that of qualitative research is to understand a subject or event or identify reasons for observed patterns.
Quantitative research methods are used to observe events that affect a particular group of individuals, which is the sample population. In this type of research, diverse numerical data are collected through various methods and then statistically analyzed to aggregate the data, compare them, or show relationships among the data. Quantitative research methods broadly include questionnaires, structured observations, and experiments.
Here are two quantitative research examples:
- Satisfaction surveys sent out by a company regarding their revamped customer service initiatives. Customers are asked to rate their experience on a rating scale of 1 (poor) to 5 (excellent).
- A school has introduced a new after-school program for children, and a few months after commencement, the school sends out feedback questionnaires to the parents of the enrolled children. Such questionnaires usually include close-ended questions that require either definite answers or a Yes/No option. This helps in a quick, overall assessment of the program’s outreach and success.

Table of Contents
What is quantitative research ? 1,2
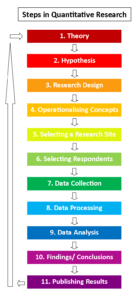
The steps shown in the figure can be grouped into the following broad steps:
- Theory : Define the problem area or area of interest and create a research question.
- Hypothesis : Develop a hypothesis based on the research question. This hypothesis will be tested in the remaining steps.
- Research design : In this step, the most appropriate quantitative research design will be selected, including deciding on the sample size, selecting respondents, identifying research sites, if any, etc.
- Data collection : This process could be extensive based on your research objective and sample size.
- Data analysis : Statistical analysis is used to analyze the data collected. The results from the analysis help in either supporting or rejecting your hypothesis.
- Present results : Based on the data analysis, conclusions are drawn, and results are presented as accurately as possible.
Quantitative research characteristics 4
- Large sample size : This ensures reliability because this sample represents the target population or market. Due to the large sample size, the outcomes can be generalized to the entire population as well, making this one of the important characteristics of quantitative research .
- Structured data and measurable variables: The data are numeric and can be analyzed easily. Quantitative research involves the use of measurable variables such as age, salary range, highest education, etc.
- Easy-to-use data collection methods : The methods include experiments, controlled observations, and questionnaires and surveys with a rating scale or close-ended questions, which require simple and to-the-point answers; are not bound by geographical regions; and are easy to administer.
- Data analysis : Structured and accurate statistical analysis methods using software applications such as Excel, SPSS, R. The analysis is fast, accurate, and less effort intensive.
- Reliable : The respondents answer close-ended questions, their responses are direct without ambiguity and yield numeric outcomes, which are therefore highly reliable.
- Reusable outcomes : This is one of the key characteristics – outcomes of one research can be used and replicated in other research as well and is not exclusive to only one study.

Quantitative research methods 5
Quantitative research methods are classified into two types—primary and secondary.
Primary quantitative research method:
In this type of quantitative research , data are directly collected by the researchers using the following methods.
– Survey research : Surveys are the easiest and most commonly used quantitative research method . They are of two types— cross-sectional and longitudinal.
->Cross-sectional surveys are specifically conducted on a target population for a specified period, that is, these surveys have a specific starting and ending time and researchers study the events during this period to arrive at conclusions. The main purpose of these surveys is to describe and assess the characteristics of a population. There is one independent variable in this study, which is a common factor applicable to all participants in the population, for example, living in a specific city, diagnosed with a specific disease, of a certain age group, etc. An example of a cross-sectional survey is a study to understand why individuals residing in houses built before 1979 in the US are more susceptible to lead contamination.
->Longitudinal surveys are conducted at different time durations. These surveys involve observing the interactions among different variables in the target population, exposing them to various causal factors, and understanding their effects across a longer period. These studies are helpful to analyze a problem in the long term. An example of a longitudinal study is the study of the relationship between smoking and lung cancer over a long period.
– Descriptive research : Explains the current status of an identified and measurable variable. Unlike other types of quantitative research , a hypothesis is not needed at the beginning of the study and can be developed even after data collection. This type of quantitative research describes the characteristics of a problem and answers the what, when, where of a problem. However, it doesn’t answer the why of the problem and doesn’t explore cause-and-effect relationships between variables. Data from this research could be used as preliminary data for another study. Example: A researcher undertakes a study to examine the growth strategy of a company. This sample data can be used by other companies to determine their own growth strategy.

– Correlational research : This quantitative research method is used to establish a relationship between two variables using statistical analysis and analyze how one affects the other. The research is non-experimental because the researcher doesn’t control or manipulate any of the variables. At least two separate sample groups are needed for this research. Example: Researchers studying a correlation between regular exercise and diabetes.
– Causal-comparative research : This type of quantitative research examines the cause-effect relationships in retrospect between a dependent and independent variable and determines the causes of the already existing differences between groups of people. This is not a true experiment because it doesn’t assign participants to groups randomly. Example: To study the wage differences between men and women in the same role. For this, already existing wage information is analyzed to understand the relationship.
– Experimental research : This quantitative research method uses true experiments or scientific methods for determining a cause-effect relation between variables. It involves testing a hypothesis through experiments, in which one or more independent variables are manipulated and then their effect on dependent variables are studied. Example: A researcher studies the importance of a drug in treating a disease by administering the drug in few patients and not administering in a few.
The following data collection methods are commonly used in primary quantitative research :
- Sampling : The most common type is probability sampling, in which a sample is chosen from a larger population using some form of random selection, that is, every member of the population has an equal chance of being selected. The different types of probability sampling are—simple random, systematic, stratified, and cluster sampling.
- Interviews : These are commonly telephonic or face-to-face.
- Observations : Structured observations are most commonly used in quantitative research . In this method, researchers make observations about specific behaviors of individuals in a structured setting.
- Document review : Reviewing existing research or documents to collect evidence for supporting the quantitative research .
- Surveys and questionnaires : Surveys can be administered both online and offline depending on the requirement and sample size.
The data collected can be analyzed in several ways in quantitative research , as listed below:
- Cross-tabulation —Uses a tabular format to draw inferences among collected data
- MaxDiff analysis —Gauges the preferences of the respondents
- TURF analysis —Total Unduplicated Reach and Frequency Analysis; helps in determining the market strategy for a business
- Gap analysis —Identify gaps in attaining the desired results
- SWOT analysis —Helps identify strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats of a product, service, or organization
- Text analysis —Used for interpreting unstructured data
Secondary quantitative research methods :
This method involves conducting research using already existing or secondary data. This method is less effort intensive and requires lesser time. However, researchers should verify the authenticity and recency of the sources being used and ensure their accuracy.
The main sources of secondary data are:
- The Internet
- Government and non-government sources
- Public libraries
- Educational institutions
- Commercial information sources such as newspapers, journals, radio, TV

When to use quantitative research 6
Here are some simple ways to decide when to use quantitative research . Use quantitative research to:
- recommend a final course of action
- find whether a consensus exists regarding a particular subject
- generalize results to a larger population
- determine a cause-and-effect relationship between variables
- describe characteristics of specific groups of people
- test hypotheses and examine specific relationships
- identify and establish size of market segments
A research case study to understand when to use quantitative research 7
Context: A study was undertaken to evaluate a major innovation in a hospital’s design, in terms of workforce implications and impact on patient and staff experiences of all single-room hospital accommodations. The researchers undertook a mixed methods approach to answer their research questions. Here, we focus on the quantitative research aspect.
Research questions : What are the advantages and disadvantages for the staff as a result of the hospital’s move to the new design with all single-room accommodations? Did the move affect staff experience and well-being and improve their ability to deliver high-quality care?
Method: The researchers obtained quantitative data from three sources:
- Staff activity (task time distribution): Each staff member was shadowed by a researcher who observed each task undertaken by the staff, and logged the time spent on each activity.
- Staff travel distances : The staff were requested to wear pedometers, which recorded the distances covered.
- Staff experience surveys : Staff were surveyed before and after the move to the new hospital design.
Results of quantitative research : The following observations were made based on quantitative data analysis:
- The move to the new design did not result in a significant change in the proportion of time spent on different activities.
- Staff activity events observed per session were higher after the move, and direct care and professional communication events per hour decreased significantly, suggesting fewer interruptions and less fragmented care.
- A significant increase in medication tasks among the recorded events suggests that medication administration was integrated into patient care activities.
- Travel distances increased for all staff, with highest increases for staff in the older people’s ward and surgical wards.
- Ratings for staff toilet facilities, locker facilities, and space at staff bases were higher but those for social interaction and natural light were lower.
Advantages of quantitative research 1,2
When choosing the right research methodology, also consider the advantages of quantitative research and how it can impact your study.
- Quantitative research methods are more scientific and rational. They use quantifiable data leading to objectivity in the results and avoid any chances of ambiguity.
- This type of research uses numeric data so analysis is relatively easier .
- In most cases, a hypothesis is already developed and quantitative research helps in testing and validatin g these constructed theories based on which researchers can make an informed decision about accepting or rejecting their theory.
- The use of statistical analysis software ensures quick analysis of large volumes of data and is less effort intensive.
- Higher levels of control can be applied to the research so the chances of bias can be reduced.
- Quantitative research is based on measured value s, facts, and verifiable information so it can be easily checked or replicated by other researchers leading to continuity in scientific research.
Disadvantages of quantitative research 1,2
Quantitative research may also be limiting; take a look at the disadvantages of quantitative research.
- Experiments are conducted in controlled settings instead of natural settings and it is possible for researchers to either intentionally or unintentionally manipulate the experiment settings to suit the results they desire.
- Participants must necessarily give objective answers (either one- or two-word, or yes or no answers) and the reasons for their selection or the context are not considered.
- Inadequate knowledge of statistical analysis methods may affect the results and their interpretation.
- Although statistical analysis indicates the trends or patterns among variables, the reasons for these observed patterns cannot be interpreted and the research may not give a complete picture.
- Large sample sizes are needed for more accurate and generalizable analysis .
- Quantitative research cannot be used to address complex issues.

Frequently asked questions on quantitative research
Q: What is the difference between quantitative research and qualitative research? 1
A: The following table lists the key differences between quantitative research and qualitative research, some of which may have been mentioned earlier in the article.
Q: What is the difference between reliability and validity? 8,9
A: The term reliability refers to the consistency of a research study. For instance, if a food-measuring weighing scale gives different readings every time the same quantity of food is measured then that weighing scale is not reliable. If the findings in a research study are consistent every time a measurement is made, then the study is considered reliable. However, it is usually unlikely to obtain the exact same results every time because some contributing variables may change. In such cases, a correlation coefficient is used to assess the degree of reliability. A strong positive correlation between the results indicates reliability.
Validity can be defined as the degree to which a tool actually measures what it claims to measure. It helps confirm the credibility of your research and suggests that the results may be generalizable. In other words, it measures the accuracy of the research.
The following table gives the key differences between reliability and validity.
Q: What is mixed methods research? 10
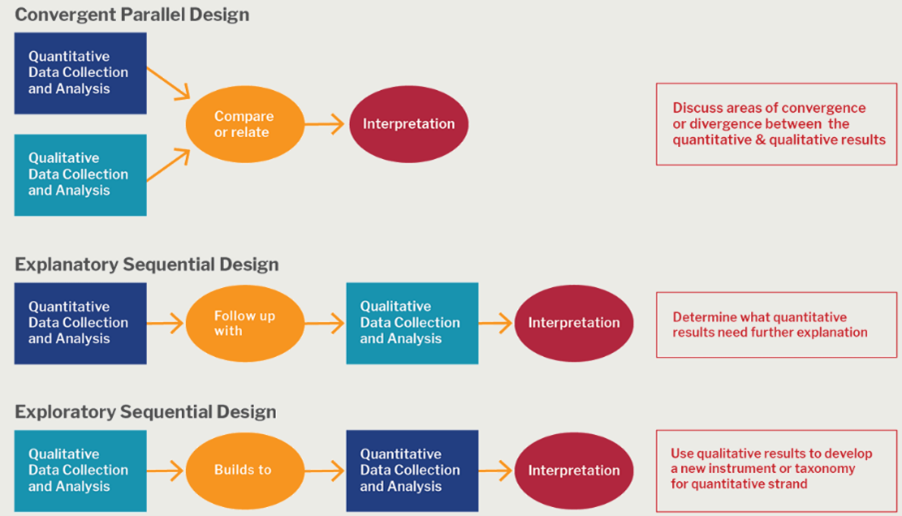
A: A mixed methods approach combines the characteristics of both quantitative research and qualitative research in the same study. This method allows researchers to validate their findings, verify if the results observed using both methods are complementary, and explain any unexpected results obtained from one method by using the other method. A mixed methods research design is useful in case of research questions that cannot be answered by either quantitative research or qualitative research alone. However, this method could be more effort- and cost-intensive because of the requirement of more resources. The figure 3 shows some basic mixed methods research designs that could be used.
Thus, quantitative research is the appropriate method for testing your hypotheses and can be used either alone or in combination with qualitative research per your study requirements. We hope this article has provided an insight into the various facets of quantitative research , including its different characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages, and a few tips to quickly understand when to use this research method.
References
- Qualitative vs quantitative research: Differences, examples, & methods. Simply Psychology. Accessed Feb 28, 2023. https://simplypsychology.org/qualitative-quantitative.html#Quantitative-Research
- Your ultimate guide to quantitative research. Qualtrics. Accessed February 28, 2023. https://www.qualtrics.com/uk/experience-management/research/quantitative-research/
- The steps of quantitative research. Revise Sociology. Accessed March 1, 2023. https://revisesociology.com/2017/11/26/the-steps-of-quantitative-research/
- What are the characteristics of quantitative research? Marketing91. Accessed March 1, 2023. https://www.marketing91.com/characteristics-of-quantitative-research/
- Quantitative research: Types, characteristics, methods, & examples. ProProfs Survey Maker. Accessed February 28, 2023. https://www.proprofssurvey.com/blog/quantitative-research/#Characteristics_of_Quantitative_Research
- Qualitative research isn’t as scientific as quantitative methods. Kmusial blog. Accessed March 5, 2023. https://kmusial.wordpress.com/2011/11/25/qualitative-research-isnt-as-scientific-as-quantitative-methods/
- Maben J, Griffiths P, Penfold C, et al. Evaluating a major innovation in hospital design: workforce implications and impact on patient and staff experiences of all single room hospital accommodation. Southampton (UK): NIHR Journals Library; 2015 Feb. (Health Services and Delivery Research, No. 3.3.) Chapter 5, Case study quantitative data findings. Accessed March 6, 2023. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK274429/
- McLeod, S. A. (2007). What is reliability? Simply Psychology. www.simplypsychology.org/reliability.html
- Reliability vs validity: Differences & examples. Accessed March 5, 2023. https://statisticsbyjim.com/basics/reliability-vs-validity/
- Mixed methods research. Community Engagement Program. Harvard Catalyst. Accessed February 28, 2023. https://catalyst.harvard.edu/community-engagement/mmr
Editage All Access is a subscription-based platform that unifies the best AI tools and services designed to speed up, simplify, and streamline every step of a researcher’s journey. The Editage All Access Pack is a one-of-a-kind subscription that unlocks full access to an AI writing assistant, literature recommender, journal finder, scientific illustration tool, and exclusive discounts on professional publication services from Editage.
Based on 22+ years of experience in academia, Editage All Access empowers researchers to put their best research forward and move closer to success. Explore our top AI Tools pack, AI Tools + Publication Services pack, or Build Your Own Plan. Find everything a researcher needs to succeed, all in one place – Get All Access now starting at just $14 a month !
Related Posts

How to Calculate H-Index in Google Scholar?

What is a good h-index?
- (855) 776-7763
Training Maker
All Products
Qualaroo Insights
ProProfs.com
- Get Started Free
FREE. All Features. FOREVER!
Try our Forever FREE account with all premium features!
What Is Quantitative Research? Types, Characteristics & Methods

Market Research Specialist
Emma David, a seasoned market research professional, specializes in employee engagement, survey administration, and data management. Her expertise in leveraging data for informed decisions has positively impacted several brands, enhancing their market position.

Ever wondered how companies figure out what we want? The answer lies in numbers. Quantitative research is the art of turning numerical data into valuable insights by uncovering hidden trends and patterns.
From understanding customer behaviors to making smarter business decisions, numbers can tell a powerful story.
In this blog, we’ll explore how this research method can help your business and learn about its types, examples, and expert-backed tips.
What Is Quantitative Research?
Quantitative research is a method that uses numbers and statistics to gather precise, measurable data on the research subject.
Offering numbers and stats-based insights, this research methodology is a crucial part of primary research and helps understand how well an organizational decision will work out.
This approach mainly uses online surveys, questionnaires , polls , and quizzes to collect measurable and unbiased data from large groups.
For example, qualitative research can let you know whether your product is a hit or miss, but quantitative data allows you to know exactly what percentage of consumers like it, and what numbers think you still need to improve. As a result of this precision , you can make decisions that are likely to be more in tune with the market demands
Quantitative research thus provides crucial, numbers-based insights that help organizations make informed decisions and predict outcomes effectively .
What Is the Purpose of Quantitative Research?
Quantitative research is the backbone of evidence-based decision-making. Its core purpose is to transform raw data into actionable insights. Researchers can uncover hidden patterns, trends, and relationships that might otherwise go unnoticed by employing statistical methods to analyze numerical information.
Here’s an in-depth analysis of its true objectives:
- Prediction: Quantitative research excels at forecasting future trends or outcomes. By identifying historical patterns, researchers can model potential scenarios and make informed predictions.
- Generalization: By studying a representative sample, researchers can draw conclusions about a larger population. This allows for extrapolating findings to broader groups, providing valuable insights for businesses, policymakers, and scientists.
- Testing Hypotheses: Quantitative research is essential for testing theories and hypotheses. By collecting empirical data, researchers can determine if their assumptions are supported by evidence.
- Measuring Outcomes: Evaluating the effectiveness of interventions or programs is a key application of quantitative research. By tracking specific metrics, researchers can assess the impact of initiatives and make necessary adjustments.
- Understanding Relationships: This research method helps uncover correlations and causal relationships between variables. By identifying how factors influence each other, researchers can develop strategies to optimize outcomes.
What Are the Types and Examples of Quantitative Research?
Quantitative research is usually conducted using two methods. They are-
- Primary quantitative research methods
- Secondary quantitative research methods
Let’s discuss each type in detail.
I. Primary Methods
Primary quantitative research is the most popular method of conducting market research. This method differs from others in that the researcher collects data firsthand instead of using data collected from previous research.
There are multiple types of primary quantitative research. They can be distinguished based on three distinctive aspects: Techniques & types of studies, Data collection methodologies, and Data analysis techniques .
A. Techniques & Types of Studies:
1. survey research.
Surveys are the easiest, most common, and one of the most sought-after quantitative research techniques. The main aim of a survey is to widely gather and describe the characteristics of a target population or customers. Surveys are the foremost quantitative method preferred by both small and large organizations.
Surveys can be conducted using various methods, such as online polls, web-based surveys, paper questionnaires, phone calls, or face-to-face interviews. Survey research allows organizations to understand customer opinions, preferences, and behavior, making it crucial for market research and decision-making.
You can watch this quick video to learn more about creating surveys.
Watch: How to Create a Survey Using ProProfs Survey Maker
Surveys, again, are of two types:
2. Cross-Sectional Surveys
Cross-sectional surveys are used to collect data from a sample of the target population at a specific point in time. Researchers evaluate various variables simultaneously to understand the relationships and patterns within the data.
Cross-sectional surveys are popular in retail, small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), and healthcare industries, where they assess customer satisfaction, market trends, and product feedback.
3. Longitudinal Surveys
Longitudinal surveys are conducted over an extended period, observing changes in respondent behavior and thought processes.
Researchers gather data from the same sample multiple times, enabling them to study trends and developments over time. These surveys are valuable in fields such as medicine, applied sciences, and market trend analysis.
4. Correlational Research:
Correlational research aims to establish relationships between two or more variables.
Researchers use statistical analysis to identify patterns and trends in the data, but it does not determine causality between the variables. This method helps understand how changes in one variable may impact another.
Examples of correlational research questions include studying the relationship between stress and depression, fame and money, or classroom activities and student performance.
5. Causal-Comparative Research:
Causal-comparative research, or quasi-experimental research, seeks to determine cause-and-effect relationships between variables.
Researchers analyze how an independent variable influences a dependent variable, but they do not manipulate the independent variable. Instead, they observe and compare different groups to conclude.
Causal-comparative research is useful when it’s not ethical or feasible to conduct true experiments.
Questions for this type of research include analyzing the effect of training programs on employee performance, studying the influence of customer support on client retention, investigating the impact of supply chain efficiency on cost reduction, etc.
6. Experimental Research:
Experimental research is based on testing theories to validate or disprove them. Researchers conduct experiments and manipulate variables to observe their impact on the outcomes.
This type of research is prevalent in natural and social sciences, and it is a powerful method to establish cause-and-effect relationships. By randomly assigning participants to experimental and control groups, researchers can draw more confident conclusions.
Examples of experimental research include studying the effectiveness of a new drug, the impact of teaching methods on student performance, or the outcomes of a marketing campaign.
B. Data Collection Methodologies
After defining research objectives, the next significant step in primary quantitative research is data collection. This involves using two main methods: sampling and conducting surveys or polls. Quantitative research can also be categorized according to their sampling methods .
In quantitative research, there are two primary sampling methods: Probability and Non-probability sampling .
1. Probability Sampling
In probability sampling, researchers use the concept of probability to create samples from a population. This method ensures that every individual in the target audience has an equal chance of being selected for the sample.
There are four main types of probability sampling:
- Simple random sampling : Here, the elements or participants of a sample are selected randomly, and this technique is used in studies that are conducted over considerably large audiences. It works well for large target populations.
- Stratified random sampling : In this method, the entire population is divided into strata or groups, and the sample members get chosen randomly from these strata only. It is always ensured that different segregated strata do not overlap with each other.
- Cluster sampling : Here, researchers divide the population into clusters, often based on geography or demographics. Then, random clusters are selected for the sample.
- Systematic sampling : In this method, only the starting point of the sample is randomly chosen. All the other participants are chosen using a fixed interval. Researchers calculate this interval by dividing the size of the study population by the target sample size.

2. Non-probability Sampling
Non-probability sampling is a method where the researcher’s knowledge and experience guide the selection of samples. This approach doesn’t give all members of the target population an equal chance of being included in the sample.
There are five non-probability sampling models:
- Convenience sampling : The elements or participants are chosen on the basis of their nearness to the researcher. The people in close proximity can be studied and analyzed easily and quickly, as there is no other selection criterion involved. Researchers simply choose samples based on what is most convenient for them.
- Consecutive sampling : Similar to convenience sampling, researchers select samples one after another over a significant period. They can opt for a single participant or a group of samples to conduct quantitative research in a consecutive manner for a significant period of time. Once this is over, they can conduct the research from the start.
- Quota sampling : With quota sampling, researchers use their understanding of target traits and personalities to form groups (strata). They then choose samples from each stratum based on their own judgment.
- Snowball sampling : This method is used where the target audiences are difficult to contact and interviewed for data collection. Researchers start with a few participants and then ask them to refer others, creating a snowball effect.
- Judgmental sampling : In judgmental sampling, researchers rely solely on their experience and research skills to handpick samples that they believe will be most relevant to the study.
C. Data Analysis Techniques
Once the raw data is collected, the next step in primary quantitative research is data analysis. This crucial process helps draw inferences from the research. It’s essential to connect the results with the objectives and determine their statistical significance.
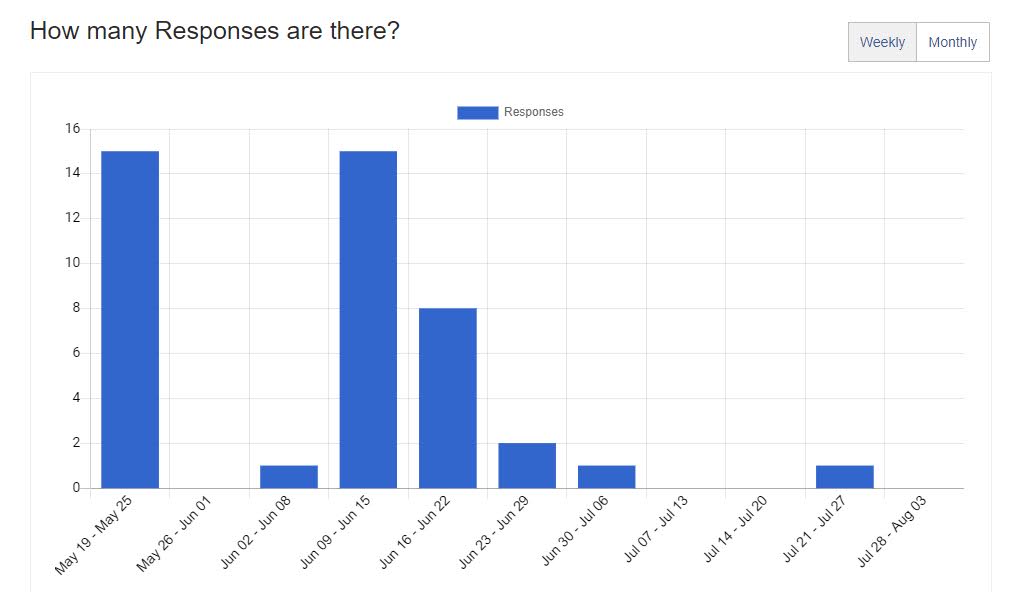
To analyze the quantitative data accurately, you’ll need to use specific statistical methods such as:
- SWOT Analysis : This stands for Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats analysis. Organizations use SWOT analysis to evaluate their performance internally and externally. It helps develop effective improvement strategies.
- Conjoint Analysis : This market research method uncovers how individuals make complex purchasing decisions. It involves considering trade-offs in their daily activities when choosing from a list of product/service options.
- Cross-tabulation : A preliminary statistical market analysis method that reveals relationships, patterns, and trends within various research study parameters.
- TURF Analysis : Short for Totally Unduplicated Reach and Frequency Analysis, this method helps analyze the reach and frequency of favorable communication sources. It provides insights into the potential of a target market.
By using these statistical techniques and inferential statistics methods like confidence intervals and margin of error , you can draw meaningful insights from your primary quantitative research that you can use in making informed decisions.
II. Secondary Methods
Secondary quantitative research, also known as desk research, is a valuable method that uses existing data, called secondary data.
Instead of collecting new data, researchers analyze and combine already available information to enhance their research. This approach involves gathering quantitative data from various sources such as the internet, government databases, libraries, and research reports.
Secondary quantitative research is crucial in validating data collected through primary quantitative research. It helps reinforce or challenge existing findings.
Here are five commonly used secondary quantitative research methods :
A. Data Available on the Internet:
The Internet has become a vast repository of data, making it easier for researchers to access a wealth of information. Online databases, websites, and research repositories provide valuable quantitative data for researchers to analyze and validate their primary research findings.
B. Government and Non-Government Sources:
Government agencies and non-government organizations often conduct extensive research and publish reports. These reports cover a wide range of topics, providing researchers with reliable and comprehensive data for quantitative analysis.
C. Public Libraries:
While less commonly used in the digital age, public libraries still hold valuable research reports, historical data, and publications that can contribute to quantitative research.
D. Educational Institutions:
Educational institutions frequently conduct research on various subjects. Their research reports and publications can serve as valuable sources of information for researchers, validating and supporting primary quantitative research outcomes.
E. Commercial Information Sources:
Commercial sources such as local newspapers, journals, magazines, and media outlets often publish relevant data on economic trends, market research, and demographic analyses. Researchers can access this data to supplement their own findings and draw better conclusions.
Now, let’s discuss some real-world examples of quantitative research.
Here are two excellent examples of quantitative research methods used by highly distinguished business and consulting organizations. Both examples show how different types of analysis can be performed with qualitative approaches and how the analysis is done once the data is collected.
1. STEP Project Global Consortium / KPMG 2019 Global Family Business Survey
This research utilized quantitative methods to identify ways that kept the family businesses sustainably profitable with time.
The study also identified the ways in which the family business behavior changed with demographic changes and had “why” and “how” questions. Their qualitative research methods allowed the KPMG team to dig deeper into the mindsets and perspectives of the business owners and uncover unexpected research avenues as well.
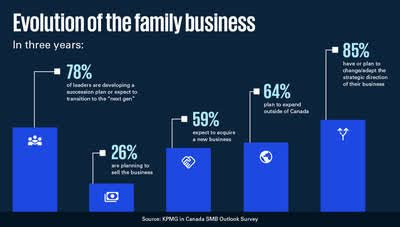
It was a joint effort in which STEP Project Global Consortium collected 26 cases, and KPMG collected 11 cases.
The research reached the stage of data analysis in 2020, and the analysis process spanned over 4 stages.
The results, which were also the reasons why family businesses tend to lose their strength with time, were found to be:
- Family governance
- Family business legacy
2. EY Seren Teams Research 2020
This is yet another commendable example of qualitative research where the EY Seren Team digs into the unexplored depths of human behavior and how it affected their brand or service expectations.
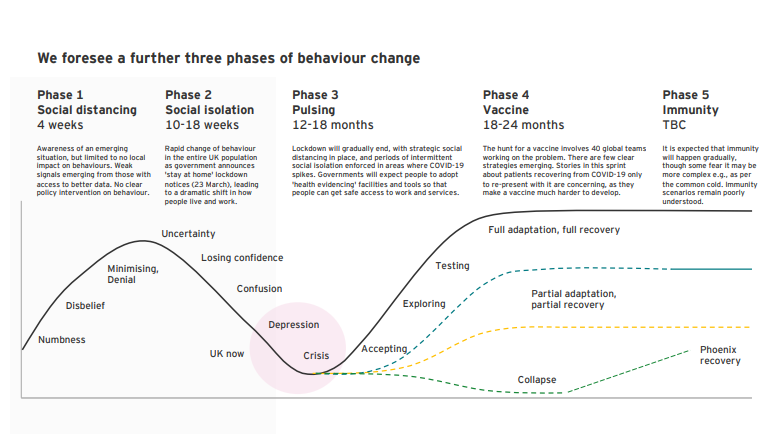
The research was done across 200+ sources and involved in-depth virtual interviews with people in their homes, exploring their current needs and wishes. It also involved diary studies across the entire UK customer base to analyze human behavior changes and patterns.
The study also included interviews with professionals and design leaders from a wide range of industries to explore how COVID-19 transformed their industries. Finally, quantitative surveys were conducted to gain insights into the EY community after every 15 days.
The insights and results were:
- A culture of fear, daily resilience, and hopes for a better world and a better life – these were the macro trends.
- People felt massive digitization was a resourceful yet demanding aspect as they had to adapt every day.
- Some people wished to have a new world with lots of possibilities, and some were looking for a new purpose.
Advantages of Quantitative Research
Quantitative research data is often standardized and can be easily used to generalize findings for making crucial business decisions and uncover insights to supplement the qualitative research findings.
Here are some core benefits this research methodology offers.
A. Objectivity and Reliability
- Unbiased Insights: By relying on numerical data, quantitative research minimizes researcher bias, leading to more objective findings.
- Reproducibility: The standardized methods used in quantitative research allow for the replication of studies, enhancing the reliability and credibility of results.
B. Efficiency and Scalability
- Large Sample Sizes: Quantitative methods enable researchers to gather data from large populations, providing a comprehensive understanding of trends and patterns.
- Rapid Data Collection: Efficient data collection techniques, such as online surveys, expedite the research process.
- Cost-Effective: Compared to qualitative research, quantitative methods can be more cost-effective due to their efficiency and scalability.
C. Precision and Generalizability
- Numerical Precision: Quantitative data provides precise measurements and statistical analysis, allowing for accurate comparisons and predictions.
- Generalizability: Findings from large, representative samples can be generalized to the broader population more confidently.
D. Data-Driven Decision-Making
- Informed Choices: Quantitative research offers actionable insights to inform strategic decisions in business, healthcare, policymaking, and other fields.
- Performance Measurement: By tracking key performance indicators (KPIs), organizations can measure the effectiveness of their initiatives and make necessary adjustments.
Disadvantages of Quantitative Research
Despite its numerous benefits, quantitative research has some cons as well, such as:
A. Lack of Depth and Context
Quantitative research excels at providing numerical data but falls short when it comes to understanding the underlying reasons for behaviors or opinions. It offers a snapshot of what happened but not necessarily why it happened. Researchers may struggle to delve into the complexities of human experiences and motivations.
B. Overreliance on Structured Data
The rigid nature of quantitative research limits the exploration of unexpected findings. Researchers are confined to pre-determined questions and response options, potentially overlooking valuable insights from open-ended exploration.
C. Potential for Bias
While striving for objectivity, quantitative research is not immune to bias. Factors such as sample selection, question-wording, and data analysis methods can introduce biases that distort the results. Careful planning and execution are essential to mitigate these risks.
E. Difficulty Establishing Causality
Correlation does not equal causation. While quantitative research can identify relationships between variables, establishing definitive cause-and-effect links is challenging. Other factors may influence the observed relationship, making it difficult to isolate the true cause.
F. Resource Intensive
Conducting quantitative research often requires significant time and financial resources. Collecting large datasets, employing statistical analysis, and ensuring data quality can be costly and time-consuming. Additionally, specialized expertise may be needed for data analysis and interpretation.
Characteristics of Quantitative Research
Quantitative research clarifies the fuzziness of research data from qualitative research analysis. With numerical insights, you can formulate a better and more profitable business decision.
Hence, quantitative research is more readily contestable, sharpens intelligent discussion, helps you see the rival hypotheses, and dynamically contributes to the research process.
Let us have a quick look at some of its characteristics.
1. Measurable Variables
The data collection methods in quantitative research are structured and contain items requiring measurable variables, such as age, number of family members, salary range, highest education, etc.
These structured data collection methods comprise polls, surveys, questionnaires, etc., and may have questions like the ones shown in the following image:

As you can see, all the variables are measurable. This ensures the research is in-depth and provides less erroneous data for reliable, actionable insights.
2. Sample Size
No matter what data analysis methods are used for quantitative research, the sample size is kept small enough to represent the target market.
The main aim of the research methodology is to obtain numerical insights, so the sample size should be fairly large. Depending on the survey objective and scope, it might include hundreds of thousands of people.
3. Normal Population Distribution
To maintain the reliability of a quantitative research methodology, we assume that the population distribution curve is normal.
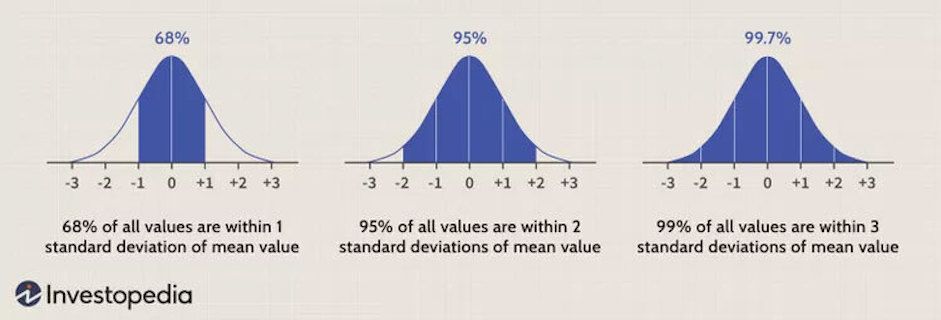
This type of population distribution curve is preferred over a non-normal distribution as the sample size is large, and the characteristics of the sample vary with its size.
This requires adhering to the random sampling principle to avoid the researcher’s bias in interpreting the results. Any bias can ruin the fairness of the entire process and defeat the purpose of the research.
4. Well-Structured Data Representation
Data analysis in quantitative research produces highly structured results and can form well-defined graphical representations. Some common examples include tables, figures, graphs, etc., that combine large blocks of data.
This way, you can discover hidden data trends, relationships, and differences among various measurable variables. This can help researchers understand the survey data and formulate actionable insights for decision-making.
5. Predictable Outcomes
Quantitative data analysis can also be used to estimate and predict outcomes. You can construct if-then scenarios and analyze the data to identify upcoming trends or events.
However, this requires advanced analytics and involves complex mathematical computations. So, it is mostly done via quantitative research tools with advanced analytics capabilities.
When to Use Quantitative Research
Quantitative research is particularly suited for the following scenarios:
1. Testing Hypotheses and Theories
- Hypothesis Verification: When you have a specific prediction about a relationship between variables, quantitative research can be used to test its validity.
- Theory Building: By gathering numerical data, you can identify patterns and trends that contribute to the development of new theories or the refinement of existing ones.
2. Measuring and Comparing
- Market Research: Assessing market size, share, and customer preferences to inform product development or marketing strategies.
- Performance Evaluation: Quantifying the effectiveness of programs, policies, or interventions through metrics and benchmarks.
- Comparative Analysis: Comparing different groups or conditions to identify similarities, differences, and relationships.
3. Generalizing Findings
- Population Representation: When you aim to draw conclusions about a larger population based on a representative sample.
- Predictive Modeling: Building models to forecast future trends or outcomes based on historical data.
4. Identifying Cause-and-Effect Relationships
- Experimental Design: While challenging, quantitative research can be used to establish causal relationships through controlled experiments.
- Correlational Analysis: Identifying patterns and associations between variables, though caution is needed to avoid assuming causation.
In essence, quantitative research is most appropriate when you seek precise, measurable data to answer specific research questions and make informed decisions.
Best Practices for Conducting Quantitative Research
Here are some best practices to keep in mind while conducting quantitative research:
1. Understand Your Research Objectives
There are many ways to collect data via quantitative research methods chosen according to the research objective and scope . These methods allow you to make your own observations regarding any hypotheses—unknown, entirely new, or unexplained.
Based on that, you can hypothesize proof and build a prediction of outcomes that support the same. You can also create a detailed stepwise plan for data collection, analysis, and testing.
2. Keep Your Questions Simple
The surveys are meant to reach people en-masse, including a wide demographic range with recipients from all walks of life. Asking simple questions will ensure that they grasp what’s being asked easily.
3. Develop a Solid Research Design
Choose an appropriate research design that aligns with your objectives, whether experimental, quasi-experimental, or correlational . You also need to pay attention to the sample size and sampling technique so that they accurately represent the target population.
4. Use Reliable & Valid Instruments
It’s crucial to select or develop measurement instruments such as questionnaires, scales, or tests that have been validated and are reliable. Before proceeding with the main study, pilot-test these instruments on a small sample to assess their effectiveness and make any necessary improvements.
5. Ensure Data Quality
Double-check data entries and cleaning procedures to eliminate any inconsistencies or missing values that may affect the accuracy of your results. For instance, you might regularly cross-verify data entries to identify and correct any discrepancies.
6. Employ Appropriate Data Analysis Techniques
Select statistical methods that match the nature of your data and research questions. Whether it’s regression analysis, t-tests, ANOVA, or other techniques, using the right approach is important for drawing meaningful conclusions. Utilize software tools like SPSS or R for data analysis to ensure the accuracy and reproducibility of your findings.
7. Interpret Results Objectively
Present your findings clearly and unbiasedly . Avoid making unwarranted causal claims, especially in correlational studies . Instead, focus on describing the relationships and patterns observed in your data.
8. Address Ethical Considerations
Prioritize ethical considerations throughout your research process. Obtain informed consent from participants, ensuring their voluntary participation and confidentiality of data . Comply with ethical guidelines and gain approval from a governing body if necessary.
Enhance Your Quantitative Research With Cutting-Edge Software
While no single research methodology can produce 100% reliable results, you can always opt for a hybrid method by selecting the most relevant methods for your objective.
For the best results, opt for smart, efficient, and scalable research tools that offer delightful reporting and advanced analytics. These tools will make every research initiative a success.
Advanced software tools, such as ProProfs Survey Maker, come with pre-built survey templates and question libraries and allow you to create a high-converting survey in just a few minutes.

About the author
Emma David is a seasoned market research professional with 8+ years of experience. Having kick-started her journey in research, she has developed rich expertise in employee engagement, survey creation and administration, and data management. Emma believes in the power of data to shape business performance positively. She continues to help brands and businesses make strategic decisions and improve their market standing through her understanding of research methodologies.
Related Posts

How to Create Thoughtful & Inclusive Gender Survey Questions

What Is a Business Survey Question? Definition, Importance & Examples

How to Write Quantitative Research Questions: Types With Examples

How to Use Open-Ended Questions: Tips, Advantages & Examples

Surveys vs Questionnaires: Compare the Differences

Why & How to Ask Employee Survey Questions About Workplace Culture

Home » Types of Quantitative Research Methods
Types of Quantitative Research Methods
Quantitative Research is essentially about numbers and statistical analysis. It’s how we turn observations into data that we can measure and analyze in a structured way. This type of research allows us to quantify behaviors, opinions, or phenomena and translate that into figures and statistics that can be used to uncover patterns, test theories, or make predictions.
Table of Contents

Now, let’s explore the main types of Quantitative Research Methods:
Imagine you have a big jar of jellybeans, and you want to know which color is the most popular. So, you ask everyone in your class to pick their favorite color. That’s like doing a survey! You’re asking lots of people questions to gather lots of number-based information or data.
Experiments
This is like doing a science experiment in class. You might change one thing, like the amount of sunlight a plant gets, to see how it affects something else, like how tall the plant grows. You’re trying different things and watching what happens, keeping track of the results with numbers.
Observational Studies
Imagine you’re bird watching, and you’re writing down every time a bird comes to the feeder and what type it is. You’re not changing anything; you’re just watching and noting down numbers and facts.
Longitudinal Studies
Think of this like taking a picture of the same tree every day for a whole year. You’re trying to see how the tree changes over time, from winter to spring, and all the way back to winter again. You’re collecting data over a long period to see trends or changes.
Cross-Sectional Studies
This is like taking a single snapshot of a crowded park. You’re getting a lot of information all at once, but just for one point in time. It’s like a group photo that tells you who was there at that moment, but not what happens before or after.
Correlational Studies
Now, imagine you noticed that the taller your classmates are, the bigger their shoe size. You start to think there’s a connection between height and shoe size. So, you measure everyone’s height and shoe size to see if taller people really do have bigger feet, looking for a pattern or correlation.
Each of these tools helps you collect different kinds of number-based information for solving different kinds of mysteries. Just like a detective, you need to pick the right tool for the job to find the clues you need!
You may also like

Types of Mixed Research Methods

What is Mixed Research Methods

Quantitative Research Methods

Types of Qualitative Research Methods

Qualitative Research Methods

Types of Research Methods

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Quantitative Research. Quantitative research is a research approach that seeks to quantify data and generalize results from a sample to a larger population. It relies on structured data collection methods and employs statistical analysis to interpret results. This type of research is objective, and findings are typically presented in numerical ...
Quantitative research serves as the cornerstone of evidence-based decision-making. Its importance cannot be overstated: quantitative methods provide empirical rigor, enabling preachers (academia), practitioners (industry), and policymakers (government; i.e. the 3Ps) to derive actionable insights from data.
Quantitative research is the process of collecting and analyzing numerical data to describe, predict, or control variables of interest. This type of research helps in testing the causal relationships between variables, making predictions, and generalizing results to wider populations. The purpose of quantitative research is to test a predefined ...
This is thanks in large part to your strategic research design. As you prepare for your quantitative dissertation research, you'll need to think about structuring your research design. There are several types of quantitative research designs, such as the experimental, comparative or predictive correlational designs.
Research in which collected data is converted into numbers or numerical data is quantitative research. It is widely used in surveys, demographic studies, census information, marketing, and other studies that use numerical data to analyze results. Primary quantitative research yields results that are objective, statistical, and unbiased.
Revised on June 22, 2023. Quantitative research is the process of collecting and analyzing numerical data. It can be used to find patterns and averages, make predictions, test causal relationships, and generalize results to wider populations. Quantitative research is the opposite of qualitative research, which involves collecting and analyzing ...
This study on airline alliances and operational efficiency and cost-effectiveness should use quantitative research methods to accurately assess and analyse key factors (Ghanad, 2023). Researcher ...
Quantitative research design is defined as a research method used in various disciplines, including social sciences, psychology, economics, and market research. It aims to collect and analyze numerical data to answer research questions and test hypotheses. Quantitative research design offers several advantages, including the ability to ...
Quantitative research is the backbone of evidence-based decision-making. Its core purpose is to transform raw data into actionable insights. Researchers can uncover hidden patterns, trends, and relationships that might otherwise go unnoticed by employing statistical methods to analyze numerical information.
Quantitative Research is essentially about numbers and statistical analysis. It's how we turn observations into data that we can measure and analyze in a structured way. This type of research allows us to quantify behaviors, opinions, or phenomena and translate that into figures and statistics that can be used to uncover patterns, test ...