Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456

Early Experiments on Photosynthesis

Photosynthesis is a process by which plants produce their food. It is a photochemical process in which the light energy is absorbed by the plants and is converted into chemical energy to produce oxygen. This process was followed by the plants for ages. But it’s discovery and identification were done only in 1800 and several scientists conducted many different types of experiments to prove the existence of photosynthesis.
Photosynthesis Discovery – Early Experiments
The process of photosynthesis is carried by some of the required raw materials like water, carbon dioxide, and cellular components like plastids. Plants make use of these raw materials to synthesize carbohydrates in the presence of sunlight. These key features of photosynthesis were revealed during the mid-nineteenth century.
Some of the experiments that were conducted by the early scientists to explore photosynthesis in a better way are -
Experiment to Prove the Importance of Carbon Dioxide in Photosynthesis
Materials Required: A healthy potted plant, a wide-mouthed glass bottle with a split cork, potassium hydroxide solution (KOH), and starch solution.
Experiment:
Take a healthy potted plant and keep it in the darkroom for two to three days to ensure leaves are free from starch.
In a wide-mouthed glass bottle add 10-15 ml of potassium hydroxide solution and split the cork vertically.
Now minutely, insert half part of a leaf into a glass bottle through the split cork and the other half exposed to air.
Place the complete unit undisturbed in sunlight for about 3 – 4 hours.
Remove the leaf after 4 hours from the plant and slowly remove it out from the bottle and test it with the starch solution.
We can observe that the half part leaf which was inside the glass bottle (KOH solution) did not show any colour change but the other half part exposed to surroundings became dark brown indicating the presence of starch in it.
Conclusion: In this experiment, we can conclude that carbon dioxide is essential for photosynthesis. Both portions of leaf received the same amount of water, chloroplasts, and sunlight but the half part which was inside the glass bottle did not receive carbon dioxide.
Later, many improvised experiments were conducted by scientists to analyze the essential components for photosynthesis. Joseph Priestley (1733-1804) was the first scientist amongst others to carry out these experiments.
Experiment by Joseph Priestley
After conducting a series of experiments in 1770, Joseph Priestley concluded that the essentiality of air for photosynthesis and also for the growth of plants.
Materials Required: A candle, rat, a bell jar, and a plant.
Firstly, a burning candle and a rat were kept together in the single bell jar.
After some time, the candle extinguished and the rat died.
For the second time, he kept a burning candle, rat, and a green plant all together in the bell jar.
He observed that neither the candle got extinguished, nor did the rat die.
Conclusion: Based on his observations, the scientist Priestley concluded that in the first case, the air in the bell jar got polluted by the candle and the existence of the rat. However, in the second case, the plant restored the air that was spoiled by the candle and the rat. But this function of the plants was not revealed quite soon by scientists.
Other Experiments
Scientist Jan Ingenhousz also conducted experiments using the same set-up but the twist was the presence of sunlight that was highlighted as being an essential product for plants to refresh the air that was polluted by the candle or rat.
Jean Senebier came to a conclusion which said that plants absorb carbon dioxide and release oxygen during photosynthesis.
Julius Robert Mayer demonstrated that plants convert light energy into chemical energy.
Later, Julius von Sachs revealed that glucose was produced by plants.
T.W Engelmann discovered the role of chlorophylls and Cornelius van Niel uncovered that the release of oxygen by plants is from water (H 2 O), not from carbon dioxide. He also gave the general photosynthesis equation.
An outline was drawn for the process of photosynthesis by scientists. They concluded that light is essential for photosynthesis, and plants use carbon dioxide and water for the preparation of glucose (carbohydrate), where water molecules are the hydrogen donors and oxygen (O 2 ) is the by-product of this biological process.
FAQs on Early Experiments on Photosynthesis
1. Define Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a process by which plants produce their food. It is a photochemical process in which the light energy is absorbed by the plants and is converted into chemical energy to produce oxygen. This process was followed by the plants for ages. But it’s discovery and identification were done only in 1800 and several scientists conducted many different types of experiments to prove the existence of photosynthesis.
2. What Were the Materials Used for the Experiment of Photosynthesis?
The materials used for the experiment of Photosynthesis was -
A healthy potted plant
A wide-mouthed glass bottle with a split cork
Potassium hydroxide solution (KOH)
Starch solution
Biology • Class 11
- Class 6 Maths
- Class 6 Science
- Class 6 Social Science
- Class 6 English
- Class 7 Maths
- Class 7 Science
- Class 7 Social Science
- Class 7 English
- Class 8 Maths
- Class 8 Science
- Class 8 Social Science
- Class 8 English
- Class 9 Maths
- Class 9 Science
- Class 9 Social Science
- Class 9 English
- Class 10 Maths
- Class 10 Science
- Class 10 Social Science
- Class 10 English
- Class 11 Maths
- Class 11 Computer Science (Python)
- Class 11 English
- Class 12 Maths
- Class 12 English
- Class 12 Economics
- Class 12 Accountancy
- Class 12 Physics
- Class 12 Chemistry
- Class 12 Biology
- Class 12 Computer Science (Python)
- Class 12 Physical Education
- GST and Accounting Course
- Excel Course
- Tally Course
- Finance and CMA Data Course
- Payroll Course
Interesting
- Learn English
- Learn Excel
- Learn Tally
- Learn GST (Goods and Services Tax)
- Learn Accounting and Finance
- GST Tax Invoice Format
- Accounts Tax Practical
- Tally Ledger List
- GSTR 2A - JSON to Excel
CBSE Class 10 Sample Paper Science Solution - For 2023 Boards
- Practice Questions CBSE - Science Class 10 (2023 Boards)
- CBSE Class 10 Sample Paper for 2022 Boards [Term 2] - Science Solution
- Solutions - CBSE Class 10 Sample Paper for 2022 Boards - Science [MCQ]
- CBSE Class 10 Sample Paper Science Solution - For 2024 Boards
Question 9 - CBSE Class 10 Sample Paper Science Solution - For 2023 Boards - Solutions to CBSE Sample Paper - Science Class 10
Last updated at Dec. 13, 2024 by Teachoo
Observe the experimental setup shown below. Name the chemical indicated as ‘X’ that can absorb the gas which is evolved as a byproduct of respiration

- This is an activity to show that Carbon Dioxide is necessary for photosynthesis .
- Carbon dioxide is a gas that is released as a byproduct of respiration in both humans and plants.
- KOH is kept in a watch glass under a bell jar to absorb all CO2 present in the bell jar.

Maninder Singh
CA Maninder Singh is a Chartered Accountant for the past 14 years and a teacher from the past 18 years. He teaches Science, Economics, Accounting and English at Teachoo
Hi, it looks like you're using AdBlock :(
Please login to view more pages. it's free :), solve all your doubts with teachoo black.
- Privacy policy
- Term & Conditions
REMEDIAL CLASSES
All Solutions
- NCERTSOLUTIONS
- _CLASS 10 SCIENCE
- _class 10 SCIENCE extra questions
- _MCQs Class 10 Science
- _All Activities Science
- _class 9 SCIENCE
- ENGLISHGRAMMAR
- _Letter Writing
- __Informal Letters
- ___Letter to Father
- _E-Mail Writing
- __Informal e-mails
- Online Test
- _MCQ Quiz Class 10 Science
- GENERAL KNOWLEDGE
- Study Material
- _Chemical Reactions
- _Electron dot structures
- Mathematics
- _Class 10 Science
- __Chapter 1
- __Chapter 2
- _Class 10 Science Solutions
Wednesday, February 9, 2022
Explain activity 6.2 class 10 science ncert.
In this post, you will find Activity 6.2 Class 10 Science NCERT of NCERT Science book. This NCERT Science Class 10 Chapter 6.2 Activity solution will help you to understand the complete procedure, observations, conclusions, and precautions. You can also go through Activity 6.1 class 10 NCERT Science .
After reading Activity 6.2 Class 10 Science NCERT , you can better understand NCERT Science Class 10 Chapter 6.2 Activity solution . Here you will find all NCERT Class 10 Science chapter 6 activities solutions with the complete explanation.
Activity 6.2 Class 10 Science NCERT
Activity - 6.2.
Object – Carbon dioxide is essential for photosynthesis
Materials Required : Two same-sized healthy potted plants, two bell jars, two glass slabs, grease or vaseline, potassium hydroxide, watch glass, iodine solution, water bath, alcohol, dropper, forceps, water, beaker, Petri dish, spirit lamp, tripod stand, wire gauze matchbox, etc.
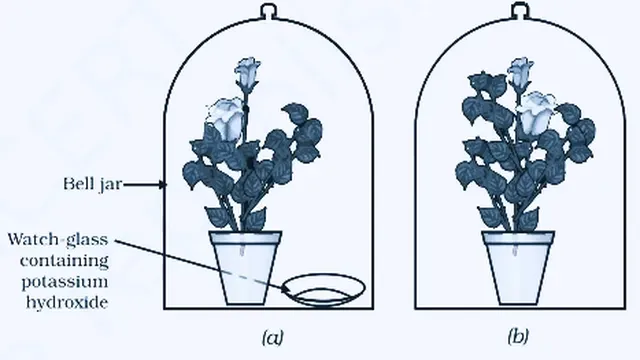
Procedure :
(i) Take a potted plant and destarch the plants by keeping them in a dark room for three days.
(ii) Place each plant on a separate glass slab or glass plate.
(iii)Take potassium hydroxide in the watch glass and place this watch glass by the side of one of the plants. Potassium hydroxide has the ability to absorb carbon dioxide.
(iv) Cover bath the plants with separate bell jars. See figure.
(v) Use vaseline/grease to seal the bottom of the jars to the glass plates to make the apparatus airtight.
(vi) Keep the plants in sunlight for 2-6 hours.
(vii) After that pluck a leaf from each plant.
(viii) Perform a test for the presence of starch in both the leaves separately.
Observation : The part that was outside and free to absorb carbon dioxide turns blue-black and the part that was inside the bottle and not getting carbon dioxide does not turn blue-black. So there starch is not formed or no photosynthesis occurs. The presence of starch can be tested through Iodine Test .
Conclusion: In the leaf of a plant that was kept without potassium hydroxide normal photosynthesis occurred. It got all the materials needed for photosynthesis.
But in the plant with potassium hydroxide photosynthesis did not occur. Because the setup was airtight, carbon dioxide present in the bell jar was absorbed by potassium hydroxide. Therefore, the plant could not make starch in the absence of carbon dioxide.
So this experiment shows that carbon dioxide is essential for the process of photosynthesis.
Requirement of carbon dioxide
Atmosphere contains about 0.036% carbon dioxide. All terrestrial (land) plants get it directly from the atmosphere. Carbon dioxide enters the leaves through stomata .
some exchange of gases occurs across the surface of stem, roots, and leaves also. In land plants to minimize the loss of water in the form of water vapour, a plant closes the stomata when carbon dioxide is not required.
The stomata remain open during the daytime. When carbon dioxide is utilized in the process of photosynthesis more of it diffuses from outside. Some amount of carbon dioxide is produced internally in the process of respiration. During the daytime, it is used in the process of photosynthesis.
Carbon dioxide evolved in respiration during night remains unutilized. The stomata remain closed during the night. Aquatic plants absorb the carbon dioxide dissolved in water through the general surface of the aquatic plants.
Iodine test for the starch present in the leaves of green plants
An iodine test is performed to detect the presence of starch in any substance or compound.
Theory – When iodine solution is added to starch, it gives a blue-black colour. This test is known as the iodine-starch test for starch.
Requirement – alcohol, beaker, spirit lamp, iodine solution, water bath, Petri dishes, and substance containing starch(green leaves).
Procedure- Take green leaves of plants(money plant) and boil the leaves for 10 minutes in water and then boil the leaves in alcohol. The beaker containing alcohol should be placed in the water bath.
This process makes the leaves completely free of chlorophyll and washes the leaves. Now place the leaves in iodine solution for a few minutes.
Observation- The leaves turn blue-black.
Result- This test shows the presence of starch in the leaves.
So now you can understand activity 6.2 Class 10 Science
NCERT , for better practice you can also search for solutions in chapter 6 Life Processes.
Q1.Which are the important activities to learn in 10th science NCERT textbook Kseeb?
Ans. In 10th Science NCERT textbook Kseeb, you should learn all activities because all chapters are compulsory for the Board examination.
Related Topics –
1. P revious activity – Activity 6.1
2. Next activity - Activity 6.3
3. Solution of Chapter 6 Life Processes
4. MCQof chapter 6 Life Processes
5. Extra questions of chapter 6 Life Processes
6. Solutions of Class 10 Science Book

About Remedial Classes Remedial Classes provides free educational content. Our only aim is to help you.On this site , you will get free study material regarding NCERT books,CBSE ,RBSE and all bords, English grammar and general knowledge.

No comments:
Post a comment, today's quiz, class 10 science activities solutions.
- All Activities Chapter 1
- All Activities Chapter 2
- All Activities Chapter 3
- All Activities Chapter 4
- All Activities Chapter 5
General Knowledge
- scientific Instruments and Uses
- Physical Quantities
- Inventors and their Inventions
- Chemical Compounds- Common names & Formula
- Mind Blowing Amazing Facts of Human Body
Class 9 Science Activities solutions
- All Activities Chapter 9
- All Activities Chapter 10
- All Activities Chapter 11
- All Activities Chapter 12
Class 10 Science Extra Study Material
- Chemical Compounds list of class 10
- Contribution of 10 Scientists of Class 10 Book
- MCQs Class 10 Science
- All Formulas of Electricity Class 10
- How to balance chemical equation
- What happens during a chemical reaction
- CBSE SYLLABUS
- Chemical Reactions
Class 8 Science Activities Solutions
- image formed by plane mirror and definitions related to spherical mirrors
- Reflection of specific rays by spherical mirrors
- image formation by convex mirror
- image formation by concave mirror
Search Your Topic
Most popular.
.jpg)
Activity 1.2 Class 10 Science

Activity 1.3 Class 10 Science
.webp)
Activity 1.1 Class 10 Science
You may also like.
- Tautomerism class 1th
- Isomerism class 11th
- Common naming of hydrocarbons
- concept of electronic confoguration
- Basic iupac naming rules
- Bohrs atomic model
Class 10 Solutions
- Class 10 Science
- MCQS Class 10 Science
- All Activities Science
- Important Extra Science Questions
Category List
- Electron dot structures
Class 9 Solutions
- recentPostsHeadline
Class 9 Maths
- All theorems Chapter 6
- Rutherfords atomic model
- Thomson's atomic model
- elctrons,protons and neutrons
- atomic mass and molecular mass
- polynomials maths classes
- Web Stories

- _PDF Printed Notes
- _PPT Slides
- _PPT Slides in PDF format
- _Intext Questions & Answers
- _Exercise and Answers
- _MCQs and Answers
- _Online Test Series
- _Activity Solutions
- _PDF Printed notes
- _Capsule Notes
- _Class 10 PPT
- _Class 11 PPT
- _Class 12 PPT
- _Exam Capsule PPT
- Online Tests
- _Chemistry Notes
- _Animal Facts
- _Body Facts
- _Comparison between
- _What and Why
Life Processes | Class 10 | Activity 6.2 with Solution
Life processes | activities in text book with solution.

- Activity 6.1
- Activity 6.2
- Activity 6.3
- Activity 6.4
- Activity 6.5
- Activity 6.6
- Activity 6.7
- Activity 6.8
👉 Other Chapters

thanku really helpfull :)
Write the experiment of the bell jar and pudina plant, performed by Priestly to prove that air plays a key role in photosynthesis.
Priestley performed the experiment to prove that the plants are responsible for the recycling of the gas present in the air which is used during burning and respiration. the experiments which were performed are as follows: 1) there was a bell-shaped jar placed upon a burning candle and a live mouse. 2) when the mouse and the candle were placed under the bell jar, the mouse used all the oxygen from the air. this resulted in the extinguishing of the candle due to the absence of oxygen in the air. the mouse also dies after some time due to the absence of oxygen. 3) then a mint plant was placed in the bell jar along with a live mouse and the burning candle. 4) the plant help in recycling the oxygen in the air by using carbon dioxide. this causes the replenishing of the oxygen in the air which is lost by the respiration by mouse and the burning of the candle. thus, the plant can perform photosynthesis and replenish the oxygen in the air which is used by the animals for breathing..
In this experiment, how does KOH affect the process of photosynthesis in the plant kept in a bell jar?


IMAGES
COMMENTS
Oct 9, 2017 · For the second time, he kept a burning candle, a rat, and a green plant together in the bell jar. He observed that neither the candle got extinguished nor did the rat die. Conclusion: Based on his observations, Priestley concluded that in the first case, the air in the bell jar got polluted by the candle and rat.
The correct options are B. Inhibits CO 2 intake by plant.. C. Stops the glucose/ starch production in leaves. KOH or Potassium hydroxide is an absorbent of carbon dioxide.
Materials Required: A candle, rat, a bell jar, and a plant. Experiment: Firstly, a burning candle and a rat were kept together in the single bell jar. After some time, the candle extinguished and the rat died. For the second time, he kept a burning candle, rat, and a green plant all together in the bell jar.
Dec 13, 2024 · Observe the experimental setup shown below. Name the chemical indicated as ‘X’ that can absorb the gas which is evolved as a byproduct of respirationNaOHKOHCa (OH)2K2CO3Answer:This is anactivity to show that Carbon Dioxide is necessary for photosynthesis.Carbon dioxideis a gas that is released as ab
|| Biology Video for CBSE Students belonging to Class 10 ||Topic: || Chapter-6 Life Processes ||Sub-topics: || Bell Jar Experiment | Experiment to show that ...
Feb 9, 2022 · You can also go through Activity 6.1 class 10 NCERT Science. Explain Activity 6.2 Class 10 Science NCERT. After reading Activity 6.2 Class 10 Science NCERT, you can better understand NCERT Science Class 10 Chapter 6.2 Activity solution. Here you will find all NCERT Class 10 Science chapter 6 activities solutions with the complete explanation.
Oct 12, 2021 · PDF Notes, PPTs, Online Tests and Question Banks for Class 10, Class 11, Class 12, NEET etc. ... Cover both plants with separate bell-jars as shown in Fig. 6.4 ...
CBSE Class 10 Biology Activity Chapter :Heredity and Evolution Activity 1:- Observe the ears of all the students in the class. Method:- Prepare a list of students having free or attached ear lobes and calculate the percentage of students having each. Find out about the ear lobes of the parents of each student in the class. Correlate
1) There was a bell-shaped jar placed upon a burning candle and a live mouse. 2) When the mouse and the candle were placed under the bell jar, the mouse used all the oxygen from the air. This resulted in the extinguishing of the candle due to the absence of oxygen in the air.
Joseph Priestly performed a series of experiments to reveal that air is essential for the growth of plants. he performed bell jar experiment and hypothesized...