

20 Fun Facts About Homework
Written by Maddi Jacobsen
Modified & Updated: 12 Sep 2024
Reviewed by Jessica Corbett

Homework is a topic that elicits mixed emotions from students, parents, and educators alike. Some see it as a necessary part of the learning process, while others view it as a burden that adds unnecessary stress to students’ lives. Regardless of where you stand on the issue, homework has become a common aspect of education systems around the world. In this article, we will delve into the world of homework and explore 20 fascinating facts that you may not have known. From its historical origins to its impact on academic performance, we will uncover intriguing tidbits that shed light on this contentious topic. So, whether you’re a student looking for a break from the grind or simply curious about the ins and outs of homework, join us on this informative journey to discover some fun and surprising facts about homework.
Key Takeaways:
- Homework has been around for centuries, and it can improve academic performance by reinforcing learning outside the classroom. It also helps develop time management and study skills.
- While homework can be beneficial, it’s important to find a balance to avoid overwhelming stress. It fosters independent learning, but its effectiveness and purpose continue to be debated.
Homework has been around for centuries.
Even though it may seem like a modern educational practice, homework has been assigned to students for centuries. In fact, evidence of homework assignments has been found in ancient civilizations such as Rome and Egypt.
The word “homework” was first used in the 14th century.
The term “homework” was first recorded in the English language in the 14th century. It originally referred to any work that was done at home, not only academic assignments.
Homework can improve academic performance.
Research has shown that doing homework can lead to improved academic performance. When students complete their assignments outside of the classroom, they have the opportunity to reinforce what they have learned and apply it in different contexts.
The amount of homework assigned varies by country.
The amount of homework assigned to students varies greatly across different countries. While some countries have a heavy emphasis on homework, others prioritize non-academic activities and have minimal homework requirements.
Homework can help develop time management skills.
By completing homework assignments, students learn to manage their time effectively and prioritize their tasks. These skills are valuable not only in academics but also in personal and professional life.
Online platforms have revolutionized homework.
With the rise of online platforms and educational tools, homework assignments have become more interactive and engaging. Students can now access resources, submit assignments, and receive feedback online.
Homework can enhance parental involvement.
Homework assignments provide an opportunity for parents to be involved in their children’s education. Parents can help their children with their assignments, review their work, and provide support and encouragement.
Homework has cultural variations.
Homework practices can vary significantly across different cultures. In some cultures, homework is highly valued and regarded as essential for academic success , while in others, it may have less emphasis.
Homework can improve study habits.
Regularly completing homework assignments can help students develop effective study habits , such as time management, organization, and self-discipline. These skills are beneficial throughout their academic journey.
Homework can be differentiated based on student’s needs.
Teachers may assign different types of homework or adapt assignments to meet the specific needs and learning styles of individual students. This helps cater to the diverse learning abilities within a classroom.
Homework can contribute to stress levels.
While homework has its benefits, excessive amounts of homework can increase stress levels in students. It is important for educators to strike a balance and ensure that homework does not become overwhelming.
Homework can promote independent learning.
Homework provides an opportunity for students to practice and reinforce what they have learned independently. This helps develop their critical thinking skills and encourages a deeper understanding of the subject matter.
Homework completion rates vary among students.
Research suggests that homework completion rates vary among students. Factors such as motivation, parental involvement, and individual learning styles can influence students’ willingness to complete their assignments.
Homework can improve time management skills.
Regularly completing homework assignments can help students develop effective time management skills. They learn to allocate their time wisely, prioritize tasks, and meet deadlines.
Homework can foster independent responsibility.
By completing homework assignments, students take ownership of their learning and develop a sense of responsibility. They learn to manage their workload and meet academic expectations.
Homework can provide a platform for practice.
Homework assignments give students the opportunity to practice what they have learned in class. This repetition helps reinforce concepts and helps students retain information in the long term.
Homework is not always graded.
While many homework assignments are graded, some are designed for practice and reinforcement purposes and may not carry a formal grade. These assignments still contribute to the overall learning process.
Homework can vary in format.
Homework assignments can take various formats, including written assignments, research projects, online quizzes , collaborative activities, and more. This allows for different learning styles and preferences to be accommodated.
Homework completion rates decrease with age.
Studies have shown that the completion rates of homework assignments tend to decrease as students progress through higher grades. This may be attributed to increased extracurricular activities and academic demands.
Homework has a long-standing debate on its effectiveness.
The effectiveness of homework has been a subject of debate among educators, researchers, and parents for many years. While it has its benefits, there are ongoing discussions on the appropriate amount and purpose of homework.
In conclusion, homework can sometimes be seen as a mundane and tedious task, but it is also packed with interesting facts and trivia. From its historical roots to its impact on academic performance, homework has been a subject of debate and research for many years. Whether you love it or hate it, there’s no denying the influence that homework has on our education system.
So the next time you find yourself buried in assignments, remember these fun facts about homework. It might just make the process a little more enjoyable and enlightening. Homework serves as a valuable tool in reinforcing learning, developing essential skills, and fostering discipline. Keep these facts in mind as you tackle your assignments and make the most out of your educational journey.
1. Why do we have homework?
Homework serves as a way for students to practice and reinforce what they have learned in class. It helps to solidify knowledge, develop critical thinking skills, and promote independent learning.
2. How much homework is too much?
The amount of homework considered “too much” can vary depending on factors such as age, grade level, and individual capabilities. It is important for educators to strike a balance and assign a reasonable amount of homework that is manageable and beneficial for students.
3. Does homework improve academic performance?
Research suggests a positive correlation between homework and academic performance, especially when it is well-designed and appropriate for the student’s level. However, excessive homework or poorly designed assignments may have diminishing returns.
4. Can homework be fun?
Yes , homework can be made fun by incorporating creative and interactive learning strategies. Using games, group activities, and real-life applications can make the homework experience more enjoyable and engaging.
5. Should parents help with homework?
Parents can provide support and guidance to their children with homework when needed. However, it is important for students to take responsibility for their own learning and problem-solving skills. Parents should encourage independence and only offer assistance when necessary.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
Share this Fact:

Home » Tips for Teachers » 7 Research-Based Reasons Why Students Should Not Have Homework: Academic Insights, Opposing Perspectives & Alternatives
7 Research-Based Reasons Why Students Should Not Have Homework: Academic Insights, Opposing Perspectives & Alternatives
In recent years, the question of why students should not have homework has become a topic of intense debate among educators, parents, and students themselves. This discussion stems from a growing body of research that challenges the traditional view of homework as an essential component of academic success. The notion that homework is an integral part of learning is being reevaluated in light of new findings about its effectiveness and impact on students’ overall well-being.

The push against homework is not just about the hours spent on completing assignments; it’s about rethinking the role of education in fostering the well-rounded development of young individuals. Critics argue that homework, particularly in excessive amounts, can lead to negative outcomes such as stress, burnout, and a diminished love for learning. Moreover, it often disproportionately affects students from disadvantaged backgrounds, exacerbating educational inequities. The debate also highlights the importance of allowing children to have enough free time for play, exploration, and family interaction, which are crucial for their social and emotional development.
Checking 13yo’s math homework & I have just one question. I can catch mistakes & help her correct. But what do kids do when their parent isn’t an Algebra teacher? Answer: They get frustrated. Quit. Get a bad grade. Think they aren’t good at math. How is homework fair??? — Jay Wamsted (@JayWamsted) March 24, 2022
As we delve into this discussion, we explore various facets of why reducing or even eliminating homework could be beneficial. We consider the research, weigh the pros and cons, and examine alternative approaches to traditional homework that can enhance learning without overburdening students.
Once you’ve finished this article, you’ll know:
- Insights from Teachers and Education Industry Experts →
- 7 Reasons Why Students Should Not Have Homework →
- Opposing Views on Homework Practices →
- Exploring Alternatives to Homework →
Insights from Teachers and Education Industry Experts: Diverse Perspectives on Homework
In the ongoing conversation about the role and impact of homework in education, the perspectives of those directly involved in the teaching process are invaluable. Teachers and education industry experts bring a wealth of experience and insights from the front lines of learning. Their viewpoints, shaped by years of interaction with students and a deep understanding of educational methodologies, offer a critical lens through which we can evaluate the effectiveness and necessity of homework in our current educational paradigm.
Check out this video featuring Courtney White, a high school language arts teacher who gained widespread attention for her explanation of why she chooses not to assign homework.
Here are the insights and opinions from various experts in the educational field on this topic:
“I teach 1st grade. I had parents ask for homework. I explained that I don’t give homework. Home time is family time. Time to play, cook, explore and spend time together. I do send books home, but there is no requirement or checklist for reading them. Read them, enjoy them, and return them when your child is ready for more. I explained that as a parent myself, I know they are busy—and what a waste of energy it is to sit and force their kids to do work at home—when they could use that time to form relationships and build a loving home. Something kids need more than a few math problems a week.” — Colleen S. , 1st grade teacher
“The lasting educational value of homework at that age is not proven. A kid says the times tables [at school] because he studied the times tables last night. But over a long period of time, a kid who is drilled on the times tables at school, rather than as homework, will also memorize their times tables. We are worried about young children and their social emotional learning. And that has to do with physical activity, it has to do with playing with peers, it has to do with family time. All of those are very important and can be removed by too much homework.” — David Bloomfield , education professor at Brooklyn College and the City University of New York graduate center
“Homework in primary school has an effect of around zero. In high school it’s larger. (…) Which is why we need to get it right. Not why we need to get rid of it. It’s one of those lower hanging fruit that we should be looking in our primary schools to say, ‘Is it really making a difference?’” — John Hattie , professor
”Many kids are working as many hours as their overscheduled parents and it is taking a toll – psychologically and in many other ways too. We see kids getting up hours before school starts just to get their homework done from the night before… While homework may give kids one more responsibility, it ignores the fact that kids do not need to grow up and become adults at ages 10 or 12. With schools cutting recess time or eliminating playgrounds, kids absorb every single stress there is, only on an even higher level. Their brains and bodies need time to be curious, have fun, be creative and just be a kid.” — Pat Wayman, teacher and CEO of HowtoLearn.com
7 Reasons Why Students Should Not Have Homework
Let’s delve into the reasons against assigning homework to students. Examining these arguments offers important perspectives on the wider educational and developmental consequences of homework practices.
1. Elevated Stress and Health Consequences

The ongoing debate about homework often focuses on its educational value, but a vital aspect that cannot be overlooked is the significant stress and health consequences it brings to students. In the context of American life, where approximately 70% of people report moderate or extreme stress due to various factors like mass shootings, healthcare affordability, discrimination, racism, sexual harassment, climate change, presidential elections, and the need to stay informed, the additional burden of homework further exacerbates this stress, particularly among students.
Key findings and statistics reveal a worrying trend:
- Overwhelming Student Stress: A staggering 72% of students report being often or always stressed over schoolwork, with a concerning 82% experiencing physical symptoms due to this stress.
- Serious Health Issues: Symptoms linked to homework stress include sleep deprivation, headaches, exhaustion, weight loss, and stomach problems.
- Sleep Deprivation: Despite the National Sleep Foundation recommending 8.5 to 9.25 hours of sleep for healthy adolescent development, students average just 6.80 hours of sleep on school nights. About 68% of students stated that schoolwork often or always prevented them from getting enough sleep, which is critical for their physical and mental health.
- Turning to Unhealthy Coping Mechanisms: Alarmingly, the pressure from excessive homework has led some students to turn to alcohol and drugs as a way to cope with stress.
This data paints a concerning picture. Students, already navigating a world filled with various stressors, find themselves further burdened by homework demands. The direct correlation between excessive homework and health issues indicates a need for reevaluation. The goal should be to ensure that homework if assigned, adds value to students’ learning experiences without compromising their health and well-being.
By addressing the issue of homework-related stress and health consequences, we can take a significant step toward creating a more nurturing and effective educational environment. This environment would not only prioritize academic achievement but also the overall well-being and happiness of students, preparing them for a balanced and healthy life both inside and outside the classroom.
2. Inequitable Impact and Socioeconomic Disparities
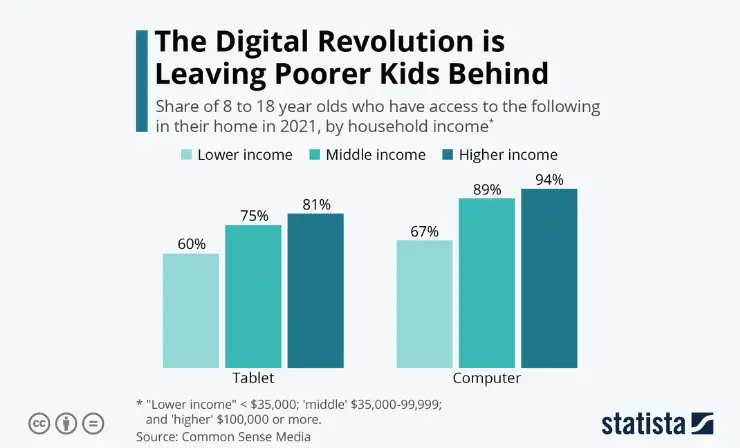
In the discourse surrounding educational equity, homework emerges as a factor exacerbating socioeconomic disparities, particularly affecting students from lower-income families and those with less supportive home environments. While homework is often justified as a means to raise academic standards and promote equity, its real-world impact tells a different story.
The inequitable burden of homework becomes starkly evident when considering the resources required to complete it, especially in the digital age. Homework today often necessitates a computer and internet access – resources not readily available to all students. This digital divide significantly disadvantages students from lower-income backgrounds, deepening the chasm between them and their more affluent peers.
Key points highlighting the disparities:
- Digital Inequity: Many students lack access to necessary technology for homework, with low-income families disproportionately affected.
- Impact of COVID-19: The pandemic exacerbated these disparities as education shifted online, revealing the extent of the digital divide.
- Educational Outcomes Tied to Income: A critical indicator of college success is linked more to family income levels than to rigorous academic preparation. Research indicates that while 77% of students from high-income families graduate from highly competitive colleges, only 9% from low-income families achieve the same . This disparity suggests that the pressure of heavy homework loads, rather than leveling the playing field, may actually hinder the chances of success for less affluent students.
Moreover, the approach to homework varies significantly across different types of schools. While some rigorous private and preparatory schools in both marginalized and affluent communities assign extreme levels of homework, many progressive schools focusing on holistic learning and self-actualization opt for no homework, yet achieve similar levels of college and career success. This contrast raises questions about the efficacy and necessity of heavy homework loads in achieving educational outcomes.
The issue of homework and its inequitable impact is not just an academic concern; it is a reflection of broader societal inequalities. By continuing practices that disproportionately burden students from less privileged backgrounds, the educational system inadvertently perpetuates the very disparities it seeks to overcome.
3. Negative Impact on Family Dynamics

Homework, a staple of the educational system, is often perceived as a necessary tool for academic reinforcement. However, its impact extends beyond the realm of academics, significantly affecting family dynamics. The negative repercussions of homework on the home environment have become increasingly evident, revealing a troubling pattern that can lead to conflict, mental health issues, and domestic friction.
A study conducted in 2015 involving 1,100 parents sheds light on the strain homework places on family relationships. The findings are telling:
- Increased Likelihood of Conflicts: Families where parents did not have a college degree were 200% more likely to experience fights over homework.
- Misinterpretations and Misunderstandings: Parents often misinterpret their children’s difficulties with homework as a lack of attention in school, leading to feelings of frustration and mistrust on both sides.
- Discriminatory Impact: The research concluded that the current approach to homework disproportionately affects children whose parents have lower educational backgrounds, speak English as a second language, or belong to lower-income groups.
The issue is not confined to specific demographics but is a widespread concern. Samantha Hulsman, a teacher featured in Education Week Teacher , shared her personal experience with the toll that homework can take on family time. She observed that a seemingly simple 30-minute assignment could escalate into a three-hour ordeal, causing stress and strife between parents and children. Hulsman’s insights challenge the traditional mindset about homework, highlighting a shift towards the need for skills such as collaboration and problem-solving over rote memorization of facts.
The need of the hour is to reassess the role and amount of homework assigned to students. It’s imperative to find a balance that facilitates learning and growth without compromising the well-being of the family unit. Such a reassessment would not only aid in reducing domestic conflicts but also contribute to a more supportive and nurturing environment for children’s overall development.
4. Consumption of Free Time

In recent years, a growing chorus of voices has raised concerns about the excessive burden of homework on students, emphasizing how it consumes their free time and impedes their overall well-being. The issue is not just the quantity of homework, but its encroachment on time that could be used for personal growth, relaxation, and family bonding.
Authors Sara Bennett and Nancy Kalish , in their book “The Case Against Homework,” offer an insightful window into the lives of families grappling with the demands of excessive homework. They share stories from numerous interviews conducted in the mid-2000s, highlighting the universal struggle faced by families across different demographics. A poignant account from a parent in Menlo Park, California, describes nightly sessions extending until 11 p.m., filled with stress and frustration, leading to a soured attitude towards school in both the child and the parent. This narrative is not isolated, as about one-third of the families interviewed expressed feeling crushed by the overwhelming workload.
Key points of concern:
- Excessive Time Commitment: Students, on average, spend over 6 hours in school each day, and homework adds significantly to this time, leaving little room for other activities.
- Impact on Extracurricular Activities: Homework infringes upon time for sports, music, art, and other enriching experiences, which are as crucial as academic courses.
- Stifling Creativity and Self-Discovery: The constant pressure of homework limits opportunities for students to explore their interests and learn new skills independently.
The National Education Association (NEA) and the National PTA (NPTA) recommend a “10 minutes of homework per grade level” standard, suggesting a more balanced approach. However, the reality often far exceeds this guideline, particularly for older students. The impact of this overreach is profound, affecting not just academic performance but also students’ attitudes toward school, their self-confidence, social skills, and overall quality of life.
Furthermore, the intense homework routine’s effectiveness is doubtful, as it can overwhelm students and detract from the joy of learning. Effective learning builds on prior knowledge in an engaging way, but excessive homework in a home setting may be irrelevant and uninteresting. The key challenge is balancing homework to enhance learning without overburdening students, allowing time for holistic growth and activities beyond academics. It’s crucial to reassess homework policies to support well-rounded development.
5. Challenges for Students with Learning Disabilities
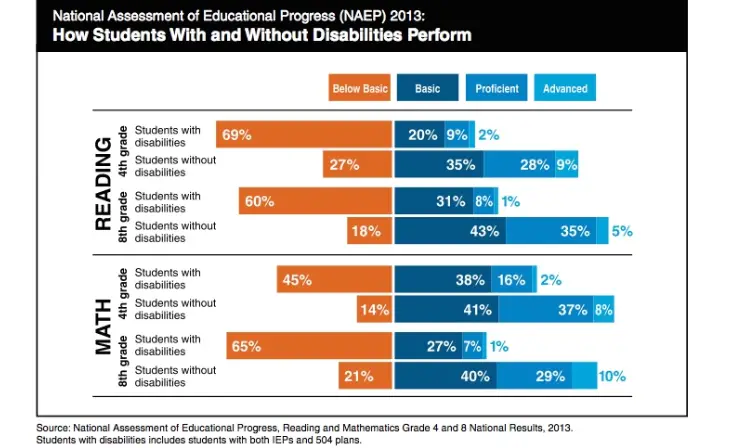
Homework, a standard educational tool, poses unique challenges for students with learning disabilities, often leading to a frustrating and disheartening experience. These challenges go beyond the typical struggles faced by most students and can significantly impede their educational progress and emotional well-being.
Child psychologist Kenneth Barish’s insights in Psychology Today shed light on the complex relationship between homework and students with learning disabilities:
- Homework as a Painful Endeavor: For students with learning disabilities, completing homework can be likened to “running with a sprained ankle.” It’s a task that, while doable, is fraught with difficulty and discomfort.
- Misconceptions about Laziness: Often, children who struggle with homework are perceived as lazy. However, Barish emphasizes that these students are more likely to be frustrated, discouraged, or anxious rather than unmotivated.
- Limited Improvement in School Performance: The battles over homework rarely translate into significant improvement in school for these children, challenging the conventional notion of homework as universally beneficial.
These points highlight the need for a tailored approach to homework for students with learning disabilities. It’s crucial to recognize that the traditional homework model may not be the most effective or appropriate method for facilitating their learning. Instead, alternative strategies that accommodate their unique needs and learning styles should be considered.
In conclusion, the conventional homework paradigm needs reevaluation, particularly concerning students with learning disabilities. By understanding and addressing their unique challenges, educators can create a more inclusive and supportive educational environment. This approach not only aids in their academic growth but also nurtures their confidence and overall development, ensuring that they receive an equitable and empathetic educational experience.
6. Critique of Underlying Assumptions about Learning
The longstanding belief in the educational sphere that more homework automatically translates to more learning is increasingly being challenged. Critics argue that this assumption is not only flawed but also unsupported by solid evidence, questioning the efficacy of homework as an effective learning tool.
Alfie Kohn , a prominent critic of homework, aptly compares students to vending machines in this context, suggesting that the expectation of inserting an assignment and automatically getting out of learning is misguided. Kohn goes further, labeling homework as the “greatest single extinguisher of children’s curiosity.” This critique highlights a fundamental issue: the potential of homework to stifle the natural inquisitiveness and love for learning in children.
The lack of concrete evidence supporting the effectiveness of homework is evident in various studies:
- Marginal Effectiveness of Homework: A study involving 28,051 high school seniors found that the effectiveness of homework was marginal, and in some cases, it was counterproductive, leading to more academic problems than solutions.
- No Correlation with Academic Achievement: Research in “ National Differences, Global Similarities ” showed no correlation between homework and academic achievement in elementary students, and any positive correlation in middle or high school diminished with increasing homework loads.
- Increased Academic Pressure: The Teachers College Record published findings that homework adds to academic pressure and societal stress, exacerbating performance gaps between students from different socioeconomic backgrounds.
These findings bring to light several critical points:
- Quality Over Quantity: According to a recent article in Monitor on Psychology , experts concur that the quality of homework assignments, along with the quality of instruction, student motivation, and inherent ability, is more crucial for academic success than the quantity of homework.
- Counterproductive Nature of Excessive Homework: Excessive homework can lead to more academic challenges, particularly for students already facing pressures from other aspects of their lives.
- Societal Stress and Performance Gaps: Homework can intensify societal stress and widen the academic performance divide.
The emerging consensus from these studies suggests that the traditional approach to homework needs rethinking. Rather than focusing on the quantity of assignments, educators should consider the quality and relevance of homework, ensuring it truly contributes to learning and development. This reassessment is crucial for fostering an educational environment that nurtures curiosity and a love for learning, rather than extinguishing it.
7. Issues with Homework Enforcement, Reliability, and Temptation to Cheat
In the academic realm, the enforcement of homework is a subject of ongoing debate, primarily due to its implications on student integrity and the true value of assignments. The challenges associated with homework enforcement often lead to unintended yet significant issues, such as cheating, copying, and a general undermining of educational values.
Key points highlighting enforcement challenges:
- Difficulty in Enforcing Completion: Ensuring that students complete their homework can be a complex task, and not completing homework does not always correlate with poor grades.
- Reliability of Homework Practice: The reliability of homework as a practice tool is undermined when students, either out of desperation or lack of understanding, choose shortcuts over genuine learning. This approach can lead to the opposite of the intended effect, especially when assignments are not well-aligned with the students’ learning levels or interests.
- Temptation to Cheat: The issue of cheating is particularly troubling. According to a report by The Chronicle of Higher Education , under the pressure of at-home assignments, many students turn to copying others’ work, plagiarizing, or using creative technological “hacks.” This tendency not only questions the integrity of the learning process but also reflects the extreme stress that homework can induce.
- Parental Involvement in Completion: As noted in The American Journal of Family Therapy , this raises concerns about the authenticity of the work submitted. When parents complete assignments for their children, it not only deprives the students of the opportunity to learn but also distorts the purpose of homework as a learning aid.
In conclusion, the challenges of homework enforcement present a complex problem that requires careful consideration. The focus should shift towards creating meaningful, manageable, and quality-driven assignments that encourage genuine learning and integrity, rather than overwhelming students and prompting counterproductive behaviors.
Addressing Opposing Views on Homework Practices
While opinions on homework policies are diverse, understanding different viewpoints is crucial. In the following sections, we will examine common arguments supporting homework assignments, along with counterarguments that offer alternative perspectives on this educational practice.
1. Improvement of Academic Performance

Homework is commonly perceived as a means to enhance academic performance, with the belief that it directly contributes to better grades and test scores. This view posits that through homework, students reinforce what they learn in class, leading to improved understanding and retention, which ultimately translates into higher academic achievement.
However, the question of why students should not have homework becomes pertinent when considering the complex relationship between homework and academic performance. Studies have indicated that excessive homework doesn’t necessarily equate to higher grades or test scores. Instead, too much homework can backfire, leading to stress and fatigue that adversely affect a student’s performance. Reuters highlights an intriguing correlation suggesting that physical activity may be more conducive to academic success than additional homework, underscoring the importance of a holistic approach to education that prioritizes both physical and mental well-being for enhanced academic outcomes.
2. Reinforcement of Learning

Homework is traditionally viewed as a tool to reinforce classroom learning, enabling students to practice and retain material. However, research suggests its effectiveness is ambiguous. In instances where homework is well-aligned with students’ abilities and classroom teachings, it can indeed be beneficial. Particularly for younger students , excessive homework can cause burnout and a loss of interest in learning, counteracting its intended purpose.
Furthermore, when homework surpasses a student’s capability, it may induce frustration and confusion rather than aid in learning. This challenges the notion that more homework invariably leads to better understanding and retention of educational content.
3. Development of Time Management Skills

Homework is often considered a crucial tool in helping students develop important life skills such as time management and organization. The idea is that by regularly completing assignments, students learn to allocate their time efficiently and organize their tasks effectively, skills that are invaluable in both academic and personal life.
However, the impact of homework on developing these skills is not always positive. For younger students, especially, an overwhelming amount of homework can be more of a hindrance than a help. Instead of fostering time management and organizational skills, an excessive workload often leads to stress and anxiety . These negative effects can impede the learning process and make it difficult for students to manage their time and tasks effectively, contradicting the original purpose of homework.
4. Preparation for Future Academic Challenges

Homework is often touted as a preparatory tool for future academic challenges that students will encounter in higher education and their professional lives. The argument is that by tackling homework, students build a foundation of knowledge and skills necessary for success in more advanced studies and in the workforce, fostering a sense of readiness and confidence.
Contrarily, an excessive homework load, especially from a young age, can have the opposite effect . It can instill a negative attitude towards education, dampening students’ enthusiasm and willingness to embrace future academic challenges. Overburdening students with homework risks disengagement and loss of interest, thereby defeating the purpose of preparing them for future challenges. Striking a balance in the amount and complexity of homework is crucial to maintaining student engagement and fostering a positive attitude towards ongoing learning.
5. Parental Involvement in Education

Homework often acts as a vital link connecting parents to their child’s educational journey, offering insights into the school’s curriculum and their child’s learning process. This involvement is key in fostering a supportive home environment and encouraging a collaborative relationship between parents and the school. When parents understand and engage with what their children are learning, it can significantly enhance the educational experience for the child.
However, the line between involvement and over-involvement is thin. When parents excessively intervene by completing their child’s homework, it can have adverse effects . Such actions not only diminish the educational value of homework but also rob children of the opportunity to develop problem-solving skills and independence. This over-involvement, coupled with disparities in parental ability to assist due to variations in time, knowledge, or resources, may lead to unequal educational outcomes, underlining the importance of a balanced approach to parental participation in homework.
Exploring Alternatives to Homework and Finding a Middle Ground

In the ongoing debate about the role of homework in education, it’s essential to consider viable alternatives and strategies to minimize its burden. While completely eliminating homework may not be feasible for all educators, there are several effective methods to reduce its impact and offer more engaging, student-friendly approaches to learning.
Alternatives to Traditional Homework
- Project-Based Learning: This method focuses on hands-on, long-term projects where students explore real-world problems. It encourages creativity, critical thinking, and collaborative skills, offering a more engaging and practical learning experience than traditional homework. For creative ideas on school projects, especially related to the solar system, be sure to explore our dedicated article on solar system projects .
- Flipped Classrooms: Here, students are introduced to new content through videos or reading materials at home and then use class time for interactive activities. This approach allows for more personalized and active learning during school hours.
- Reading for Pleasure: Encouraging students to read books of their choice can foster a love for reading and improve literacy skills without the pressure of traditional homework assignments. This approach is exemplified by Marion County, Florida , where public schools implemented a no-homework policy for elementary students. Instead, they are encouraged to read nightly for 20 minutes . Superintendent Heidi Maier’s decision was influenced by research showing that while homework offers minimal benefit to young students, regular reading significantly boosts their learning. For book recommendations tailored to middle school students, take a look at our specially curated article .
Ideas for Minimizing Homework
- Limiting Homework Quantity: Adhering to guidelines like the “ 10-minute rule ” (10 minutes of homework per grade level per night) can help ensure that homework does not become overwhelming.
- Quality Over Quantity: Focus on assigning meaningful homework that is directly relevant to what is being taught in class, ensuring it adds value to students’ learning.
- Homework Menus: Offering students a choice of assignments can cater to diverse learning styles and interests, making homework more engaging and personalized.
- Integrating Technology: Utilizing educational apps and online platforms can make homework more interactive and enjoyable, while also providing immediate feedback to students. To gain deeper insights into the role of technology in learning environments, explore our articles discussing the benefits of incorporating technology in classrooms and a comprehensive list of educational VR apps . These resources will provide you with valuable information on how technology can enhance the educational experience.
For teachers who are not ready to fully eliminate homework, these strategies offer a compromise, ensuring that homework supports rather than hinders student learning. By focusing on quality, relevance, and student engagement, educators can transform homework from a chore into a meaningful component of education that genuinely contributes to students’ academic growth and personal development. In this way, we can move towards a more balanced and student-centric approach to learning, both in and out of the classroom.
Useful Resources
- Is homework a good idea or not? by BBC
- The Great Homework Debate: What’s Getting Lost in the Hype
- Alternative Homework Ideas
The evidence and arguments presented in the discussion of why students should not have homework call for a significant shift in homework practices. It’s time for educators and policymakers to rethink and reformulate homework strategies, focusing on enhancing the quality, relevance, and balance of assignments. By doing so, we can create a more equitable, effective, and student-friendly educational environment that fosters learning, well-being, and holistic development.
- “Here’s what an education expert says about that viral ‘no-homework’ policy”, Insider
- “John Hattie on BBC Radio 4: Homework in primary school has an effect of zero”, Visible Learning
- HowtoLearn.com
- “Time Spent On Homework Statistics [Fresh Research]”, Gitnux
- “Stress in America”, American Psychological Association (APA)
- “Homework hurts high-achieving students, study says”, The Washington Post
- “National Sleep Foundation’s updated sleep duration recommendations: final report”, National Library of Medicine
- “A multi-method exploratory study of stress, coping, and substance use among high school youth in private schools”, Frontiers
- “The Digital Revolution is Leaving Poorer Kids Behind”, Statista
- “The digital divide has left millions of school kids behind”, CNET
- “The Digital Divide: What It Is, and What’s Being Done to Close It”, Investopedia
- “COVID-19 exposed the digital divide. Here’s how we can close it”, World Economic Forum
- “PBS NewsHour: Biggest Predictor of College Success is Family Income”, America’s Promise Alliance
- “Homework and Family Stress: With Consideration of Parents’ Self Confidence, Educational Level, and Cultural Background”, Taylor & Francis Online
- “What Do You Mean My Kid Doesn’t Have Homework?”, EducationWeek
- “Excerpt From The Case Against Homework”, Penguin Random House Canada
- “How much homework is too much?”, neaToday
- “The Nation’s Report Card: A First Look: 2013 Mathematics and Reading”, National Center for Education Statistics
- “Battles Over Homework: Advice For Parents”, Psychology Today
- “How Homework Is Destroying Teens’ Health”, The Lion’s Roar
- “ Breaking the Homework Habit”, Education World
- “Testing a model of school learning: Direct and indirect effects on academic achievement”, ScienceDirect
- “National Differences, Global Similarities: World Culture and the Future of Schooling”, Stanford University Press
- “When school goes home: Some problems in the organization of homework”, APA PsycNet
- “Is homework a necessary evil?”, APA PsycNet
- “Epidemic of copying homework catalyzed by technology”, Redwood Bark
- “High-Tech Cheating Abounds, and Professors Bear Some Blame”, The Chronicle of Higher Education
- “Homework and Family Stress: With Consideration of Parents’ Self Confidence, Educational Level, and Cultural Background”, ResearchGate
- “Kids who get moving may also get better grades”, Reuters
- “Does Homework Improve Academic Achievement? A Synthesis of Research, 1987–2003”, SageJournals
- “Is it time to get rid of homework?”, USAToday
- “Stanford research shows pitfalls of homework”, Stanford
- “Florida school district bans homework, replaces it with daily reading”, USAToday
- “Encouraging Students to Read: Tips for High School Teachers”, wgu.edu
- Recent Posts

Simona Johnes is the visionary being the creation of our project. Johnes spent much of her career in the classroom working with students. And, after many years in the classroom, Johnes became a principal.
- Overview of 22 Low-Code Agencies for MVP, Web, or Mobile App Development - October 23, 2024
- Tips to Inspire Your Young Child to Pursue a Career in Nursing - July 24, 2024
- How Parents Can Advocate for Their Children’s Journey into Forensic Nursing - July 24, 2024
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Latest Facts
27 Facts About Whole Grains
21 Facts About Water
34 facts about homework.
Written by Hayden
Modified & Updated: 31 Oct 2024
- Education Facts
- Educational

Homework has been a subject of debate for decades, with strong opinions on both sides. Some argue that it helps reinforce learning and build essential skills, while others believe it adds unnecessary stress and detracts from family and personal time. Understanding the various aspects of homework, from its historical origins to its modern-day implementation, can provide valuable insights into its true impact on students. Here are 34 facts that offer a comprehensive look into homework’s role in education , its benefits, drawbacks, and how it continues to shape student experiences today.
Key Takeaways:
- Homework can improve academic performance and essential skills, but excessive assignments may cause stress and inequity among students, highlighting the need for balance.
- The discussion about homework is evolving, with a focus on quality over quantity, driven by research and changing societal attitudes toward student engagement and well-being.
Historical Context
Homework has been a part of education for centuries, with a mixed reception. This section covers the origins and legislative shifts that shaped homework policies.
- Origin of Homework : Homework is often attributed to Roberto Nevelis of Venice , though this claim remains disputed. Horace Mann helped promote it in the U.S.
- Homework Ban in California : In 1901, California passed a law banning homework for children under 15 due to concerns over health and well-being.
- British Homework Trends : British students typically receive more homework than their European peers, averaging about 5 hours per week.
- Spanish Homework Time : Students in Spain reportedly spend around 6.4 hours per week on homework, sparking calls for reduced assignments from parent associations.
Types of Homework
Different types of homework serve various educational purposes. This section breaks down the common forms.
- Practice Exercises : Tasks designed to reinforce classroom learning, such as solving math problems .
- Reading Assignments : These encourage comprehension and critical thinking through book or text analysis.
- Research Projects : These assignments require students to explore specific topics in-depth.
- Experimental Assignments : Students conduct hands-on experiments to apply theoretical knowledge practically.
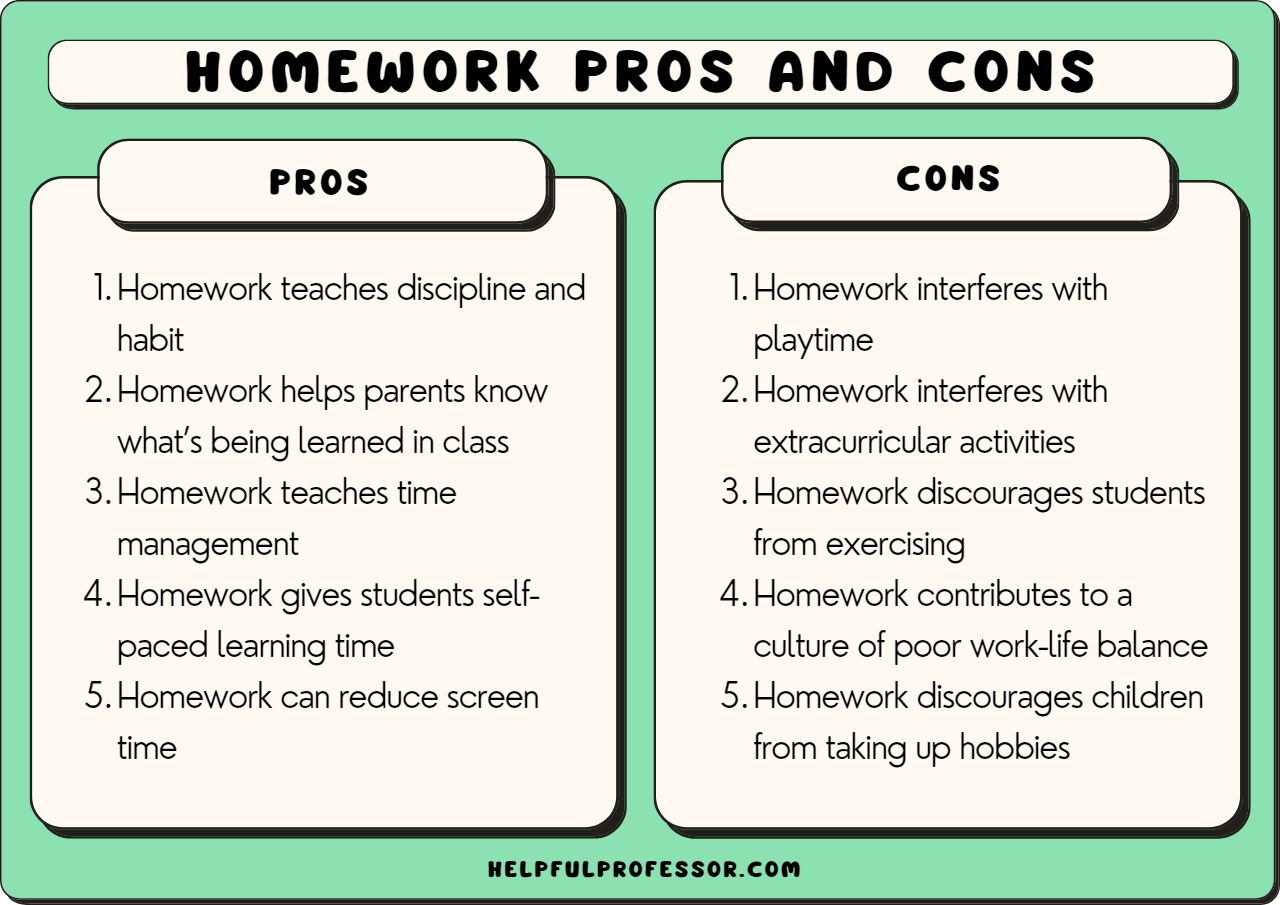
Benefits of Homework
Homework isn’t without merit. There are clear academic and personal development benefits, especially for older students.
- Improved Academic Performance : Studies show that homework can positively impact grades and test scores, particularly for high school students.
- Skill Development : Homework fosters critical thinking, self-regulation, and problem-solving abilities .
- Time Management : Students learn to manage their time effectively by juggling assignments and deadlines.
- Increased Independence : Completing assignments on their own can build a student’s confidence and autonomy.
- Parental Involvement : Homework often creates an opportunity for parents to engage in their children’s education.
Drawbacks of Homework
Despite the benefits, homework has its downsides. This section explores the negative impacts, from stress to equity issues.
- Student Stress : A large percentage of students report that homework is a leading cause of stress, contributing to anxiety and sleep deprivation.
- Reduced Free Time : Excessive homework can limit time for extracurricular activities , socializing, and family interactions.
- Negative Attitudes : Many students view homework as a burden, leading to disengagement from the learning process.
- Inequality in Access : Students from disadvantaged backgrounds may struggle with homework due to a lack of resources or support at home.
- Questionable Effectiveness for Young Learners : Research suggests that while homework can be beneficial for older students, younger children may not see significant academic gains.
Current Trends in Homework
Homework trends have evolved over time, particularly with the rise of digital learning and new educational philosophies.
- Increased Workload : The amount of homework assigned has risen over the years, leading to concerns about student well-being.
- COVID-19 Impact : Remote learning during the pandemic shifted how homework is perceived and executed, blending in-class activities with at-home tasks.
- Homework Strikes : Movements advocating for reduced homework have emerged, with parents and educators questioning its necessity.
- Finnish Approach : Finland’s education system, known for assigning minimal homework and offering more recess time, presents a successful alternative model.
Educational Perspectives on Homework
Educators and researchers have differing views on homework’s effectiveness. Here are some perspectives that shape its use in schools.
- Teacher Perspectives : Some teachers emphasize quality over quantity, assigning meaningful tasks that reinforce classroom learning without overwhelming students.
- Mixed Research Findings : Studies show varying results on homework’s correlation with academic performance, particularly between younger and older students.
- Policy Changes : Schools across the globe are reconsidering their homework policies in response to feedback on workload, stress, and student engagement.
The Future of Homework
As education evolves, the future of homework continues to be a topic of interest, shaping how students learn both in and out of the classroom.
- Balancing Act : Finding the right balance between beneficial homework assignments and student well-being remains a key challenge.
- Self-Directed Learning : Future trends may involve fostering more independent, self-guided learning through manageable, meaningful assignments.
- Parental Involvement : Encouraging healthy parental involvement is crucial, but excessive pressure can hinder a student’s motivation.
- Cultural Shifts : Changing societal attitudes towards education are influencing how homework is viewed, with more focus on holistic student development.
- Integration of Technology : Homework increasingly incorporates digital tools, offering varied and interactive learning experiences.
- Mental Health Considerations : Growing awareness of mental health issues among students has prompted schools to rethink homework load and its effects on well-being.
- Holistic Education : The push for more well-rounded education models continues, prioritizing student health and happiness alongside academic achievement.
- Technological Influence : As digital learning tools evolve, so too will the nature of homework, with more opportunities for interactive and personalized learning.
- Ongoing Debate : The conversation around homework will continue to evolve as educators, parents, and policymakers seek the best approaches for future generations .
The Homework Debate Continues
The homework debate continues as educators seek the best ways to support student success. While homework can improve academic performance, particularly when paired with tools like multiplication games or after-school tuition , it can also create stress and limit free time. As education evolves, balancing meaningful assignments with student well-being will be key. By integrating fun learning methods like games and personalized tuition, homework can become more engaging and manageable, helping students build skills without overwhelming them. The future of homework will depend on creating this balance.
Frequently Asked Questions
Was this page helpful.
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
Share this Fact:

13 Interesting Facts About Homework
Homework is a staple of the educational experience, often viewed with a mix of dread and necessity by students of all ages. While it can sometimes feel overwhelming, homework serves important purposes in reinforcing learning, developing skills, and preparing for future academic challenges. Here are over 10 fascinating facts about homework that shed light on its history, benefits, and impact on education.

1. The Origin of Homework
Homework has a long history, with roots tracing back to ancient civilizations. The concept of assigning tasks for students to complete outside of class can be found as far back as the Roman Empire, where tutors often assigned exercises to reinforce lessons. However, the modern idea of homework began to take shape in the late 19th century, particularly in the United States, as education systems evolved and the need for structured learning became more apparent.
2. Homework Has Educational Benefits
Research shows that homework can improve student learning and academic performance. It provides opportunities for students to practice and apply what they’ve learned in class, helping to reinforce knowledge and develop critical thinking skills. A study by the National Center for Research on Education Access and Choice found that students who complete homework consistently outperform those who do not, indicating the positive effects of practice and review on learning outcomes.

3. Different Types of Homework
Not all homework is created equal. Educators assign various types of homework, including:
- Practice Homework: Reinforces skills learned in class.
- Preparation Homework: Prepares students for upcoming lessons or topics.
- Extension Homework: Challenges students to apply knowledge in new contexts or explore topics in greater depth.
- Creative Homework: Encourages creativity and critical thinking, such as projects or presentations.
This diversity in homework types allows educators to target different learning objectives and engage students in meaningful ways.
4. The “10-Minute Rule”
Many educators follow the “10-minute rule” when assigning homework. This guideline suggests that students should receive about 10 minutes of homework per grade level each night. For example, a 2nd grader might have 20 minutes of homework, while a 12th grader could receive up to 120 minutes. This rule aims to balance the academic workload and prevent overwhelming students, ensuring that homework remains a beneficial part of the learning process.
5. The Debate Over Homework Load
The appropriate amount of homework has been a topic of debate among educators, parents, and students. Some argue that excessive homework can lead to stress, burnout, and negative attitudes toward learning. Research from Stanford University found that students with excessive homework reported higher stress levels, physical health problems, and a lack of balance in their lives. This has led many schools to reevaluate their homework policies and consider how to assign meaningful, manageable tasks that promote learning without overwhelming students.
6. The Role of Technology in Homework
Technology has transformed the way students approach homework. Online resources, educational apps, and digital platforms allow for interactive learning experiences and collaboration among peers. Students can access a wealth of information, participate in virtual study groups, and submit assignments electronically. However, this reliance on technology also raises questions about digital distractions and the importance of fostering self-discipline and time management skills.
7. Cultural Differences in Homework Practices
Homework practices vary significantly across cultures. In countries like Japan and South Korea, students often face rigorous homework expectations and long hours of study, while in Scandinavian countries, there’s a stronger emphasis on balanced lifestyles, with less homework assigned. These cultural differences reflect diverse educational philosophies and societal values, influencing how students engage with homework and their overall academic experiences.
8. Parental Involvement in Homework
Parental involvement can play a significant role in students’ homework success. Research shows that when parents actively engage in their child’s homework, providing support and encouragement, students tend to perform better academically. However, the extent of parental involvement should be balanced; excessive help can lead to dependency rather than fostering independent learning. Educators often encourage parents to create a conducive homework environment and offer guidance without taking over the learning process.
9. The Impact of Homework on Study Habits
Homework helps students develop essential study habits and skills that are crucial for academic success. Regularly completing homework assignments fosters time management, organization, and responsibility. It also teaches students to prioritize tasks and manage their schedules effectively, skills that will serve them well throughout their academic and professional lives. These habits can be particularly beneficial as students transition to higher education, where self-directed learning becomes increasingly important.
10. The Future of Homework
As education continues to evolve, so does the concept of homework. Many educators are exploring innovative approaches to homework assignments, such as project-based learning, flipped classrooms, and experiential learning. These methods aim to make homework more engaging and relevant to real-world applications. Additionally, the shift towards personalized learning allows for tailored homework assignments that cater to individual student needs and interests, enhancing motivation and engagement.
11. The Effects of Homework on Social Life
Homework can have a significant impact on students’ social lives and extracurricular activities. While it’s essential for reinforcing learning, excessive homework can limit the time students have for sports, clubs, and socializing with friends. Finding a balance between homework and leisure is crucial for promoting well-rounded development, helping students cultivate social skills and pursue interests outside of academics.
12. Homework and Mental Health
The pressure of homework can sometimes contribute to mental health issues among students. High levels of stress, anxiety, and feelings of inadequacy can arise from struggling with homework or feeling overwhelmed by assignments. Schools are increasingly recognizing the importance of mental health and well-being, leading to initiatives aimed at promoting a healthier homework balance and providing resources for students who may be struggling.
13. Homework During the Pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic has significantly changed the landscape of homework and education. With the sudden shift to remote learning, students faced new challenges related to homework assignments, including access to technology and the need for self-motivation. Educators adapted their approaches, incorporating more flexible and engaging assignments to accommodate students’ diverse situations. This experience has prompted ongoing discussions about the future of homework in a post-pandemic world.
Homework is a vital component of the educational process, serving to reinforce learning, develop essential skills, and prepare students for future challenges. These facts about homework highlight its complexity, benefits, and the ongoing discussions surrounding its role in education. As we continue to adapt to the changing landscape of learning, understanding the significance of homework can help students, parents, and educators create a more effective and enjoyable academic experience. Whether you see it as a necessary task or an opportunity for growth, homework is an integral part of the journey toward knowledge and success.
Related Posts

Formal Communication Advantages and Disadvantages

Multipurpose River Projects Advantages and Disadvantages
Leave a comment cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Homework has been a significant part of education for centuries, sparking continuous debate. While some argue it reinforces learning, others feel it adds unnecessary stress. This blog dives into the facts about homework-dispelling myths, understanding its history, and examining its impact on students and teachers alike.
Historical Origins of Homework: How It All Began
The origins of homework are rooted in the evolution of formal education itself. In ancient Rome, teachers used assignments to strengthen students' oratory and memory skills. A fact about homework is that it originally focused on oral recitations rather than written tasks. This foundation evolved over centuries, laying the groundwork for homework as we know it today. Need help with homework writing assignments help then Assignment in Need is a good choice for any type of homework help.
The Evolution of Homework and Education
Homework has transformed alongside educational practices. As societies shifted from oral traditions to written documentation, homework became more structured. During the Enlightenment, educational reformers promoted learning methods emphasizing practical skills, reinforcing the 10 facts about homework we still discuss today: that homework aids retention, fosters self-discipline, and encourages independent study. Visit for homework help
The Middle Ages to the Renaissance: Early Homework Practices
In medieval Europe, students received assignments mainly in religious and philosophical studies, often memorizing passages and prayers. Facts about homework show it was largely exclusive to the elite, as only a privileged few had access to schooling. However, During the Renaissance, increased literacy rates led to broader educational opportunities, meaning homework became a standardized expectation.
The Industrial Revolution’s Influence on Homework
With the rise of the Industrial Revolution, society required educated, skilled workers. Education adapted to prepare students for the workforce, and homework became essential to academic training. Important facts about homework in education during this period highlight how assignments taught discipline and time management, aligning students’ habits with industrial schedules.
Today’s Modern Take on Homework
In modern times, homework has diversified, with assignments reflecting varied learning goals and age-specific requirements. Today, myths vs facts about homework frequently emerge in educational debates. For instance, the myth that "more homework equals better grades" overlooks nuanced research indicating that excessive homework may not enhance learning outcomes and can lead to burnout.
Homework Through the Teacher’s Point Of View
From a teacher's perspective, homework is essential for reinforcing concepts taught in class. A fact about homework that teachers emphasize is its ability to give students extra practice outside the classroom. However, teachers are aware of the potential downsides, including the pressure it may put on students, especially when workloads are high.
Homework Through the Students' Perspective
Students often view homework as burdensome and time-consuming. Facts against homework are commonly cited among students, who feel overwhelmed balancing academics with extracurriculars and personal life. Nonetheless, students recognize that homework can deepen their understanding, although they hope for more balanced assignments and realistic deadlines.
The Purpose and Goals of Homework
Homework has specific purposes, primarily to consolidate learning, enhance self-discipline, and develop time management skills. Facts and statistics about homework show that students who consistently complete assignments tend to perform better in exams. However, educators caution that the volume and complexity of homework should be age-appropriate to avoid unnecessary stress.
Best Motivational Facts About Homework
Here are some fun facts about homework to boost motivation:
1.Homework helps reinforce memory through repetition.
2.Small, regular assignments prevent the need for intense cramming before exams.
3.Completing homework fosters a sense of accomplishment, boosting self-confidence.
4.Homework introduces independent study skills crucial for higher education.
5.It encourages students to seek help when needed, fostering collaboration skills.
Key Facts Teachers Should Know About Homework
10 facts about homework that educators should keep in mind include:
1.Clear instructions reduce confusion.
2.Assignments should be tailored to individual skill levels.
3.Feedback on homework fosters improvement.
4.Realistic deadlines respect students' time management.
5.Homework shouldn’t substitute for in-class learning.
6.Creative assignments increase engagement.
7.Allowing students choice can make homework more enjoyable.
8.Group assignments build teamwork.
9.Reviewing homework helps identify gaps in understanding.
10Homework is most effective when aligned with learning objectives.
Limited Research on Homework’s Benefits
While some studies support the positive impact of homework, the facts and statistics about homework reveal limited, inconsistent data on its long-term academic benefits. In primary education, homework appears to have minimal impact on learning outcomes. However, for older students, especially in high school, homework can improve grades and test scores, though only when assigned in moderation.
How Students Often Find Ways Around Homework
A fact about homework is that students often find creative ways to avoid completing assignments. From copying answers to using online resources, students are adept at minimizing their homework load. Understanding these behaviors helps educators create assignments that are harder to bypass, promoting genuine engagement.
The Link Between Homework and Student Stress
Facts against homework assignments highlight the potential for high levels of stress among students. Studies show that excessive homework contributes to sleep deprivation, anxiety, and even depression. Balancing academics with personal life is challenging, making stress management essential in promoting student well-being.
How Homework Impacts Students’ Social Lives
Homework can sometimes limit students' ability to engage in social activities. Facts about no homework policies show that schools implementing such practices report positive outcomes, with students more engaged in extracurriculars and community activities. Social interactions are crucial for development, and homework policies should reflect this need for balance.
The Risk of Burnout from Too Much Homework
Excessive homework can lead to burnout, causing students to lose motivation and interest in learning. Facts against homework demonstrate that after a certain threshold, additional assignments do not improve academic performance but rather increase exhaustion, resulting in diminishing returns.
Facts About Homework Every Student Should Know
For students, here are some important facts about homework in education:
1.Homework is a form of active revision.
2.It builds self-discipline and independence.
3.Homework supports knowledge retention.
4.Group assignments improve social skills.
5.Short, daily assignments are often more effective than lengthy projects.
Essays Are Easier Than You Think!
For students who dread essays, here’s a fun fact about homework: essays improve critical thinking skills, allowing you to express your thoughts in structured ways. With clear outlines and planning, essays become less daunting, and students often find them to be an effective way to explore subjects deeply.
Students Have a Voice in Homework Discussions
Student input is increasingly valued in shaping homework policies. Facts and statistics about homework indicate that involving students in discussions about workload and deadlines leads to more positive attitudes toward assignments. When students feel heard, they are more likely to approach homework with enthusiasm.
Time Management is a Key to Homework Success
Effective time management is essential for managing homework loads. By setting aside specific study times, students can reduce last-minute stress. Facts about homework highlight that those who manage time well achieve better academic outcomes.
Homework Isn’t Disappearing Anytime Soon
Despite debates, facts about no homework policies are the exception, not the rule. Homework remains a cornerstone of educational practice worldwide, especially for secondary and higher education. The benefits, when well-balanced, continue to make homework an integral part of learning.
Homework Can Supplement Your Study Routine
Using homework as a supplement to regular study is a proven way to master topics. Important facts about homework in education reveal that revisiting topics through assignments can reinforce understanding, providing a structured study routine outside the classroom.
Types of Homework Assignments
Assignments come in various forms, each serving unique educational goals. Below are 10 facts about homework types and their roles:
Practice Assignments to Reinforce Skills
These assignments focus on applying learned skills, such as math problems or grammar exercises, allowing students to solidify understanding through repetition.
Preparatory Homework for Upcoming Lessons
Preparatory tasks, like reading ahead or watching videos, lay the foundation for future lessons. They prime students’ minds, making upcoming topics easier to grasp.
Extension Assignments to Deepen Understanding
Extension tasks push students beyond the basics, fostering critical thinking and analytical skills. For example, a science project could encourage exploring concepts beyond what was covered in class.
Integration Tasks that Combine Multiple Skills
Integration assignments require students to apply various skills simultaneously, such as a research project requiring writing, analysis, and presentation skills.
Creative Projects to Encourage Original Thinking
Creative homework promotes innovation, giving students the freedom to express ideas in unique ways. Art projects, creative writing, or multimedia presentations are examples.
Research-Based Homework to Build Inquiry Skills
Research tasks encourage students to explore topics in depth, promoting independent learning and investigative skills-an essential aspect of higher education preparation.
Collaborative Homework for Group Learning
Group assignments help students learn teamwork and cooperation, emphasizing the importance of collective effort and communication.
Review and Revision Assignments for Mastery
Review assignments aim to reinforce previous lessons, helping students retain information through repetition. They’re particularly useful for exam preparation.
Final Thoughts: Homework’s Role in Education Today
In conclusion, facts about homework reveal a nuanced picture: while it supports learning, it also requires careful planning and balance. Homework is not a “one-size-fits-all” practice but a flexible tool that, when used wisely, enriches students’ educational experiences. By understanding these myths vs facts about homework, educators and students alike can approach assignments more effectively, turning homework into a powerful part of academic growth.
Frequently asked questions
Q1.What is the purpose of homework?
The purpose of homework is to reinforce classroom learning by allowing students to practice skills independently. It strengthens understanding, promotes self-discipline, and improves time management. Facts about homework indicate that well-designed assignments help students retain information and develop problem-solving abilities essential for academic success and lifelong learning.
Q2.How much homework should students have?
Experts recommend a balanced amount of homework based on age and grade. Studies and facts and statistics about homework suggest that younger students benefit from shorter assignments, while high schoolers can handle more. Excessive homework may lead to stress, so educators aim for effective, manageable workloads that optimize learning.
Q3.Does homework improve academic performance?
Research shows homework can improve academic performance when assigned appropriately. Important facts about homework in education reveal that short, consistent tasks enhance knowledge retention and boost test scores, especially for older students. However, too much homework may reduce effectiveness, so moderation is key to achieving positive academic results.
Q4.What types of homework assignments are most effective?
The most effective types of homework assignments include practice assignments for skill reinforcement, research-based tasks to encourage inquiry, and collaborative projects to promote teamwork. Important facts about homework in education show that varied assignments enhance understanding, enabling students to apply concepts practically and creatively while supporting diverse learning styles.
Q5.What is the role of technology in homework?
Technology plays a significant role in modern homework by providing resources, interactive tools, and collaborative platforms. It allows students to access digital textbooks, educational apps, and online forums, enhancing engagement. Facts and statistics about homework reveal that technology-based assignments improve flexibility, especially for research and project-based tasks.
Q6.Are there any statistics about homework?
Yes, there are many facts and statistics about homework. Research shows that moderate homework improves academic performance, especially in high school. For younger students, however, the benefits are less pronounced. Studies indicate that excessive homework can lead to stress, underlining the importance of balanced, age-appropriate assignments for optimal outcomes.
Q7.Are there benefits to not assigning homework?
Yes, there are facts about no homework policies that highlight benefits, such as improved mental health, reduced student stress, and more time for extracurricular activities. In some cases, removing homework encourages students to engage in creative pursuits and family time, creating a balanced approach to learning outside the classroom.
Our Trending Services
Our popular subjects.
10 Surprising Fun Facts About Homework You Didn’t Know
Hey there, Fact Finders! Are you ready to dive into the world of homework? Get ready to discover some fun and fascinating facts about this timeless academic tradition. From its historical origins to some quirky statistics, you’re in for a homework-themed adventure. Let’s uncover the intriguing side of hitting the books!
Content structure
Exploring the Surprising World of Homework: Fun Facts You Didn’t Know
Did you know that homework has been a part of education for over a century? The concept first emerged in the early 20th century as a way to reinforce lessons learned in the classroom. Today, homework is a common practice in schools worldwide, but its impact and effectiveness continue to be a subject of debate.
One surprising fact about homework is that it wasn’t always seen as beneficial. In the 1940s, there was a belief that too much homework could actually be detrimental to a child’s well-being. However, over time, the perception of homework has shifted, and it is now generally viewed as an important tool for reinforcing learning and developing essential skills such as time management and responsibility.
Another interesting tidbit is that the amount of homework assigned can vary significantly depending on the country. For example, students in some Asian countries such as China and Japan are known to receive large amounts of homework compared to their counterparts in Western countries.
Furthermore, research has shown that the effectiveness of homework can depend on various factors, including the student’s age and the type of assignment given. While some studies suggest that homework can improve academic performance, others indicate that excessive homework may lead to stress and burnout.
In recent years, there has been a growing emphasis on the quality rather than the quantity of homework. Educators are increasingly exploring innovative approaches to homework, such as project-based assignments and personalized learning tasks, aiming to make the experience more engaging and meaningful for students.
As our understanding of education continues to evolve, so too does the role of homework in the learning process. It remains a fascinating and complex aspect of the educational landscape, provoking ongoing discussions and research into how to optimize its impact on student learning and development.
Most popular facts
The average high school student spends about.
The average high school student spends about 6.5 hours a day in school.
5 hours a week on homework.
Spending 5 hours a week on homework is essential for academic success and learning retention.
Homework was first used in the 19th century as a form of punishment for students.
No , homework was not first used in the 19th century as a form of punishment for students.
Studies have shown that excessive homework can have negative effects on students’ mental health.
Excessive homework can have negative effects on students’ mental health .
The recommended time for elementary students to spend on homework is 10 minutes per grade level.
The recommended time for elementary students to spend on homework is 10 minutes per grade level .
Homework can help reinforce learning and improve academic performance when used effectively.
In Finland, known for its top-performing education system, students rarely have homework.
Students in Finland rarely have homework.
Homework completion is linked to improved self-regulation skills in students.
Homework completion is indeed linked to improved self-regulation skills in students.
The debate over the effectiveness of homework has been ongoing for decades.
The ongoing debate over the effectiveness of homework has been a topic of discussion for decades.
Homework can provide an opportunity for parents to be involved in their child’s education.
Homework can provide an opportunity for parents to be involved in their child’s education by allowing them to monitor their child’s progress, provide assistance when needed, and communicate with teachers about their child’s academic development.
In some countries, such as India, there are reports of heavy homework burdens leading to student stress and sleep deprivation.
Heavy homework burdens in some countries, such as India, lead to student stress and sleep deprivation.
Homework can contribute to the development of time management skills in students.
Research has shown that homework has a greater impact on academic achievement in the middle and high school years.
Research has shown that homework has a greater impact on academic achievement in the middle and high school years .
Some studies suggest that the benefits of homework may vary based on the subject and the student’s individual characteristics.
Homework benefits may vary based on the subject and the student’s individual characteristics .
Homework can be a source of tension between students and their parents.
Homework can create tension between students and their parents, affecting their relationship and communication .
The amount of homework assigned can vary greatly between different schools and education systems.
In conclusion, homework can be both challenging and rewarding, and understanding these fun facts about homework can help us appreciate its importance in the context of education and learning. Whether it’s knowing the benefits of music or finding motivation through interesting trivia, homework continues to play a significant role in shaping students’ academic growth and development.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Homework has been around for centuries. Even though it may seem like a modern educational practice, homework has been assigned to students for centuries. In fact, evidence of homework assignments has been found in ancient civilizations such as Rome and Egypt.. The word "homework" was first used in the 14th century.
Here are the figures for math homework: 46% of parents think their child's math homework is too easy. 25% of parents think their child's math homework is not too easy. 29% of parents offered no opinion. Here are the figures for language arts homework: 44% of parents think their child's language arts homework is too easy.
Their brains and bodies need time to be curious, have fun, be creative and just be a kid." ... This approach is exemplified by Marion County, Florida, where public schools implemented a no-homework policy for elementary students. Instead, they are encouraged to read nightly for 20 minutes. Superintendent Heidi Maier's decision was ...
The Homework Debate Continues. The homework debate continues as educators seek the best ways to support student success. While homework can improve academic performance, particularly when paired with tools like multiplication games or after-school tuition, it can also create stress and limit free time.As education evolves, balancing meaningful assignments with student well-being will be key.
Extension Homework: Challenges students to apply knowledge in new contexts or explore topics in greater depth. Creative Homework: Encourages creativity and critical thinking, such as projects or presentations. This diversity in homework types allows educators to target different learning objectives and engage students in meaningful ways. 4.
Here are some fun facts about homework to boost motivation: 1.Homework helps reinforce memory through repetition. ... Facts about no homework policies show that schools implementing such practices report positive outcomes, with students more engaged in extracurriculars and community activities. Social interactions are crucial for development ...
Most popular facts The average high school student spends about . The average high school student spends about 6.5 hours a day in school.. 5 hours a week on homework. Spending 5 hours a week on homework is essential for academic success and learning retention.. Homework was first used in the 19th century as a form of punishment for students.
3. 17% Of Teens Regularly Miss Homework Due To Lack Of High-Speed Internet Access. A 2 0 1 8 . P e w R e se a r ch p o l l. o f 7 4 3 U S t e e n s f o u n d t h a t 1 7 % , o r a l m o st 2 i n e ve r y
No efficiency, no productivity, no agenda; just parents and children hanging out. There's been a lot of research and debate on the academic value of homework for school-aged children.
5. Homework can help students prepare for future exams, projects, and other assessments, motivating some students. Conclusion. This is the end of this article, which is facts about homework. However, teachers and students both should really be aware. Teachers need to realize that having too much homework is stressful rather than helpful.