Nursing Care Plans (NCP) Ultimate Guide and List

Writing the best nursing care plan requires a step-by-step approach to complete the parts needed for a care plan correctly. This tutorial will walk you through developing a care plan. This guide has the ultimate database and list of nursing care plans (NCP) and nursing diagnosis samples for our student nurses and professional nurses to use—all for free! Care plan components, examples, objectives, and purposes are included with a detailed guide on writing an excellent nursing care plan or a template for your unit.

Table of Contents
Standardized care plans, individualized care plans, purposes of a nursing care plan, three-column format, four-column format, student care plans, step 1: data collection or assessment, step 2: data analysis and organization, step 3: formulating your nursing diagnoses, step 4: setting priorities, short-term and long-term goals, components of goals and desired outcomes, types of nursing interventions, step 7: providing rationale, step 8: evaluation, step 9: putting it on paper, basic nursing and general care plans, surgery and perioperative care plans, cardiac care plans, endocrine and metabolic care plans, gastrointestinal, hematologic and lymphatic, infectious diseases, integumentary, maternal and newborn care plans, mental health and psychiatric, musculoskeletal, neurological, pediatric nursing care plans, reproductive, respiratory, recommended resources, references and sources, what is a nursing care plan.
A nursing care plan (NCP) is a formal process that correctly identifies existing needs and recognizes a client’s potential needs or risks. Care plans provide a way of communication among nurses, their patients, and other healthcare providers to achieve healthcare outcomes. Without the nursing care planning process, the quality and consistency of patient care would be lost.
Nursing care planning begins when the client is admitted to the agency and is continuously updated throughout in response to the client’s changes in condition and evaluation of goal achievement. Planning and delivering individualized or patient-centered care is the basis for excellence in nursing practice .
Types of Nursing Care Plans
Care plans can be informal or formal: An informal nursing care plan is a strategy of action that exists in the nurse ‘s mind. A formal nursing care plan is a written or computerized guide that organizes the client’s care information.
Formal care plans are further subdivided into standardized care plans and individualized care plans: Standardized care plans specify the nursing care for groups of clients with everyday needs. Individualized care plans are tailored to meet a specific client’s unique needs or needs that are not addressed by the standardized care plan.
Standardized care plans are pre-developed guides by the nursing staff and health care agencies to ensure that patients with a particular condition receive consistent care. These care plans are used to ensure that minimally acceptable criteria are met and to promote the efficient use of the nurse’s time by removing the need to develop common activities that are done repeatedly for many of the clients on a nursing unit.
Standardized care plans are not tailored to a patient’s specific needs and goals and can provide a starting point for developing an individualized care plan .
Care plans listed in this guide are standard care plans which can serve as a framework or direction to develop an individualized care plan.
An individualized care plan care plan involves tailoring a standardized care plan to meet the specific needs and goals of the individual client and use approaches shown to be effective for a particular client. This approach allows more personalized and holistic care better suited to the client’s unique needs, strengths, and goals.
Additionally, individualized care plans can improve patient satisfaction . When patients feel that their care is tailored to their specific needs, they are more likely to feel heard and valued, leading to increased satisfaction with their care. This is particularly important in today’s healthcare environment , where patient satisfaction is increasingly used as a quality measure.
Tips on how to individualize a nursing care plan:
- Perform a comprehensive assessment of the patient’s health, history, health status, and desired goals.
- Involve the patient in the care planning process by asking them about their health goals and preferences. By involving the client, nurses can ensure that the care plan is aligned with the patient’s goals and preferences which can improve patient engagement and compliance with the care plan.
- Perform an ongoing assessment and evaluation as the patient’s health and goals can change. Adjust the care plan accordingly.
The following are the goals and objectives of writing a nursing care plan:
- Promote evidence-based nursing care and render pleasant and familiar conditions in hospitals or health centers.
- Support holistic care , which involves the whole person, including physical, psychological, social, and spiritual, with the management and prevention of the disease.
- Establish programs such as care pathways and care bundles. Care pathways involve a team effort to reach a consensus regarding standards of care and expected outcomes. In contrast, care bundles are related to best practices concerning care for a specific disease.
- Identify and distinguish goals and expected outcomes.
- Review communication and documentation of the care plan.
- Measure nursing care.
The following are the purposes and importance of writing a nursing care plan:
- Defines nurse’s role. Care plans help identify nurses’ unique and independent role in attending to clients’ overall health and well-being without relying entirely on a physician’s orders or interventions.
- Provides direction for individualized care of the client. It serves as a roadmap for the care that will be provided to the patient and allows the nurse to think critically in developing interventions directly tailored to the individual.
- Continuity of care. Nurses from different shifts or departments can use the data to render the same quality and type of interventions to care for clients, therefore allowing clients to receive the most benefit from treatment.
- Coordinate care. Ensures that all members of the healthcare team are aware of the patient’s care needs and the actions that need to be taken to meet those needs preventing gaps in care.
- Documentation . It should accurately outline which observations to make, what nursing actions to carry out, and what instructions the client or family members require. If nursing care is not documented correctly in the care plan, there is no evidence the care was provided.
- Serves as a guide for assigning a specific staff to a specific client. There are instances when a client’s care needs to be assigned to staff with particular and precise skills.
- Monitor progress. To help track the patient’s progress and make necessary adjustments to the care plan as the patient’s health status and goals change.
- Serves as a guide for reimbursement. The insurance companies use the medical record to determine what they will pay concerning the hospital care received by the client.
- Defines client’s goals. It benefits nurses and clients by involving them in their treatment and care.
A nursing care plan (NCP) usually includes nursing diagnoses , client problems, expected outcomes, nursing interventions , and rationales . These components are elaborated on below:
- Client health assessment , medical results, and diagnostic reports are the first steps to developing a care plan. In particular, client assessment relates to the following areas and abilities: physical, emotional, sexual, psychosocial, cultural, spiritual/transpersonal, cognitive, functional, age-related, economic, and environmental. Information in this area can be subjective and objective.
- Nursing diagnosis . A nursing diagnosis is a statement that describes the patient’s health issue or concern. It is based on the information gathered about the patient’s health status during the assessment.
- Expected client outcomes. These are specific goals that will be achieved through nursing interventions . These may be long and short-term.
- Nursing interventions . These are specific actions that will be taken to address the nursing diagnosis and achieve expected outcomes . They should be based on best practices and evidence-based guidelines.
- Rationales. These are evidence-based explanations for the nursing interventions specified.
- Evaluation . These includes plans for monitoring and evaluating a patient’s progress and making necessary adjustments to the care plan as the patient’s health status and goals change.
Care Plan Formats
Nursing care plan formats are usually categorized or organized into four columns: (1) nursing diagnoses, (2) desired outcomes and goals, (3) nursing interventions, and (4) evaluation. Some agencies use a three-column plan where goals and evaluation are in the same column. Other agencies have a five-column plan that includes a column for assessment cues.
The three-column plan has a column for nursing diagnosis, outcomes and evaluation, and interventions.
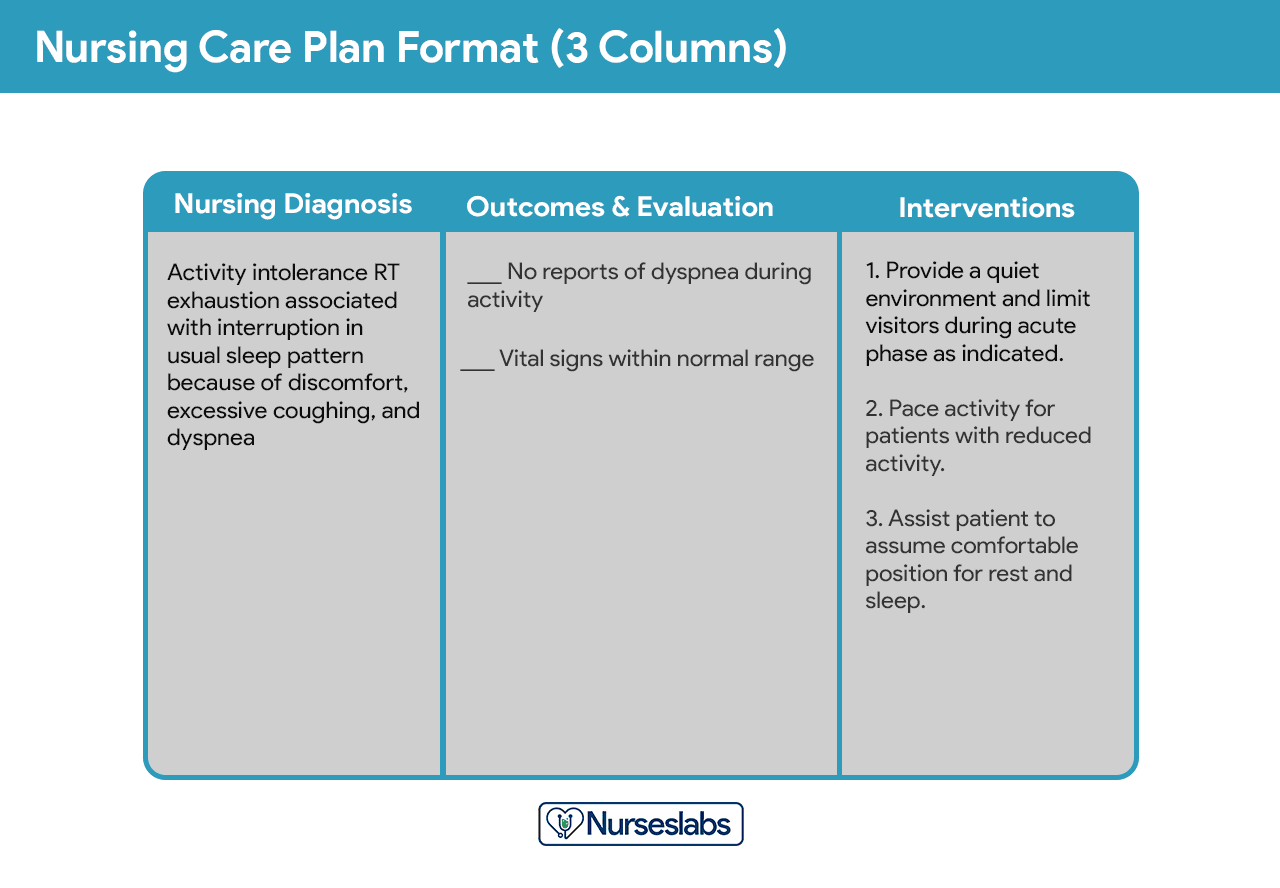
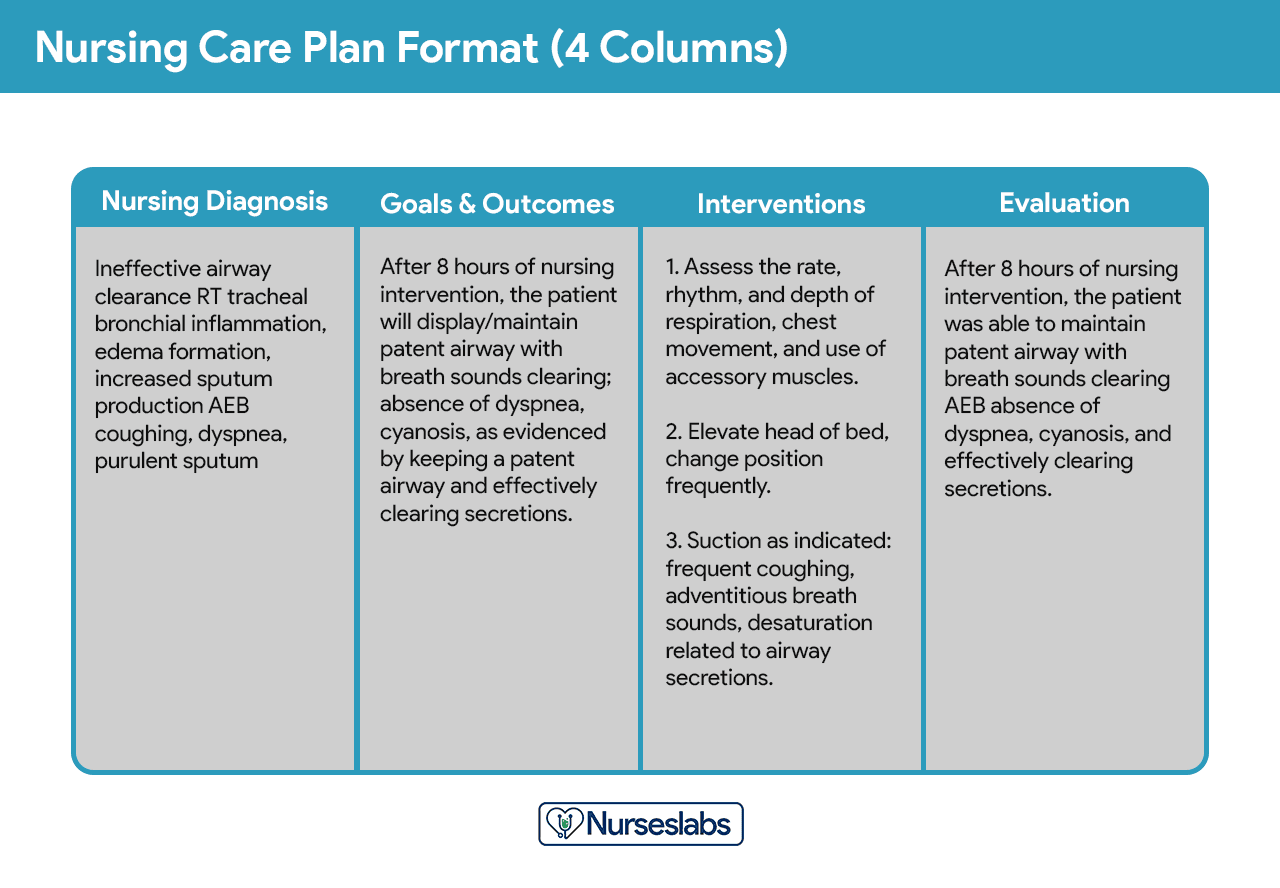
This format includes columns for nursing diagnosis, goals and outcomes, interventions, and evaluation.
Below is a document containing sample templates for the different nursing care plan formats. Please feel free to edit, modify, and share the template.
Download: Printable Nursing Care Plan Templates and Formats
Student care plans are more lengthy and detailed than care plans used by working nurses because they serve as a learning activity for the student nurse.
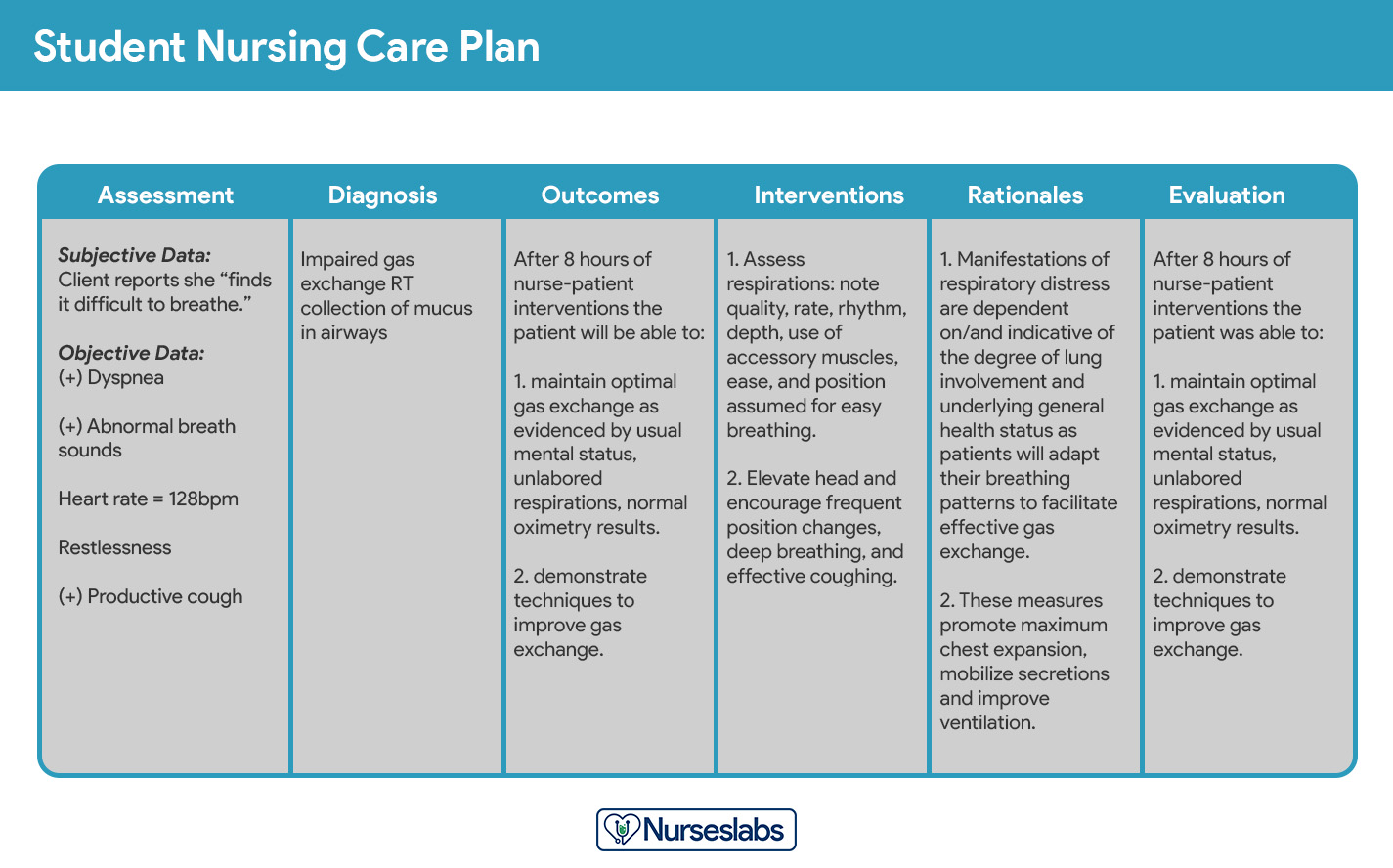
Care plans by student nurses are usually required to be handwritten and have an additional column for “Rationale” or “Scientific Explanation” after the nursing interventions column. Rationales are scientific principles that explain the reasons for selecting a particular nursing intervention.
Writing a Nursing Care Plan
How do you write a nursing care plan (NCP)? Just follow the steps below to develop a care plan for your client.
The first step in writing a nursing care plan is to create a client database using assessment techniques and data collection methods ( physical assessment , health history , interview, medical records review, and diagnostic studies). A client database includes all the health information gathered . In this step, the nurse can identify the related or risk factors and defining characteristics that can be used to formulate a nursing diagnosis. Some agencies or nursing schools have specific assessment formats you can use.
Critical thinking is key in patient assessment, integrating knowledge across sciences and professional guidelines to inform evaluations. This process, crucial for complex clinical decision-making , aims to identify patients’ healthcare needs effectively, leveraging a supportive environment and reliable information
Now that you have information about the client’s health, analyze, cluster, and organize the data to formulate your nursing diagnosis, priorities, and desired outcomes.
Nursing diagnoses are a uniform way of identifying, focusing on and dealing with specific client needs and responses to actual and high-risk problems. Actual or potential health problems that can be prevented or resolved by independent nursing intervention are termed nursing diagnoses.
We’ve detailed the steps on how to formulate your nursing diagnoses in this guide: Nursing Diagnosis (NDx): Complete Guide and List .
Setting priorities involves establishing a preferential sequence for addressing nursing diagnoses and interventions. In this step, the nurse and the client begin planning which of the identified problems requires attention first. Diagnoses can be ranked and grouped as having a high, medium, or low priority. Life-threatening problems should be given high priority.
A nursing diagnosis encompasses Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs and helps to prioritize and plan care based on patient-centered outcomes. In 1943, Abraham Maslow developed a hierarchy based on basic fundamental needs innate to all individuals. Basic physiological needs/goals must be met before higher needs/goals can be achieved, such as self-esteem and self-actualization. Physiological and safety needs are the basis for implementing nursing care and interventions. Thus, they are at the base of Maslow’s pyramid, laying the foundation for physical and emotional health.
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
- Basic Physiological Needs: Nutrition (water and food), elimination (Toileting), airway ( suction )-breathing ( oxygen )-circulation (pulse, cardiac monitor, blood pressure ) (ABCs), sleep , sex, shelter, and exercise.
- Safety and Security: Injury prevention ( side rails , call lights, hand hygiene , isolation , suicide precautions, fall precautions, car seats, helmets, seat belts), fostering a climate of trust and safety ( therapeutic relationship ), patient education (modifiable risk factors for stroke , heart disease).
- Love and Belonging: Foster supportive relationships, methods to avoid social isolation ( bullying ), employ active listening techniques, therapeutic communication , and sexual intimacy.
- Self-Esteem: Acceptance in the community, workforce, personal achievement, sense of control or empowerment, accepting one’s physical appearance or body habitus.
- Self-Actualization: Empowering environment, spiritual growth, ability to recognize the point of view of others, reaching one’s maximum potential.
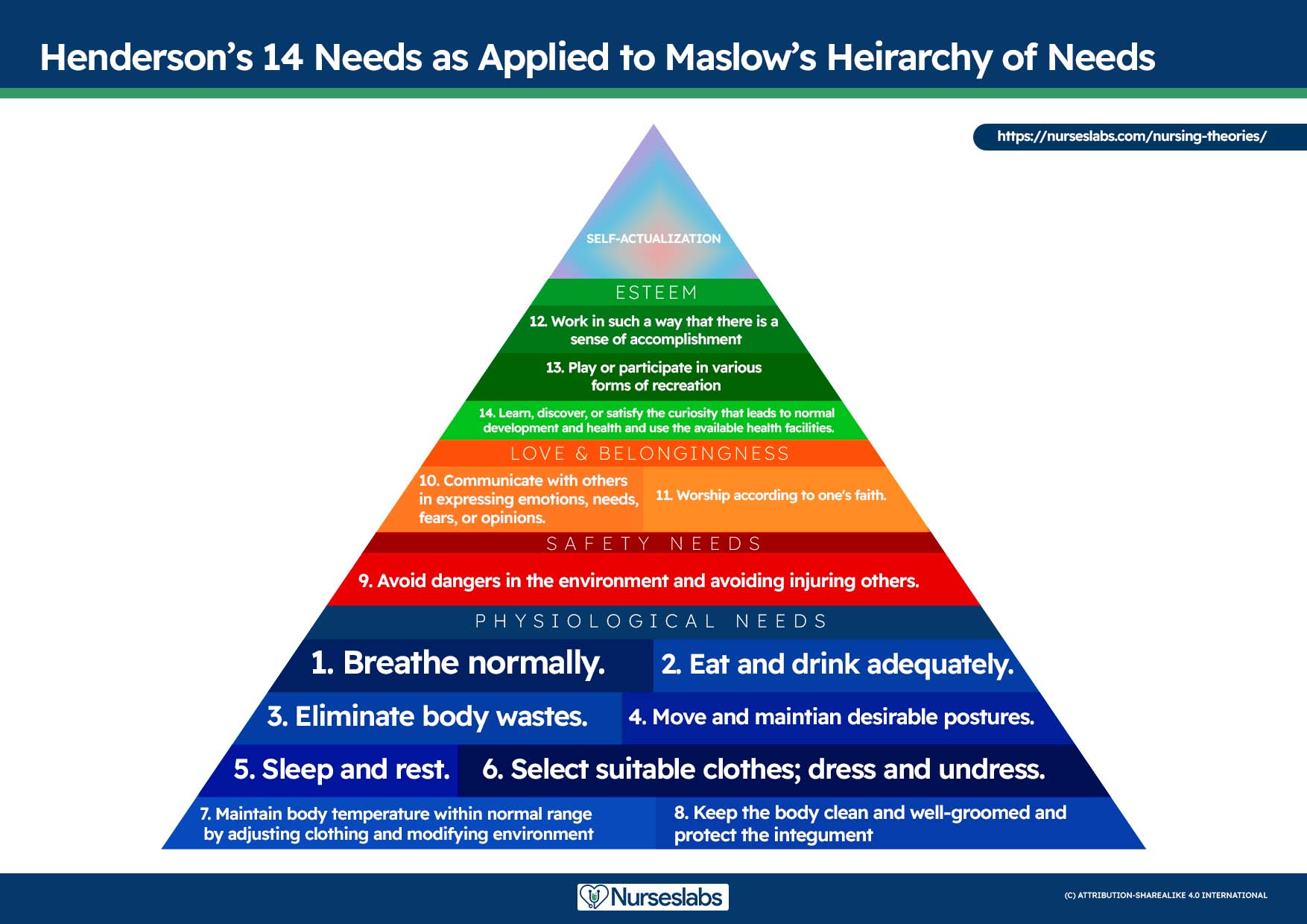
The client’s health values and beliefs, priorities, resources available, and urgency are factors the nurse must consider when assigning priorities. Involve the client in the process to enhance cooperation.
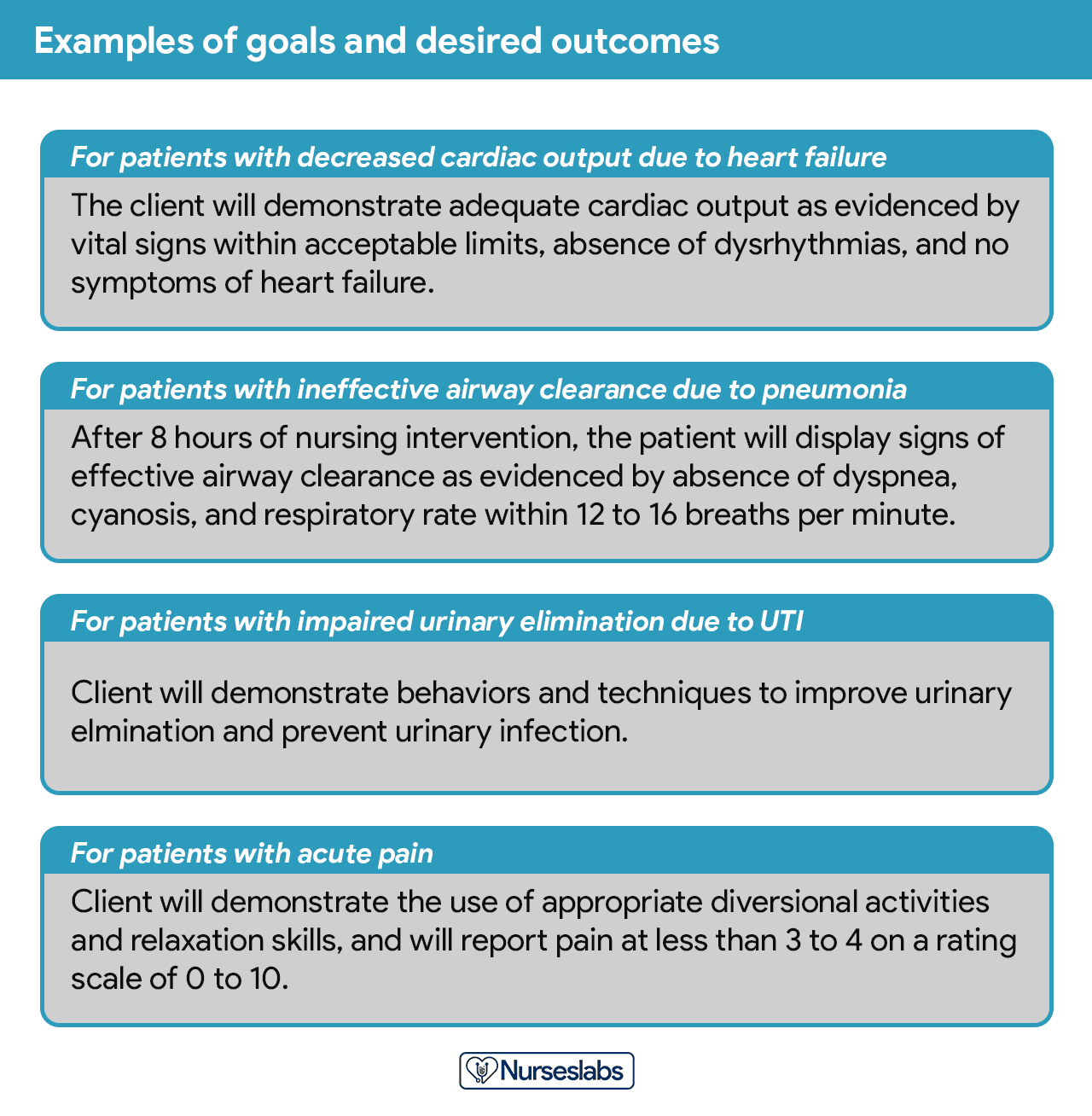
Step 5: Establishing Client Goals and Desired Outcomes
After assigning priorities for your nursing diagnosis, the nurse and the client set goals for each determined priority. Goals or desired outcomes describe what the nurse hopes to achieve by implementing the nursing interventions derived from the client’s nursing diagnoses. Goals provide direction for planning interventions, serve as criteria for evaluating client progress, enable the client and nurse to determine which problems have been resolved, and help motivate the client and nurse by providing a sense of achievement.
One overall goal is determined for each nursing diagnosis. The terms “ goal outcomes “ and “expected outcome s” are often used interchangeably.
According to Hamilton and Price (2013), goals should be SMART . SMART stands for specific, measurable, attainable, realistic, and time-oriented goals.
- Specific. It should be clear, significant, and sensible for a goal to be effective.
- Measurable or Meaningful. Making sure a goal is measurable makes it easier to monitor progress and know when it reaches the desired result.
- Attainable or Action-Oriented. Goals should be flexible but remain possible.
- Realistic or Results-Oriented. This is important to look forward to effective and successful outcomes by keeping in mind the available resources at hand.
- Timely or Time-Oriented. Every goal needs a designated time parameter, a deadline to focus on, and something to work toward.
Hogston (2011) suggests using the REEPIG standards to ensure that care is of the highest standards. By this means, nursing care plans should be:
- Realistic. Given available resources.
- Explicitly stated. Be clear about precisely what must be done, so there is no room for misinterpretation of instructions.
- Evidence-based. That there is research that supports what is being proposed.
- Prioritized. The most urgent problems are being dealt with first.
- Involve. Involve both the patient and other members of the multidisciplinary team who are going to be involved in implementing the care.
- Goal-centered. That the care planned will meet and achieve the goal set.
Goals and expected outcomes must be measurable and client-centered. Goals are constructed by focusing on problem prevention, resolution, and rehabilitation. Goals can be short-term or long-term . Most goals are short-term in an acute care setting since much of the nurse’s time is spent on the client’s immediate needs. Long-term goals are often used for clients who have chronic health problems or live at home, in nursing homes, or in extended-care facilities.
- Short-term goal . A statement distinguishing a shift in behavior that can be completed immediately, usually within a few hours or days.
- Long-term goal . Indicates an objective to be completed over a longer period, usually weeks or months.
- Discharge planning . Involves naming long-term goals, therefore promoting continued restorative care and problem resolution through home health, physical therapy, or various other referral sources.
Goals or desired outcome statements usually have four components: a subject, a verb, conditions or modifiers, and a criterion of desired performance.
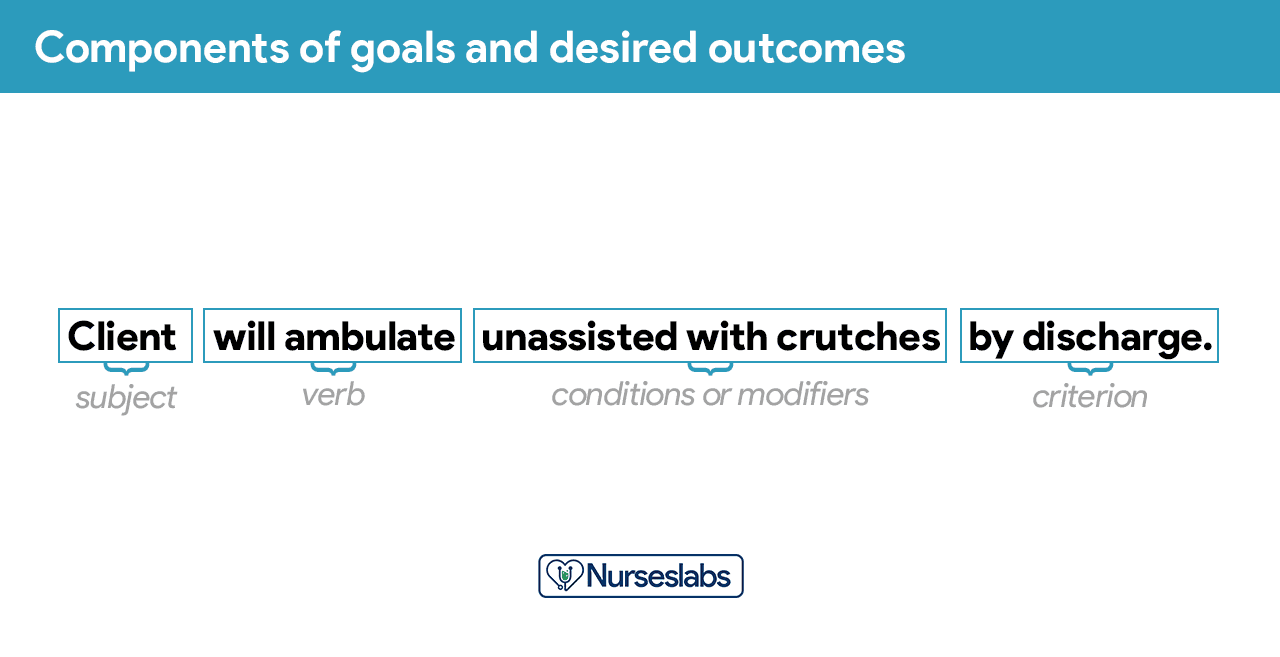
- Subject. The subject is the client, any part of the client, or some attribute of the client (i.e., pulse, temperature , urinary output ). That subject is often omitted in writing goals because it is assumed that the subject is the client unless indicated otherwise (family, significant other ).
- Verb. The verb specifies an action the client is to perform, for example, what the client is to do, learn, or experience.
- Conditions or modifiers. These are the “what, when, where, or how” that are added to the verb to explain the circumstances under which the behavior is to be performed.
- Criterion of desired performance. The criterion indicates the standard by which a performance is evaluated or the level at which the client will perform the specified behavior. These are optional.
When writing goals and desired outcomes, the nurse should follow these tips:
- Write goals and outcomes in terms of client responses and not as activities of the nurse. Begin each goal with “Client will […]” help focus the goal on client behavior and responses.
- Avoid writing goals on what the nurse hopes to accomplish, and focus on what the client will do.
- Use observable, measurable terms for outcomes. Avoid using vague words that require interpretation or judgment of the observer.
- Desired outcomes should be realistic for the client’s resources, capabilities, limitations, and on the designated time span of care.
- Ensure that goals are compatible with the therapies of other professionals.
- Ensure that each goal is derived from only one nursing diagnosis. Keeping it this way facilitates evaluation of care by ensuring that planned nursing interventions are clearly related to the diagnosis set.
- Lastly, make sure that the client considers the goals important and values them to ensure cooperation.
Step 6: Selecting Nursing Interventions
Nursing interventions are activities or actions that a nurse performs to achieve client goals. Interventions chosen should focus on eliminating or reducing the etiology of the priority nursing problem or diagnosis. As for risk nursing problems, interventions should focus on reducing the client’s risk factors. In this step, nursing interventions are identified and written during the planning step of the nursing process ; however, they are actually performed during the implementation step.
Nursing interventions can be independent, dependent, or collaborative:
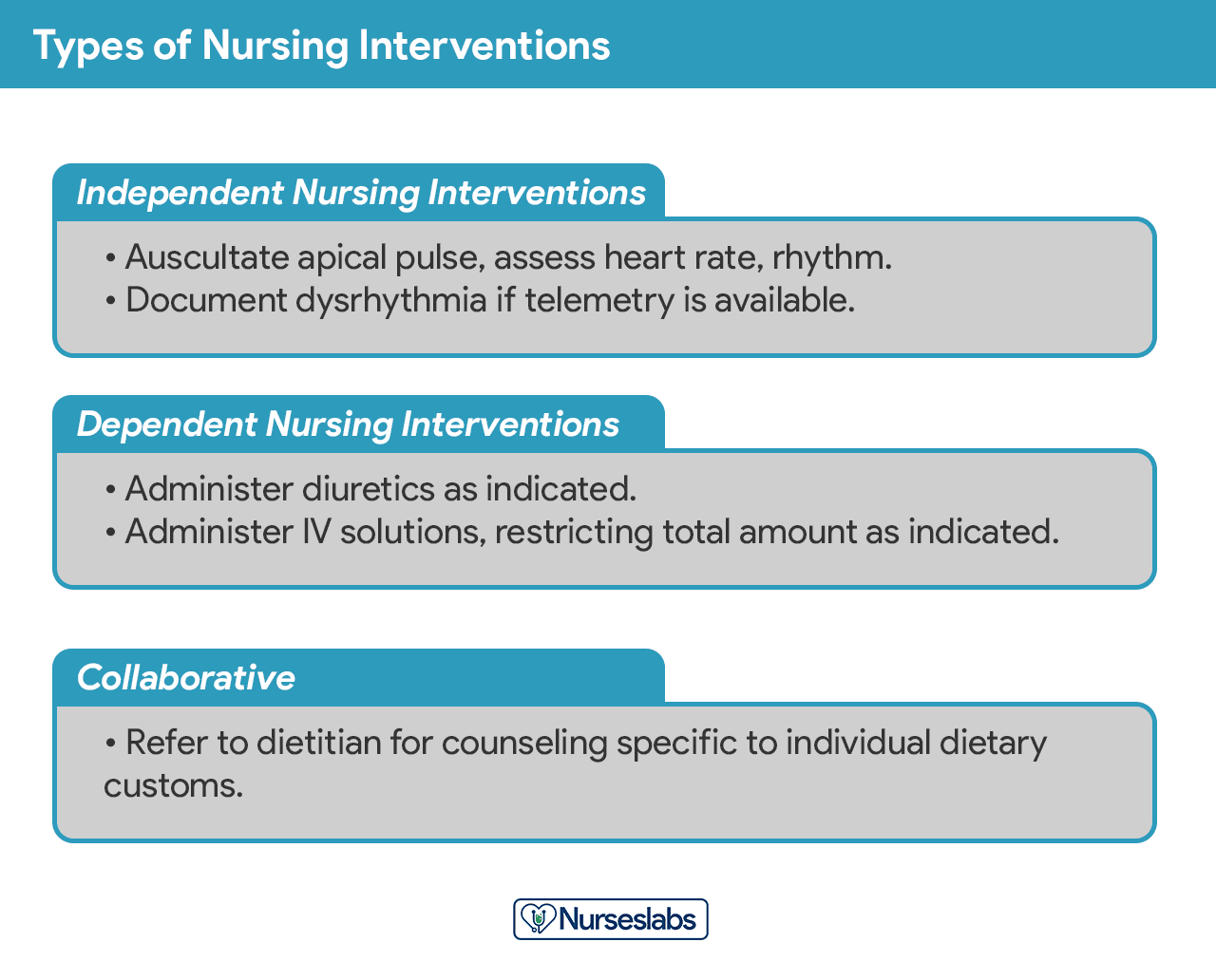
- Independent nursing interventions are activities that nurses are licensed to initiate based on their sound judgement and skills. Includes: ongoing assessment, emotional support, providing comfort , teaching, physical care, and making referrals to other health care professionals.
- Dependent nursing interventions are activities carried out under the physician’s orders or supervision. Includes orders to direct the nurse to provide medications, intravenous therapy , diagnostic tests, treatments, diet, and activity or rest. Assessment and providing explanation while administering medical orders are also part of the dependent nursing interventions.
- Collaborative interventions are actions that the nurse carries out in collaboration with other health team members, such as physicians, social workers, dietitians, and therapists. These actions are developed in consultation with other health care professionals to gain their professional viewpoint.
Nursing interventions should be:
- Safe and appropriate for the client’s age, health, and condition.
- Achievable with the resources and time available.
- Inline with the client’s values, culture, and beliefs.
- Inline with other therapies.
- Based on nursing knowledge and experience or knowledge from relevant sciences.
When writing nursing interventions, follow these tips:
- Write the date and sign the plan. The date the plan is written is essential for evaluation, review, and future planning. The nurse’s signature demonstrates accountability.
- Nursing interventions should be specific and clearly stated, beginning with an action verb indicating what the nurse is expected to do. Action verb starts the intervention and must be precise. Qualifiers of how, when, where, time, frequency, and amount provide the content of the planned activity. For example: “ Educate parents on how to take temperature and notify of any changes,” or “ Assess urine for color, amount, odor, and turbidity.”
- Use only abbreviations accepted by the institution.
Rationales, also known as scientific explanations, explain why the nursing intervention was chosen for the NCP.
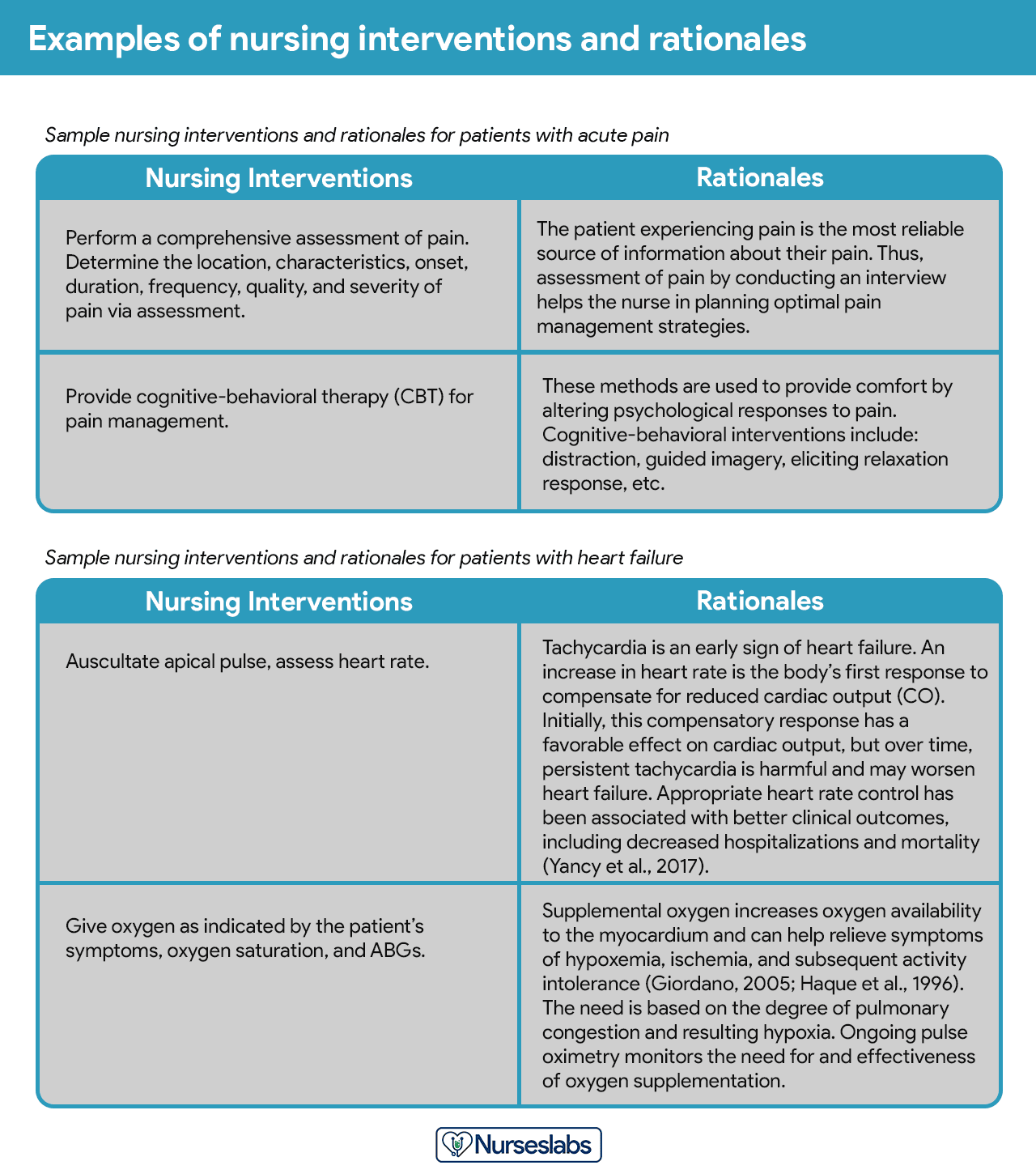
Rationales do not appear in regular care plans. They are included to assist nursing students in associating the pathophysiological and psychological principles with the selected nursing intervention.
Evaluation is a planned, ongoing, purposeful activity in which the client’s progress towards achieving goals or desired outcomes is assessed, and the effectiveness of the nursing care plan (NCP). Evaluation is an essential aspect of the nursing process because the conclusions drawn from this step determine whether the nursing intervention should be terminated, continued, or changed.
The client’s care plan is documented according to hospital policy and becomes part of the client’s permanent medical record, which may be reviewed by the oncoming nurse. Different nursing programs have different care plan formats. Most are designed so that the student systematically proceeds through the interrelated steps of the nursing process , and many use a five-column format.
Nursing Care Plan List
This section lists the sample nursing care plans (NCP) and nursing diagnoses for various diseases and health conditions. They are segmented into categories:
Miscellaneous nursing care plans examples that don’t fit other categories:
Care plans that involve surgical intervention .
Nursing care plans about the different diseases of the cardiovascular system :
Nursing care plans (NCP) related to the endocrine system and metabolism:
Care plans (NCP) covering the disorders of the gastrointestinal and digestive system :
Care plans related to the hematologic and lymphatic system:
NCPs for communicable and infectious diseases:
All about disorders and conditions affecting the integumentary system:
Nursing care plans about the care of the pregnant mother and her infant. See care plans for maternity and obstetric nursing:
Care plans for mental health and psychiatric nursing:
Care plans related to the musculoskeletal system:
Nursing care plans (NCP) for related to nervous system disorders:
Care plans relating to eye disorders:
Nursing care plans (NCP) for pediatric conditions and diseases:
Care plans related to the reproductive and sexual function disorders:
Care plans for respiratory system disorders:
Care plans related to the kidney and urinary system disorders:
Recommended nursing diagnosis and nursing care plan books and resources.
Disclosure: Included below are affiliate links from Amazon at no additional cost from you. We may earn a small commission from your purchase. For more information, check out our privacy policy .
Ackley and Ladwig’s Nursing Diagnosis Handbook: An Evidence-Based Guide to Planning Care We love this book because of its evidence-based approach to nursing interventions. This care plan handbook uses an easy, three-step system to guide you through client assessment, nursing diagnosis, and care planning. Includes step-by-step instructions showing how to implement care and evaluate outcomes, and help you build skills in diagnostic reasoning and critical thinking.

Nursing Care Plans – Nursing Diagnosis & Intervention (10th Edition) Includes over two hundred care plans that reflect the most recent evidence-based guidelines. New to this edition are ICNP diagnoses, care plans on LGBTQ health issues, and on electrolytes and acid-base balance.

Nurse’s Pocket Guide: Diagnoses, Prioritized Interventions, and Rationales Quick-reference tool includes all you need to identify the correct diagnoses for efficient patient care planning. The sixteenth edition includes the most recent nursing diagnoses and interventions and an alphabetized listing of nursing diagnoses covering more than 400 disorders.

Nursing Diagnosis Manual: Planning, Individualizing, and Documenting Client Care Identify interventions to plan, individualize, and document care for more than 800 diseases and disorders. Only in the Nursing Diagnosis Manual will you find for each diagnosis subjectively and objectively – sample clinical applications, prioritized action/interventions with rationales – a documentation section, and much more!

All-in-One Nursing Care Planning Resource – E-Book: Medical-Surgical, Pediatric, Maternity, and Psychiatric-Mental Health Includes over 100 care plans for medical-surgical, maternity/OB, pediatrics, and psychiatric and mental health. Interprofessional “patient problems” focus familiarizes you with how to speak to patients.

Recommended reading materials and sources for this NCP guide:
- Björvell, C., Thorell-Ekstrand, I., & Wredling, R. (2000). Development of an audit instrument for nursing care plans in the patient record. BMJ Quality & Safety , 9 (1), 6-13. [ Link ]
- DeLaune, S. C., & Ladner, P. K. (2011). Fundamentals of nursing: Standards and practice . Cengage learning .
- Freitas, F. A., & Leonard, L. J. (2011). Maslow’s hierarchy of needs and student academic success . Teaching and learning in Nursing , 6 (1), 9-13.
- Hamilton, P., & Price, T. (2007). The nursing process, holistic. Foundations of Nursing Practice E-Book: Fundamentals of Holistic Care , 349.
- Lee, T. T. (2004). Evaluation of computerized nursing care plan: instrument development . Journal of Professional Nursing , 20 (4), 230-238.
- Lee, T. T. (2006). Nurses’ perceptions of their documentation experiences in a computerized nursing care planning system . Journal of Clinical Nursing , 15 (11), 1376-1382.
- Rn , B. O. C., Rn, H. M., Rn, D. T., & Rn, F. E. (2000). Documenting and communicating patient care : Are nursing care plans redundant?. International Journal of Nursing Practice , 6 (5), 276-280.
- Stonehouse, D. (2017). Understanding the nursing process . British Journal of Healthcare Assistants , 11 (8), 388-391.
- Yildirim, B., & Ozkahraman, S. (2011). Critical thinking in nursing process and education . International journal of humanities and social science , 1 (13), 257-262.
69 thoughts on “Nursing Care Plans (NCP) Ultimate Guide and List”
This page is helpful!
Thank you! Hope we’ve helped you write better nursing care plans!
Will definitely use this site to help write care plans. How should I cite this link when using APA format. Thank You
HI Can some one help me to do assignment on Impaired renal perfusion. 1.Goal 2.Related Action 3.Rational 4.Evaluate outcome
Wow God bless plenty Nurseslabs really relieve my burdens 😊😊
Thank you for all this useful info! I have been looking for something like this online.
You’re welcome! :)
Quite educative thank you
The notes were indeed useful
I hope to learn more and improve my skills towards nursing
Thank you so so much! This website is of great assistance to me. God bless you.
It’s so great for nursing student
Very beautiful ,Good work keep it up
Nice work. Well done
Very helpful
Great job,thank you
Thanks so much , it’s of much support for students .
Risk for ineffective thermoregulation would be a good one for you to do next for newborn.
Hi, i have learnt a lot THANK YOU. i would kindly like to learn more on paper 1 since am yet to sit for my nursing council exams and feel challenged on the paper.please do assist me thank you.
This site is a total lifesaver!
What is a nursing care plan a mother in second stage of labour?
Please see: 36 Labor Stages, Induced and Augmented Labor Nursing Care Plans
What is the nursing care plan for pulmonary oedema?
I m interest in receiving a blank nursing care plan template for my students to type on. I was wondering if it was available and if so can you please direct me on where to find it?
Hi! You can download it here: Nursing Care Plan Template
I love this website!!! Is there a textbook version of the Nurseslabs that I can purchase??
Thank you Nurseslabs. This is a wonderful note you’ve prepared for all nurses. I would like a pdf of this. Thanks.
I wish I had had this resource when i was in nursing school 2008!!
Yeah! It’s nice
Thanks for this information!
God bless you sis…Thank you for all this useful info!
This is the kind of step-by-step guidance that I needed. Thank you!
Thank you. I have learned a lot!
Wow! This is a hidden treasure!
Thanks a lot for this, it is really helpful!
Hi Matt! I would like to purchase a textbook of your nursing care plan. Where I can purchase pls help!
Hi Criselda,
Sorry, we don’t have a textbook. All of our resources are here on the website and free to use.
Good day, I would like to know how can I use your website to help students with care plans.
Sincerely, Oscar A. Acosta DNP, RN
Oh I love your works. Your explanations
I’m glad I’ve met your website. It helps me a lot. Thank you
I love this, so helpful.
These care plans are great for using as a template. I don’t have to reinvent the wheel, and the information you provided will ensure that I include the important data without leaving things out. Thanks a million!
Hi, I have learnt a lot, this is a wonderful note you’ve prepared for all nurses thank you.
Matt, this page is very informative and I especially appreciate seeing care plans for patients with neurological disorders. I notice, though, that traumatic brain injury is not on your list. Might you add a care plan page for this?
Thanks alot I had gained much since these are detailed notes 🙏🙏
OMG, this is amazing!
Wow very helpful.thank you very much🙏🙏
Hi, is there a downloadable version of this, pdf or other files maybe this is awesome!
Hi Paul, on your browser go to File > Print > Save as PDF. Hope that helps and thanks for visiting Nurseslabs!
Matt, I’m a nursing instructor looking for tools to teach this. I am interested in where we can find “rules” for establishing “related to” sections…for example –not able to utilize medical diagnosis as a “related to” etc. Also, resources for nursing rationale.
Hello, please check out our guide on how to write nursing diagnoses here: https://nurseslabs.com/nursing-diagnosis/
Nursing care plan is very amazing
Thanks for your time. Nursing Care Plan looks great and helpful!
complete knowledge i get from here
great resource. puts it all together. Thank for making it free for all
Hello Ujunwa, Thanks a lot for the positive vibes! 🌟 It’s super important to us that everyone has access to quality resources. Just wondering, is there any specific topic or area you’d love to see more about? We’re always looking to improve and add value!
Great work.
Hi Abbas, Thank you so much! Really glad to hear you found the nursing care plans guide useful. If there’s a specific area or topic you’re keen on exploring more, or if you have any suggestions for improvement, feel free to share. Always aiming to make our resources as helpful as possible!
It has been good time me to use these nursing guides.
What is ncp for acute pain
For everything you need to know about managing acute pain, including a detailed nursing care plan (NCP), definitely check out our acute pain nursing care plan guide . It’s packed with insights on assessment, interventions, and patient education to effectively manage and alleviate acute pain.
Good morning. I love this website
what is working knowledge on nursing standard, and Basic Life Support documentation?
Thank you for the website, it is awesome. I just have one question about the 1st set of ABG (Practice Exam) – The following are the values: pH 7.3, PaCO2 68 mm Hg, HCO3 28 mmol/L, and PaO2 60 mm Hg…Definitely Respiratory Acidosis, but the HC03 is only 28 mmol/L..I thought HC03 of 28 mmol/L would be within the normal range and thus, no compensation, but the correct answer has partial compensation because of the HC03 value. What value ranges are you using for HC03. Thanks, EK Mickley, RN BSN
welcome to you can get the best way to days after the holiest month
Intra operative care ncp
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
How to Write a Nursing Care Plan
Nursing care plan components, nursing care plan fundamentals.

Knowing how to write a nursing care plan is essential for nursing students and nurses. Why? Because it gives you guidance on what the patient’s main nursing problem is, why the problem exists, and how to make it better or work towards a positive end goal. In this article, we'll dig into each component to show you exactly how to write a nursing care plan.
Popular Online RN-to-BSN Programs

Gain the skills and credentials to advance into nurse management and leadership roles, while laying the groundwork to pursue future nurse practitioner or advanced practice roles. Complete your courses online, on your schedule, at Purdue Global’s School of Nursing.
Enrollment: Nationwide, but certain programs have state restrictions. Check with Purdue for details.
- RN-to-BSN - ExcelTrack

WGU's award-winning online programs are created to help you succeed while graduating faster and with less debt. WGU is a CCNE accredited, nonprofit university offering nursing bachelor's and master's degrees.
Enrollment: Nationwide
The University of Texas at Arlington’s online programs are designed to help you achieve more in your nursing practice with a Bachelor of Science in Nursing. They offer convenient, flexible options for completing your RN to BSN online, designed to fit into your busy schedule.

GCU’s RN-BSN program is tailored to meet the needs of the RN adult learner and to maximize the strengths that the working RN already possesses. Transfer up to 90 credits and earn a BSN in as little as 12 months. GCU’s online classes allow you to study at the times that work for your schedule while still enjoying a close connection with your classmates and instructor via online discussions.

As a pioneer in distance learning since 1985, Liberty University’s online nursing programs are designed to prepare practicing nurses to serve with integrity by teaching advanced skills from an ethical perspective. Liberty's programs are based on industry best practices and up-to-date research – so you can get the tools you need to stay on the cutting edge of nursing care and innovation.
- RN-to-BSN - Global Studies
Nurses Helping Nurses: Why You Can Trust Nurse.org
As the leading educational website for nurses by nurses, Nurse.org is committed to editorial integrity, medical accuracy, and data-driven analysis.
✔ Content written by 80+ licensed, practicing nurses who are experts in their respective specialties. Learn more about our nurse contributors .
✔ Medical and expert reviews by nurses for clinical accuracy and to ensure our content reflects the latest medical and nursing standards.
✔ Reputable sources from the World Health Organization (WHO) , research institutions and associations, as well as academic, nursing, and medical journals. Learn more about our data resources .
A nursing care plan has several key components including,
- Nursing diagnosis
- Expected outcome
- Nursing interventions and rationales
Each of the five main components is essential to the overall nursing process and care plan. A properly written care plan must include these sections otherwise, it won’t make sense!
- Nursing diagnosis - A clinical judgment that helps nurses determine the plan of care for their patients
- Expected outcome - The measurable action for a patient to be achieved in a specific time frame.
- Nursing interventions and rationales - Actions to be taken to achieve expected outcomes and reasoning behind them.
- Evaluation - Determines the effectiveness of the nursing interventions and determines if expected outcomes are met within the time set.
>> Related: What is the Nursing Process?
Get 10% OFF Nursing School Study Guides From nurseinthemaking.com ! Fill out the form to get your exclusive discount.
Before writing a nursing care plan, determine the most significant problems affecting the patient. Think about medical problems but also psychosocial problems. At times, a patient's psychosocial concerns might be more pressing or even holding up discharge instead of the actual medical issues.
After making a list of problems affecting the patient and corresponding nursing diagnosis, determine which are the most important. Generally, this is done by considering the ABCs (Airway, Breathing, Circulation). However, these will not ALWAYS be the most significant or even relevant for your patient.
Step 1: Assessment
The first step in writing an organized care plan includes gathering subjective and objective nursing data . Subjective data is what the patient tells us their symptoms are, including feelings, perceptions, and concerns. Objective data is observable and measurable.
This information can come from,
Verbal statements from the patient and family
Vital signs
Blood pressure
Respirations
Temperature
Oxygen Saturation
Physical complaints
Body conditions
Head-to-toe assessment findings
Medical history
Height and weight
Intake and output
Patient feelings, concerns, perceptions
Laboratory data
Diagnostic testing
Echocardiogram
Step 2: Diagnosis
Using the information and data collected in Step 1, a nursing diagnosis is chosen that best fits the patient, the goals, and the objectives for the patient’s hospitalization.
According to North American Nursing Diagnosis Association (NANDA), defines a nursing diagnosis as “a clinical judgment about the human response to health conditions/life processes, or a vulnerability for that response, by an individual, family, group or community.”
A nursing diagnosis is based on Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs pyramid and helps prioritize treatments. Based on the nursing diagnosis chosen, the goals to resolve the patient’s problems through nursing implementations are determined in the next step.
Get 5 FREE study guides from Simplenursing.com - fill out the form for instant access! 1. Fluid & Electrolytes study guide 2. EKG Rhythms study guide 3. Congestive Heart Failure study guide 4. Lab Values study guide 5. Metabolic Acidosis & Alkalosis study guide

By clicking download, you agree to receive email newsletters and special offers from Nurse.org & Simplenursing.com. You may unsubscribe at any time by using the unsubscribe link, found at the bottom of every email.
Your request has been received. Thanks!
There are 4 types of nursing diagnoses.
Problem-focused - Patient problem present during a nursing assessment is known as a problem-focused diagnosis
Risk - Risk factors require intervention from the nurse and healthcare team prior to a real problem developing
Health promotion - Improve the overall well-being of an individual, family, or community
Syndrome - A cluster of nursing diagnoses that occur in a pattern or can all be addressed through the same or similar nursing interventions
After determining which type of the four diagnoses you will use, start building out the nursing diagnosis statement.
The three main components of a nursing diagnosis are:
Problem and its definition - Patient’s current health problem and the nursing interventions needed to care for the patient.
Etiology or risk factors - Possible reasons for the problem or the conditions in which it developed
Defining characteristics or risk factors - Signs and symptoms that allow for applying a specific diagnostic label/used in the place of defining characteristics for risk nursing diagnosis
PROBLEM-FOCUSED DIAGNOSIS
Problem-Focused Diagnosis related to ______________________ (Related Factors) as evidenced by _________________________ (Defining Characteristics).
RISK DIAGNOSIS
The correct statement for a NANDA-I nursing diagnosis would be: Risk for _____________ as evidenced by __________________________ (Risk Factors).
Step 3: Outcomes and Planning
After determining the nursing diagnosis, it is time to create a SMART goal based on evidence-based practices. SMART is an acronym that stands for,
It is important to consider the patient’s medical diagnosis, overall condition, and all of the data collected. A medical diagnosis is made by a physician or advanced healthcare practitioner. It’s important to remember that a medical diagnosis does not change if the condition is resolved, and it remains part of the patient’s health history forever.
Examples of medical diagnosis include,
Chronic Lung Disease (CLD)
Alzheimer’s Disease
Endocarditis
Plagiocephaly
Congenital Torticollis
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
It is also during this time you will consider goals for the patient and outcomes for the short and long term. These goals must be realistic and desired by the patient. For example, if a goal is for the patient to seek counseling for alcohol dependency during the hospitalization but the patient is currently detoxing and having mental distress - this might not be a realistic goal.
Step 4: Implementation
Now that the goals have been set, you must put the actions into effect to help the patient achieve the goals. While some of the actions will show immediate results (ex. giving a patient with constipation a suppository to elicit a bowel movement) others might not be seen until later on in the hospitalization.
The implementation phase means performing the nursing interventions outlined in the care plan. Interventions are classified into seven categories:
Physiological
Complex physiological
Health system interventions
Some interventions will be patient or diagnosis-specific, but there are several that are completed each shift for every patient:
Pain assessment
Position changes
Fall prevention
Providing cluster care
Infection control
Step 5: Evaluation
The fifth and final step of the nursing care plan is the evaluation phase. This is when you evaluate if the desired outcome has been met during the shift. There are three possible outcomes,
Based on the evaluation, it can determine if the goals and interventions need to be altered. Ideally, by the time of discharge, all nursing care plans, including goals should be met. Unfortunately, this is not always the case - especially if a patient is being discharged to hospice, home care, or a long-term care facility. Initially, you will find that most care plans will have ongoing goals that might be met within a few days or may take weeks. It depends on the status of the patient as well as the desired goals.
Consider picking goals that are achievable and can be met by the patient. This will help the patient feel like they are making progress but also provide relief to the nurse because they can track the patient’s overall progress.
>> Show Me Online RN-to-BSN Programs
Nursing care plans contain information about a patient’s diagnosis, goals of treatment, specific nursing interventions, and an evaluation plan. The nursing plan is constantly updated with changes and new subjective and objective data.
Key aspects of the care plan include,
Outcome and Planning
Implementation
Through subjective and objective data, constantly assessing your patient’s physical and mental well-being, and the goals of the patient/family/healthcare team, a nursing care plan can be a helpful and powerful tool.
*This website is provided for educational and informational purposes only and does not constitute providing medical advice or professional services. The information provided should not be used for diagnosing or treating a health problem or disease.

Kathleen Gaines (nee Colduvell) is a nationally published writer turned Pediatric ICU nurse from Philadelphia with over 13 years of ICU experience. She has an extensive ICU background having formerly worked in the CICU and NICU at several major hospitals in the Philadelphia region. After earning her MSN in Education from Loyola University of New Orleans, she currently also teaches for several prominent Universities making sure the next generation is ready for the bedside. As a certified breastfeeding counselor and trauma certified nurse, she is always ready for the next nursing challenge.
Education: MSN Nursing Education - Loyola University New Orleans BSN - Villanova University BA- University of Mary Washington
Expertise: Pediatric Nursing, Neonatal Nursing, Nursing Education, Women’s Health, Intensive Care, Nurse Journalism, Cardiac Nursing

How to Write a Nursing Care Plan (Steps and Tips)

Knowing how to write a good nursing care plan is critical for nursing students and practicing nurses. Care plans act as a tool that helps nursing students and nurses strategically manage the nursing process to solve different problems affecting a patient. Nursing care plans also allow effective communication within a nursing team for collaborative or individual decision-making.
In this guide, we take you through the basics of nursing care plans and steps to create the best and give examples/illustrations to make it simpler. With the best practices we outline in this guide, you can write a nursing care plan without worrying that your end product will be subpar.
This guide is valuable to nursing students as it comprehensively addresses what matters. Besides, it is written by professional nurse researchers collaborating with top talents/brains in the nursing industry. It is also updated regularly to capture any new developments as far as nursing care planning is concerned.
What is a Nursing Care Plan?
A nursing care plan, abbreviated as NCP, refers to a document that details the relevant information about the history and diagnosis of the patient, their current or potential care needs, treatment goals, risks, treatment priorities, and evaluation plan.
Nursing care plans are usually updated depending on the patient's stay at a facility, preferably during and after every shift.
As a nursing student, you will be assigned to write a nursing care plan based on a scenario. For example, your preceptor could also ask you to write a care plan based on a real patient hospitalized in a clinical center where you are doing your internship or practicum.
The process of care planning begins during admission. As we have said above, it gets updated throughout the patient's stay depending on the changes they exhibit and report and based on evaluation of the achievement of the set goals. When you can plan and execute a patient-centered care plan, you have mastered the art of giving quality and excellent nursing services to your patient.
Let's peek at why nursing care plans are written with a view of their professional and academic importance.
Reasons for Writing Nursing Care Plans
You must note that there are different types of nursing care plans, either formal or informal. The formal nursing care plans are roughly documented or exist in the minds of the nurse. On the other hand, formal nursing care plans are either written on paper or computerized to guide the nursing process. Formal nursing care plans can also be standardized or individualized/patient-centered. While the standardized care plans focus on a specific population or group of patients, say those with cardiac arrest or osteoporosis, the individualized or patient-centered care plans are customized to the unique needs of a specific patient that cannot be addressed through a standardized care plan.
Given the understanding of the typologies of nursing care plans, let's now look at why we write them. Nursing care plans are written, or they exist for different reasons, including:
- To promote the use of evidence-based practices in nursing care to address different healthcare needs of the patients
- Holistically caring for patients in recognition of the nursing metaparadigm (health, people, environment, and nursing)
- Enabling nursing teal collaboration through information sharing and collaborative decision-making
- Measuring the effectiveness of care and documenting the nursing process for care efficiency and compliance
- Offering patient-centered or individualized care to improve outcomes
- Identifying the unique roles of nurses in attending to the needs of the patient without constant consultation with physicians
- Allowing for continuity of care by allowing nurses from different shifts to render quality interventions to patients optimizes care outcomes.
- Guide for delegating duties and assigning specific staff to a patient, especially in cases of specialized care.
- Defining a patient's goals helps involve them in decision-making regarding their care.
The Main Components of a Nursing Care Plan
A well-written nursing care plan must have specific components. The main components of a nursing care plan (NCP) are:
- Expected outcomes
- Interventions
- Evaluations
Let's elaborate on these five main components of a nursing care plan.
- Assessment. Assessments are akin to data collection. It entails a detail of the physical, emotional, sexual, psychosocial, cultural, spiritual/transpersonal, cognitive, functional, age-related, economic, and environmental. Nursing assessments, combined with the results of medical findings and diagnostic studies, are documented in the client database and form the foundation for developing the client's care plan. The assessment is facilitated through observations for objective data and interviews with patients and their significant others or family for subjective data.
- Diagnosis. With a correct assessment, a nursing care plan details the clinical judgment that helps nurses determine the care plan or interventions for the specific patient.
- Expected outcomes. The outcomes entail the specific, measurable actions for a patient to be achieved within a specific time. The outcomes can be short, medium and long-term depending on the patient's condition.
- Interventions. This entails planning for actions to be taken to achieve the set goals of the patients and expected outcomes, including the rationale behind them. The rationale is evidence-based practices drawn from clinical guidelines, standard operating procedures, evidence-based guidelines, and best practices.
- Evaluations. This section of a nursing care plan entails a set of steps to determine the effectiveness of a nursing intervention or nursing interventions to assess whether the expected outcomes have been met.
What makes a good nursing care plan?
A good nursing care plan contains information about the patient's diagnosis, immediate and changing care needs, treatment goals, specific nursing interventions, and an evaluation plan to determine the effectiveness of care. Such a nursing care plan document can only be achieved through observing certain care plan fundamentals.
- The care plan must answer the questions of what, why, and how.
- A successful care plan uses the fundamental aspects of critical thinking to come up with a patient-centered approach to care
- Follows evidence-based practice guidelines when developing interventions or explaining the rationale for actions
- Has SMART goals for the patients
- Allows for effective communication
- Sharable and easily accessible. If written, it should be legible to everyone else. If you are typing it, use a readable font and good formatting.
- Up to date. It entails the latest information about the patient and changes in their conditions.
Steps for Writing a Nursing Care Plan
You will be assigned a patient scenario or case study as a student. These can be actual case studies from real cases happening on hospital floors or cases created to facilitate teaching and learning. As a professional nurse, you will write the case study based on your patient's condition. Given the understanding of the five main components of a nursing care plan, we also say that nursing care plans follow a five-step framework.
1. Assessment
The first step of writing a nursing care plan is to practice critical thinking skills and perform data collection. During this phase, you collect subjective and objective data. The source of subjective data is an interview with the caretakers, family members, or friends of the patient and the patient. The objective data are observed or measured by you, such as weight, height, heart rate, and respiratory rates. In this section of your nursing care plan, you will include the following:
- Verbal statements from the patient and those accompanying them
- Vital signs (heart rate, blood pressure, respiration, temperature, oxygen saturation)
- Physical complaints (headache, vomiting, nausea, pain, swelling)
- Body conditions (head-to-toe assessments)
- Medical history
- Physical features (height and weight)
- Concerns, perceptions, and feelings of the patient
- Lab findings
- Diagnostic tests (EKG, X-ray, echocardiogram, etc.)
2. Diagnosis
The success of this section depends on the accuracy of the data collected from the first part. Next, you need to select a nursing diagnosis that fits the goals and objectives of hospitalization. The diagnosis step entails analyzing the data from the first step or assessment. Writing good nursing diagnoses is a step in the right direction toward choosing nursing strategies targeting specific desired outcomes.
According to NANDA , nursing diagnosis is a clinical judgment about the human response to life processes or conditions. It also refers to vulnerability to that response by an individual, group, community, or family.
When writing a nursing diagnosis, it is essential to formulate it based on Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs Pyramid so that you can prioritize treatments and interventions. For instance, you need to prioritize the basic physiological needs before the higher needs, such as self-actualization and self-esteem. The rationale for first addressing the physiological/safety needs is that they form the foundations for nursing processes (care and intervention planning).
A good diagnosis identifies a problem (current health problem and the nursing interventions required), the risk factors or etiology (reasons for the problem/condition), and the characteristics of the problem (signs and symptoms).
Nursing diagnoses can be categorized into:
- Problem-focused diagnoses . The problems that present during the assessment of the patient. This is the actual diagnosis based on signs and symptoms. It could include shortness of breath, anxiety, acute pain, impaired skin integrity, etc.
- Risk nursing diagnoses . These are clinical judgments that a problem does not exist. However, the presence of risk factors predisposes the patient to the problem unless specific interventions are taken. Examples can include the risk of falls as evidenced by weak bones, the risk of injury as evidenced by altered mobility, the risk of infection as evidenced by immunosuppression, etc.
- Health Promotion or wellness diagnosis is a clinical judgment about the desire and motivation to increase well-being or reach one's health potential.
- Syndrome diagnoses . The clinical judgment concerns and combination of risk nursing diagnoses or problems that can occur due to specific events. Examples include chronic pain syndrome, frail elderly syndrome, etc.
You can read more from Nightingale College concerning nursing diagnosis .
Note that the nursing diagnoses will change as the client progresses through various stages of illness or maladaptation to resolve the problem or to the conclusion of a condition. Therefore, every decision must be time-bound, given that decisions might change as additional information is gathered.
When writing a student nursing care plan, you must provide a rationale for a specific diagnosis. This means including in-text citations from peer-reviewed nursing journal articles.
3. Outcomes
After writing the diagnosis section, you need to develop SMART (specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound) goals based on evidence-based practice (EBP) guidelines and client-centered. To do this, you must consider the patient's overall condition, relevant information, and diagnosis.
The goals and desired outcomes describe what you expect to achieve by implementing specific nursing interventions or actions based on the diagnoses. The goals direct the intervention planning process and serve to evaluate the client's progress. When writing the goals, consider the medical diagnosis made by ad advanced healthcare practitioner or physician. It could include COPD, chronic kidney disease, heart failure, diabetes mellitus, diabetes ketoacidosis, obesity, thyroidectomy, hyper/hypothyroidism, cancer, Alzheimer's disease, endocarditis, eating disorders, acid-based balance disorders, fluid/electrolyte imbalance, etc.
The goals of the patient and expected outcomes can be short-term or long-term. Short-term goals immediately focus on the shift in behavior, mainly within a few hours or days. Long-term goals are objectives to be met over a long period, months or weeks.
When writing the goals and desired outcomes, you must include the subject, verb, conditions or modified, and criterion. Usually, they are written in the future tense.
Let's explore the four components:
- Subject. This refers to the client, any part of the client, or some attribute of the client. It could be vitals (temperature, urinary output, blood pressure)
- Verb. This specifies the specific action that the client will perform.
- Conditions or modifiers. These are the "what, where, when, and how?" added to the verb to explain the situations under which behavior is performed.
- Criterion . These are indicators of the standard by which a performance is measured and evaluated or the level at which the patient can comfortably and efficiently perform a given behavior or action.
Examples of goals and outcomes
- The patient will demonstrate adequate cardiac output as evidenced by vital signs within acceptable limits, no symptoms of heart failure, and absence of dysrhythmias.
- The client will identify individual nutritional needs within 36 hours
- The client will ambulate using a cane within 24 hours of surgery
4. Nursing Interventions
Planning for nursing interventions or strategies is also called the implementation stage. You will be performing various nursing interventions, including following doctor's orders. Every intervention should be developed using evidence-based practice guidelines.
Interventions are classified into seven domains: family, physiological, community, complex physiological, safety, health system, and behavioral interventions. They can be implemented during shifts. Some interventions include pain assessment, listening, preventing falls, administering fluids, etc.
Nursing interventions refer to a set of activities or actions undertaken by a nurse in response to the diagnosis to achieve expected outcomes and meet a patient's goals.
The interventions majorly focus on eliminating or reducing the etiology of the nursing diagnosis. There are different types of nursing interventions:
- Independent nursing interventions . These are activities that the nurses can initiate based on their licensing, clinical judgment, and skills. They include ongoing assessments, emotional support, empathy, providing comfort, patient education, and referrals to other healthcare professionals.
- Dependent nursing interventions . These are activities undertaken through orders from physicians or supervisors. These can be orders to give specific medications, perform diagnostic tests, treatments, diets, or activities.
- Collaborative nursing interventions . Nurses undertake these actions in collaboration with other healthcare team members such as dietitians, physicians, social workers, and therapists.
When selecting a nursing intervention, it should be evidence-based, safe, appropriate for the client's age, health, and condition, and achievable. Every nursing intervention is followed with rationales, which are specific explanations about why a nursing intervention is the most appropriate given the diagnosis and the goals. When giving the rationales, you are expected to refer to your pathophysiological and psychological principles as a student. This means including in-text citations from peer-reviewed journals or clinical practice guidelines to support the choice of a specific intervention.
Nursing interventions are based on your identified needs during data collection or assessment. The timelines for the outcomes should reflect the anticipated length of stay and the individualized nurse-client expectations. You can create a mind map when conceptualizing the needs of the patient/client. The tool helps visualize the link between symptoms and interventions. It is why you will sometimes be asked by an instructor to do a NANDA concept or mind map before writing a nursing care plan assignment.
When writing a nursing strategy or intervention, you should be very specific. You should begin with an action verb that indicates what you are expected to do. You should also include qualifiers expressing how, when, where, time, amount, and frequency of the planned activity. For example:
- "Assist as needed with self-care activities each morning."
- "Record respiratory and pulse rates before, during, and after ambulating."
- "instruct the family in post-discharge care."
5. Evaluation and Documentation
This is the last step of the nursing care plan. As nursing care is provided, you will undertake ongoing assessments to evaluate the client's response to therapy and achieve the expected outcomes.
You should document the response to interventions, which is pretty much what evaluation is about. You can then adjust the care plan based on the information.
Evaluation helps identify the effectiveness of the nursing care plan. It also helps determine if the nursing processes were effective or if there is a need to terminate, continue, or change them.
When evaluating outcomes, you must label them as met, ongoing, or not. You can then decide whether the goals of the intervention need to be altered.
In most cases, all the goals are expected to be met by the time of discharge. However, you must prepare for that transition if a patient is discharged to a long-term care facility, nursing home, or hospice.
If everything is okay, you should document the nursing care plan (NCP) per the hospital's policy or standard operating procedure.
Nursing Care Plan Template for Nursing Students
Your instructor will give you a case study or patient scenario to write a nursing care plan. Some instructors also allow you to develop a nursing case study and write an appropriate nursing care plan. You can also use a real case from your shadowing, internship, or practicum experience. Whichever the case, you can use the template below if none is given. You should organize the nursing care plan into columns for easier entry and organization.
Your introduction should briefly revisit the case study. If requested, expound on the etiology of the medical diagnosis in the background section. The next section is your nursing care plan with columns of assessment, diagnosis, goals and outcomes, interventions, and evaluation, making it 5 columns . Some instructors only want three columns for nursing diagnosis, outcomes and evaluation, and interventions, while others insist on four columns for nursing diagnosis, goals and outcomes, interventions, and evaluation. Below is an example of the nursing care plan section:
The next section can include discharge planning, medication management, rest and activities, diet planning, ongoing care, sleeping, and follow-up.
Finally, write a conclusion that summarizes the entire nursing care plan and include a list of the references you used when writing the nursing care plan.
Sample Nursing Care Plan for Schizophrenia
Nursing Diagnosis : Ineffective coping skills and risk for hematologic side effects of Clozapine
Goals and expected outcomes
- To remain stable on medication and to transition into a less restrictive environment.
- Adequate rest and nutritional intake
- Establish communication and build trust, and encourage patients to participate in the therapeutic community.
- Increase ability to communicate with others.
- Symptom management; decrease in hallucination, delusions, and other psychotic features such as self-talk
- Increase self-esteem
- Subjective and Objective reduction of psychotic symptoms (an irrational behavior)
- Adhere to recommended therapy, including medications, psychotherapy, and lab appointments for hematology.
Nursing Interventions
- Assist the patient in identifying strengths and coping abilities ( nursing interventions) . Strength-based approaches help better recover schizophrenic patients (Xie, 2013). Emphasis on strength is a positive coping mechanism proven to buffer the impact of negative symptoms and promote rehabilitation of patients with schizophrenia (Tian et al., 2019). ( rationale)
- Meet monthly with the clinical team. Interprofessional teams help in the effective management of psychotic disorders such as schizophrenia. Psychiatrists and pharmacists can help improve the patient's status (Farinde, 2013).
- Obtain weekly Vital Signs. Interprofessional teams help in the effective management of psychotic disorders such as schizophrenia. Psychiatrists and pharmacists can help improve the patient's status (Farinde, 2013).
- Encourage all medications as prescribed. Adherence to pharmacological treatment helps alleviate the psychotic symptoms of schizophrenia, v. Non-adherence could lead to deterioration of the symptoms (El-Mallakh & Findlay, 2015).
- Provide opportunities for self-reflection, self-care, positive self-image, and effective communication. Encouraging healthy habits among schizophrenic patients helps optimize functioning, such as drug adherence, maintenance of sleep, reduced stress levels, self-care maintenance, and anxiety (Tian et al., 2019).
- Encourage outings and identify opportunities to reduce anxiety -enjoy music, poetry, and creative writing, and connect with a church spiritual group. Empathy helps the patient perceive the caregivers as caring and makes them feel accepted. It also helps the patients maintain positive coping mechanisms (Peixoto, Mour'o, & Serpa Junior, 2016).
- Monitor lab results (WBC and ANC) and report significant changes per Clozapine guidelines. Patients taking Clozapine must be monitored frequently as they are more predisposed to serious blood dyscrasias. In addition, discontinuing WBC monitoring after 6 months of starting the drug could lead to mortality and accidents (Kar, Barreto & Chandavarkar, 2016).
- Monitor for hematologic side effects: Neutropenia, leukopenia, agranulocytosis, and thrombocytopenia (secondary to bone marrow suppression caused by Clozapine). Clozapine has serious side effects such as seizures, cardiomyopathy, myocarditis, cardiomyopathy, neutropenia, ad agranulocytosis (Dixon & Dada, 2014).
- Instruct patient to report any side effects, illness, s/s of infection, fatigue, or bruising without apparent cause. Constant monitoring of psychotic symptoms helps change treatment (Holder, 2014). For instance, it can help determine if the antipsychotic medication is not working and include evidence-based psychosocial interventions (Stroup & Marder, 2015).
- Monitor anticholinergic effects; dry mouth, difficulty urinating, constipation.
- Monitor for reduction/increase of psychotic symptoms
- Discourage caffeine. Caffeine interacts with Clozapine and can lead to toxicosis. It increases the plasma concentrations of Clozapine (De Berardis et al., 2019). Caffeine inhibits the metabolism of Clozapine through the inhibition of CYP1A2 (Delacr�taz et al., 2018)
- The patient will have reduced symptoms, adhere to medication, and show improvement.
- The patient will control his feelings, perceptions, and thought processes.
- Social increasing ease of communication since starting Clozaril (date). The patient will easily interact with caregivers, family, and other patients.
- The patient will acknowledge the importance of medication in lowering suspicion.
- Self-talk has diminished since admission. The patient will also exhibit high self-esteem levels.
- The patient will have reduced anxiety and violent behavior and have remission.
Brekke, I. J., Puntervoll, L. H., Pedersen, P. B., Kellett, J., & Brabrand, M. (2019). The value of vital sign trends in predicting and monitoring clinical deterioration: A systematic review. PloS one , 14 (1), e0210875. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0210875
De Berardis, D., Rapini, G., Olivieri, L., Di Nicola, D., Tomasetti, C., Valchera, A., ... & Serafini, G. (2018). Safety of antipsychotics for the treatment of schizophrenia: a focus on the adverse effects of Clozapine. Therapeutic advances in drug safety, 9(5), 237-256.
Delacr'taz, A., Vandenberghe, F., Glatard, A., Levier, A., Dubath, C., Ansermot, N., Eap, C. B. (2018). Association Between Plasma Caffeine and Other Methylxanthines and Metabolic Parameters in a Psychiatric Population Treated with Psychotropic Drugs Inducing Metabolic Disturbances. Frontiers in psychiatry , 9 , 573. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2018.00573
Dixon, M., & Dada, C. (2014). How clozapine patients can be monitored safely and effectively. The Pharmaceutical Journal, 6 (5), 131.
El-Mallakh, P., & Findlay, J. (2015). Strategies to improve medication adherence in patients with schizophrenia: the role of support services. Neuropsychiatric disease and treatment, 11 , 10771090. https://doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S56107
Farinde, A. (2013). Interprofessional Management of Psychotic Disorders and Psychotropic Medication Polypharmacy. Health and Interprofessional Practice, 1 (4), 4.
Holder, D., S. (2014). Schizophrenia. American Family Physician, 90 (11), 775-782.
Kar, N., Barreto, S., & Chandavarkar, R. (2016). Clozapine Monitoring in Clinical Practice: Beyond the Mandatory Requirement. Clinical psychopharmacology and neuroscience: the official scientific journal of the Korean College of Neuropsychopharmacology, 14 (4), 323�329. https://doi.org/10.9758/cpn.2016.14.4.323
Lantta, T., H�t�nen, H. M., Kontio, R., Zhang, S., & V�lim�ki, M. (2016). Risk assessment for aggressive behavior in schizophrenia. The Cochrane database of systematic reviews, 2016 (10). https://doi.org/ 10.1002/14651858.CD012397
Peixoto, M. M., Mour�o, A. C. D. N., & Serpa Junior, O. D. D. (2016). Coming to terms with the other's perspective: empathy in the relation between psychiatrists and persons diagnosed with schizophrenia. Ciencia & saude coletiva, 21 (3), 881-890.
Stroup, T. S., & Marder, S. (2015). Pharmacotherapy for schizophrenia: Acute and maintenance phase treatment. UpToDate .
Tian, C. H., Feng, X. J., Yue, M., Li, S. L., Jing, S. Y., & Qiu, Z. Y. (2019). Positive Coping and Resilience as Mediators between Negative Symptoms and Disability among Patients with Schizophrenia . Frontiers in psychiatry, 10 , 641.
Xie, H. (2013). Strengths-based approach for mental health recovery. Iranian journal of psychiatry and behavioral sciences, 7 (2), 5�10.
Writing the best nursing care plan can sound easy on paper, but the process is demanding and tiresome. If you are a nursing student who wants to delegate writing nursing care plans to someone who can help you do so accurately, affordably, and reliably, you can trust our care plan writers.
We are a nursing writing service website that offers assistance with completing various nursing assignments. The writers are experienced in research and writing nursing papers online. To date, we have supported the dreams of many nursing students, saving them time and money and maintaining their mental health.
Do not miss a deadline because you are busy with a shift; we can take over and make great things happen. Our nursing care plans are original, 100% plagiarism-free, and submitted to your email within your selected deadline. We also allow you to communicate with your writer to make changes together, share perspectives, and exchange ideas.
We can help you write care plans for type 2 diabetes, risk for injury, acute kidney injury, pressure ulcer, pulmonary embolism, chest pain, hypoglycemia, dementia, PTSD, hyperlipidemia, UTI, asthma, CHF, atrial fibrillation, bipolar disorder, risk for fall, ineffective coping, anemia, seizure, constipation, and any other condition or diagnosis.
Do not hesitate to contact us if you need help.
Important NOTICE!
The information in this article and the website is provided for educational and informational purposes only and does not constitute providing medical advice or professional services. The information provided should not be used for diagnosing or treating a health problem or disease.
Related Readings:
- Topics for nursing essays and research papers.
- Steps and tips for making an abstract poster.
- How to write a complete SOAP Note assignment
- Ideas and potential topics for a nursing capstone paper.
- Approaches, tips, and steps for nursing capstone writing.
Struggling with
Related Articles

Writing a Nursing Scholarship Essay: A Step-by-Step Guide

What is Pre-Nursing Study, Where, and Why Pursue It?

Systematic Review vs. Literature Review - Nursing Research
NurseMyGrades is being relied upon by thousands of students worldwide to ace their nursing studies. We offer high quality sample papers that help students in their revision as well as helping them remain abreast of what is expected of them.
- Pre-Nursing
- Nursing School
- After Graduation
How to Write a Nursing Care Plan – A Simple Guide for Nurses

- Over 125 Years of Healthcare Expertise: 125+ years of combined healthcare experience with a focus in nursing education.
- Exceptional User Satisfaction: 4.9/5 average rating from 3,500+ reviews across TrustPilot , WorthePenny , Better Business Bureau, and other trusted review sites.
- Proven Success: Over 1 million nurses served since 2012 with a 99% NCLEX pass rate ( 2024 NCLEX average pass rate = 79%).
- Team Composition: Staff includes RNs, MSNs, DHSs, nursing professors, and current/former NCLEX question writers.
Jump to Sections
In nursing, one size rarely fits all, especially when it comes to providing top-notch client care.
Just as no two clients are alike, the care they require is unique and tailored to their needs. This is where a nursing care plan (NCP) comes into play.
An NCP is a roadmap for client care that details a structured approach to achieving the best possible health outcomes. Multiple care plans might be necessary depending on the complexity of the client’s condition and needs.
For instance, a client with diabetes might need separate plans for managing blood sugar levels, wound care, and dietary modifications. Each plan addresses various aspects of the client’s care to ensure comprehensive treatment.
If you want to learn how to write a nursing care plan , you’re in the right place. But first, let’s review the different formats and components of an NCP.
Jump to the Components of a Care Plan
Interventions, nursing care plan formats.
You can create NCPs in various formats.
Here’s a breakdown of the most common.
3 Column Format
This format is simple and effective, dividing the care plan into three columns:
- Outcomes/Evaluation
5 Column Format
A more detailed format, this divides the care plan into five columns:
- Goals and Outcomes
SimpleNursing Nursing Care Plan
Our preferred format at SimpleNursing includes six key sections:
This format provides a thorough structure for organizing client care comprehensively.
Get your free care plan template today:
Components of a nursing care plan.
Regardless of the format chosen, an effective NCP should include these key components. Follow these steps to write an effective nursing care plan:
Patient Information
Client information.
This includes the client’s name, date of birth, age, and gender.
The client’s information is a reference point for all members of the health care team involved in the client’s care.
Medical History
This section outlines the client’s past and present medical conditions, including chronic illnesses or acute health issues.
Include any known allergies to medications, foods, or environmental factors in the care plan.
This information helps prevent adverse reactions and ensure client safety.
Medications
List current medications, including dosages and frequencies.
This information helps with medication management and identifies potential drug interactions.
This section highlights the client’s physical and mental status, including vital signs, lab results, and
relevant diagnostic tests.
It serves as a baseline for evaluating the client’s progress. There are two types of data: subjective and objective.
- Subjective Data: Gather client-reported information, including symptoms and concerns—for example, pain level or feelings of nausea. Use active listening and open-ended questions to gain a comprehensive understanding of the client’s experience.
- Objective Data: Collect observable data such as vital signs, lab results, and physical exam findings. Use appropriate assessment tools and document any abnormalities or changes.
Both types of data are essential for accurately assessing the client’s condition.
Check out our head to toe assessment checklist for more info on this section.
This section informs the development of your care plan and identifies the client’s health problems or potential risks.
Components of Diagnosis
When developing nursing diagnoses , you will come across three key components integral to the assessment process.
- The problem and its definition: This includes a concise statement that describes the client’s health issue or risk.
- Etiology: This identifies the factors contributing to the problem, such as physiological, psychological, environmental, or social influences.
- Defining characteristics or risk factors: These are the cues and evidence that support the existence of the problem.
NANDA Nursing Diagnosis
Follow the NANDA International (NANDA-I) guidelines, which provide a standardized approach for nursing practice.
Here are the key steps to guide you in formulating nursing diagnoses:
- Review the assessment data. Start by thoroughly analyzing the collected subjective and objective data. Identify any patterns or significant findings regarding the client’s health status.
- Choose the appropriate NANDA-I nursing diagnosis. The latest NANDA-I nursing diagnosis lists provide a comprehensive catalog of diagnoses. Select the most relevant diagnosis that aligns with the client’s health issues and supports your findings.
- Use the diagnosis format. Formulate the diagnosis in the standard format: “Problem related to (etiology) as evidenced by (defining characteristics).” This structure enhances clarity and ensures you cover all components of the diagnosis.
- Collaborate with the health care team. Discuss with other health care professionals to validate the chosen diagnosis and ensure a multidisciplinary approach to the client’s care.
- Document clearly. Record the nursing diagnosis in the client’s chart, ensuring it reflects the NANDA-I terminology for consistency and clarity throughout treatment.
Adhering to these guidelines provides nurses with a clear framework for identifying client needs and planning effective care interventions.
Nursing diagnoses are essential for developing a comprehensive care plan that addresses a client’s specific health needs.
They also provide a basis for establishing specific, measurable goals for client recovery.
Here are five tips for setting achievable outcomes:
- Be specific. Clearly define the desired outcome in observable and measurable terms.
- Ensure relevance to the diagnosis. The outcomes should relate to the identified nursing diagnosis and address the client’s health concerns.
- Consider timeframes. Set realistic timelines for achieving the intended outcome, considering factors such as client acuity and available resources.
- Involve the client. Collaborate with the client when setting goals to ensure their active participation and motivation towards achieving them.
- Evaluate progress regularly. Continuously monitor and reassess the client’s progress towards meeting established outcomes and make necessary adjustments as needed.
When setting goals, consider short-term and long-term objectives. Short-term goals may include specific actions or interventions a client can achieve in a shorter timeframe (e.g., “Client will achieve a pain level of 3 or below within 24 hours”).
Long-term goals may encompass larger, more comprehensive outcomes (e.g., “Client will maintain a blood glucose level within the target range for three months”). It’s essential to have both types in a care plan to track progress and provide the client with a sense of accomplishment.
When developing a care plan, outline specific nursing interventions to address the identified diagnosis and facilitate progress toward the established goals.
Here are five key considerations for listing these planned actions:
- Prioritize tasks. Identify the most critical interventions to address the client’s immediate needs based on their health status and safety considerations.
- Use evidence-based practices. Incorporate interventions proven effective through research and clinical guidelines to ensure that the intervention aligns with the best practices.
- Be clear and concise. Write each intervention in straightforward language, indicating what actions the client will take, the frequency of those actions, and any specific techniques or approaches they’ll use.
- Consider client preferences. Engage with the client to determine their values and preferences regarding their care. Tailoring interventions to fit the client’s lifestyle can enhance their adherence and overall satisfaction.
- Document rationale. Include a brief justification for each planned intervention that explains how the action relates to the diagnosis and contributes to achieving the defined outcomes.
By developing a structured list of interventions, nurses can create a focused approach that enhances client care and serves as a framework for evaluating the effectiveness of the implemented strategies.
Providing rationales for each nursing intervention is critical to the care planning process.
Rationales offer insight into the reasoning behind specific actions, linking them directly to the client’s diagnosis and the anticipated outcomes. This fosters a deeper understanding of the care plan and reinforces the justification for chosen interventions to the health care team and client.
Evaluating a client’s progress toward outcomes involves systematically assessing the effectiveness of the interventions by comparing the client’s status against the expected outcomes outlined in the care plan.
Nurses should collect data through various methods, including:
- Direct observation
- Client self-reports
- Clinical assessments
When determining whether to continue, adjust, or terminate the care plan, closely observe how the client responds to the implemented interventions. If the client shows improvement toward the expected outcomes, it’s appropriate to continue the current plan while offering support and encouragement.
However, if the client’s progress is minimal or they experience setbacks, consider adjusting the interventions to suit their needs better. This may involve changing techniques, involving additional resources, or addressing barriers to compliance.
If the client exhibits no significant improvement despite these changes, consider terminating the current plan. In this case, you should thoroughly reassess the client’s goals and needs to develop a new, more targeted approach.
Always engage the client in these discussions, ensuring you consider their voice and preferences in any decisions made regarding their care.
Keep Learning and Growing with SimpleNursing
At SimpleNursing, we provide resources and tools that help you excel in your nursing career, like our nursing care plan template .
To make learning nursing concepts easier, we offer:
- 1,200+ animated videos
- 1,000+ colorful study guides
- 4,000+ practice questions to make learning nursing concepts easier
Learn more about how you can take control of your studies and get the nursing school support you need today!
Get FREE Stuff
Let us email you free weekly content to help you pass nursing school and the NCLEX
- Nursing school study guides
- Exclusive video access
- Exam practice questions
- Subscriber-only discounts
Share this post
Nursing students trust simplenursing.

SimpleNursing Student Testimonial
Most recent posts.

How to Become a Psychiatric Nurse
Mental health is a cornerstone of overall wellness, but it often doesn’t receive the attention…

Depolarization vs Repolarization of the Heart
The human heart beats approximately 100,000 times a day to drive the circulation of blood…

Where to Find Pulse Points on Your Patients
In your daily practice as a nurse, you will complete client assessments. And one of…

Comparing LPNs vs CNAs: Duties, Education, and Career Insights
What do LPNs and CNAs have in common? They're part of the big bowl of…
Find what you are interested in
Education: Bachelor of Arts in Communications, University of Alabama


- Publication date: October 21, 2024
How to Write a Nursing Care Plan: Step-by-Step Guide with Template and Example

If you’ve ever stared blankly at a nursing care plan assignment, you’re not alone. Crafting one can feel like decoding a puzzle with too many pieces — and with the pressure to balance life, studies, and work, it’s easy to feel overwhelmed. But here’s the good news: writing a care plan doesn’t have to be rocket science! In this post, we break down the process into manageable steps, provide a free template, and share an example to make things crystal clear. Whether you’re preparing for your first care plan or aiming to improve your grades, this guide will set you on the right track.
What is a Nursing Care Plan?
A nursing care plan (NCP) is a formal document that outlines the care a nurse will provide to a patient. It helps nurses deliver patient-centered care by identifying the patient’s problems, setting measurable goals, and outlining interventions to achieve those goals. These plans serve as roadmaps in clinical practice, ensuring continuity and quality care across shifts and among different healthcare providers.
Why Are Nursing Care Plans Important?
- Ensure consistent, personalized care across shifts.
- Serve as a legal record documenting the patient’s condition and care provided.
- Help in patient education and engagement.
- Promote evidence-based practice by encouraging the use of research-backed interventions.
- Develop critical thinking and planning skills in nursing students.
Components of a Nursing Care Plan
Most nursing care plans follow the ADPIE framework — Assessment, Diagnosis, Planning, Implementation, and Evaluation . Here’s a breakdown of each component:
- Collect subjective and objective patient data (e.g., patient complaints, lab results).
- Use tools like nursing health assessments or patient history forms .
- Identify current or potential health problems.
- Use NANDA-I (North American Nursing Diagnosis Association) diagnoses. Example: “Ineffective breathing pattern related to anxiety.”
- Set SMART goals (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound).
- Example: “The patient will maintain oxygen saturation above 95% within 24 hours.”
- Outline the nursing interventions that will address the patient’s problem.
- Example: “Provide oxygen therapy at 2 liters per minute via nasal cannula.”
- Assess whether the patient’s condition improved and if the goals were met.
- Example: “Oxygen saturation improved to 97%, goal met.”
How to Write a Nursing Care Plan: Step-by-Step
- Gather patient history and clinical data (vital signs, lab results).
- Interview the patient and note down relevant subjective data.
- Use NANDA-I guidelines to identify priority problems .
- Example: “Risk for falls related to muscle weakness.”
- Write goals that are specific and realistic.
- Example: “The patient will walk 50 meters without assistance within 48 hours.”
- Choose evidence-based interventions and align them with the patient’s needs.
- Example: “Teach the patient proper use of a walking aid.”
- Monitor the patient’s response and adjust the care plan as needed.
- Example: If the patient cannot walk the target distance, modify the goal or intervention.
Sample Nursing Care Plan Template
Here’s a simple template you can use when writing your nursing care plan:
Example of a Nursing Care Plan
Patient: John Doe, 68 years old, admitted with shortness of breath due to COPD.
Pro Tips for Writing Nursing Care Plans
- Prioritize diagnoses based on the severity of the patient’s condition.
- Use evidence-based interventions to improve care outcomes.
- Collaborate with other healthcare providers to enhance patient care.
- Review and revise care plans regularly to ensure they meet the patient’s evolving needs.
- Practice writing care plans to improve critical thinking and get better grades.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
- Writing vague or unrealistic goals.
- Choosing interventions not supported by research.
- Failing to assess or evaluate the patient’s progress.
- Ignoring patient preferences or cultural considerations.
5. Takeaway Points
- Nursing care plans help nurses deliver patient-centered care by organizing assessments, goals, interventions, and evaluations.
- Following the ADPIE framework simplifies the process and ensures care continuity.
- Writing SMART goals makes your care plans effective and measurable.
- Use templates and practice writing care plans regularly to improve your skills and boost your grades.
- Download the free nursing care plan template to start crafting your own care plans like a pro!
Table of Contents
Latest customer reviews.
User ID: 643300

You might also like
Master the art of soap note writing: a comprehensive guide for nursing students, how to balance work, studies, and life as a nursing student: practical tips and proven strategies, the ultimate guide to writing a nursing research paper: tips, examples, and templates, 5 proven time management strategies for nursing students: balance studies, work, and life, how to master apa formatting for nursing assignments: a complete guide, how to write an evidence-based practice paper for nursing students: a step-by-step guide.
Send us a request via Whatsapp to receive updated posts.
See How Nurscribe.com Can Help You!
- Become a private tutor
- Code of conduct
- Writing service guarantees
- Cookies Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Refund Policy
- Terms and conditions
- [email protected]
- [email protected]
Payment Methods

Nurscribe llc., is a dedicated online education partner where nursing and healthcare students meet dedicated private tutors and academic writers for their academic work.
- APA paper writing
- Buy college papers
- Do my powerpoint presentation
- Graduate essay writing
- History essay writing
- Law essay writing
- MBA essay writing
- PSYCHOLOGY ESSAY WRITING
- pAY FOR RESEARCH PAPER
- wRITE MY ANNOTATED BIBLIOGRAPHY
- wRITE MY BOOK REPORT
- wRITE MY DISCUSSION POST
- dO MY PERSONAL STATEMENT
- wRITE MY NURSING PAPER
Save time and energy with our expertise!
Chat our top writers..

(11k+ reviews)
Email or WhatsApp me at:

How to Write a Nursing Care Plan: Comprehensive 7 Step Guide
Nursing care plans play a vital role in providing effective patient-centered care. They serve as roadmaps for nurses, ensuring that every aspect of patient care is meticulously planned and executed. A well-constructed care plan promotes efficient communication among healthcare professionals and enhances patient outcomes. This article will guide you through the step-by-step process of writing a nursing care plan, equipping you with the knowledge and skills necessary to deliver holistic and individualized care.
1. Understanding the Purpose of a Nursing Care Plan
Before delving into the specifics, it is essential to grasp the purpose and significance of a nursing care plan. These plans serve as systematic guides that outline the nursing interventions and actions necessary to address a patient’s healthcare needs. They facilitate communication between healthcare team members, provide a standardized approach to care, and ensure that all aspects of patient care are addressed comprehensively.
2. Assessment and Data Collection
The first step in writing a nursing care plan is conducting a thorough assessment of the patient. This includes gathering relevant data, such as medical history, physical examination findings, laboratory results, and the patient’s subjective experiences. It is crucial to involve the patient in this process to obtain a comprehensive understanding of their individual needs, preferences, and goals.
Assessment involves collecting subjective and objective data. Subjective data is information provided by the patient, including their symptoms, concerns, and perceptions of their health. Objective data, on the other hand, includes measurable and observable data collected through physical examinations , diagnostic tests, and observations. Gathering comprehensive and accurate data is vital to formulate appropriate nursing diagnoses.
3. Identification of Nursing Diagnoses
Based on the assessment data, nursing diagnoses are formulated. Nursing diagnoses are clinical judgments about actual or potential health problems that the nursing profession can address. These diagnoses should be clear, concise, and specific to guide the development of appropriate nursing interventions. Examples of nursing diagnoses include “ Impaired Gas Exchange ” or “ Risk for Falls .”
Nursing diagnoses are derived from various sources of information, such as the patient’s assessment data, medical records, and consultation with other healthcare professionals. They are categorized into four types: actual nursing diagnoses, risk nursing diagnoses, wellness nursing diagnoses, and syndrome nursing diagnoses. Each diagnosis should be supported by evidence and relevant data.
4. Establishing Goals and Outcomes
After identifying the nursing diagnoses, the next step is to establish measurable goals and outcomes. Goals should be patient-centered, realistic, and attainable within a specified timeframe. Outcomes should be observable, measurable, and provide a clear indication of the patient’s progress. Goals and outcomes should align with the patient’s overall healthcare plan and be mutually agreed upon by the patient and healthcare team.
When developing goals and outcomes, consider the SMART framework: Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Relevant, and Time-bound. This ensures that goals are clear and can be objectively evaluated. Outcomes should reflect the desired changes in the patient’s health status, functional abilities, knowledge, and attitudes.
5. Planning Interventions
Once goals and outcomes are established, the nursing care plan should outline the interventions necessary to achieve those outcomes. Interventions can be categorized into independent (nurse-initiated), dependent (physician-initiated), or interdependent (collaborative) actions. Each intervention should be evidence-based, promoting the best possible patient outcomes. Additionally, factors such as cultural considerations, patient preferences, and available resources should be taken into account.

Nursing interventions should be specific, individualized, and tailored to the patient’s unique needs. They should address the identified nursing diagnoses, support the achievement of goals and outcomes, and consider the patient’s preferences and values. Interventions may include direct patient care, such as administering medications or providing wound care, as well as indirect care, such as patient education and counseling.
6. Implementing and Documenting the Care Plan
Once the care plan is developed, it is time to implement the identified interventions. Nurses should follow the plan diligently, documenting their actions, observations, and the patient’s response to interventions. Accurate and timely documentation is vital to ensure continuity of care, facilitate communication among healthcare team members, and provide legal protection.
Implementation involves effectively carrying out the planned interventions, monitoring the patient’s response, and modifying the plan as needed. Documentation should be detailed, objective, and include pertinent information about the patient’s condition, the nursing interventions performed, and the patient’s response. It is important to document any changes in the patient’s condition or deviations from the original care plan.
7. Evaluation and Revision
Evaluation is a crucial step in the nursing care plan process. Nurses must regularly assess the patient’s progress toward the established goals and outcomes. If the desired outcomes are not achieved, it may be necessary to revise the care plan, making adjustments to the interventions or goals. Evaluation and revision ensure that the care plan remains dynamic and responsive to the patient’s changing needs.
Evaluation involves comparing the patient’s actual outcomes with the expected outcomes. This assessment helps determine the effectiveness of the interventions and identifies areas where modifications may be necessary. If revisions are needed, the care plan should be updated accordingly, considering new information, the patient’s changing condition, and their evolving goals.
In summary, writing a nursing care plan involves a systematic approach that considers the unique needs and goals of each patient. By following the steps outlined in this guide, nurses can create effective care plans that promote optimal patient outcomes. Remember, a well-constructed care plan not only enhances communication among healthcare professionals but also empowers patients to actively participate in their own care.
By continuously evaluating and revising the care plan, nurses can ensure that it remains current and responsive to the changing needs of the patient. Ultimately, the nursing care plan serves as a valuable tool in providing holistic and individualized care, fostering positive patient experiences and outcomes.

Nursing Assignment Help
In addition to providing guidance on how to write a nursing care plan, we at Nursing Research Help understand the challenges faced by nursing students in their academic journey. That’s why we are proud to offer assignment help services specifically tailored to nursing students. Our team of experienced professionals, with a background in nursing and healthcare, is dedicated to assisting you in achieving academic success.
Whether you need assistance with writing assignments, understanding complex nursing concepts, or organizing your thoughts for a stellar care plan, our services are designed to support your learning and growth. With our expert guidance, you can excel in your nursing studies and confidently tackle any assignment that comes your way. Don’t hesitate to reach out to us for personalized assistance and take a step closer to your career goals in the nursing field.
You might also like

Nursingresearchhelp.com is the fastest, easiest and most reliable way to have content written for your website. You’ll be able to post a project and 1000s of freelance writers from across the globe will have instant access to write your content quickly, professionally, and affordably.
QUICK LINKS
- HOW IT WORKS
- OUR SERVICES
- TERMS OF USE

Call/Text: +1 608 912 3884
VIDEO LIBRARY
How to Write a Nursing Care Plan
Introduction:.
A nursing care plan is a vital tool that helps guide nursing practice and ensures holistic, individualized care for patients. It provides a structured framework for identifying patient needs, setting goals, and implementing appropriate interventions. In this article, we will outline a step-by-step guide on how to write a nursing care plan effectively.
Nursing care plans are integral to providing comprehensive and individualized care to patients. They serve as roadmaps for nurses, ensuring a structured approach to meeting patients’ healthcare needs. Developing a well-designed nursing care plan requires critical thinking, assessment skills, and effective communication. In this article, we will provide a step-by-step guide on how to write a nursing care plan.
Step 1: Assessment
A thorough patient assessment is the first step in developing a nursing care plan. Gather relevant information such as medical history, current health status, and subjective and objective data. This includes physical assessments, laboratory results, and patient, family, and healthcare team input. Identify the patient’s strengths, limitations, and potential nursing diagnoses.
Using the data collected, identify nursing diagnoses that reflect the patient’s health concerns and actual or potential problems. Nursing diagnoses should be derived from NANDA-I ( North American Nursing Diagnosis Association International ) standardized taxonomy and accurately represent the patient’s condition.
Begin by conducting a thorough patient assessment, including gathering subjective and objective data related to their health condition, physical, psychological, and social factors.
Identify and prioritize nursing diagnoses based on the assessment findings and the patient’s needs.
Video Lecture on How To Write Nursing Care Plan
Step 2: Nursing Diagnosis
Based on the assessment data, identify nursing diagnoses that accurately reflect the patient’s needs. Use standardized nursing diagnoses from established taxonomies such as NANDA International. Ensure the nursing diagnoses are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
Once nursing diagnoses are determined, establish realistic and measurable goals and outcomes for each diagnosis. Goals should be specific, achievable, and patient-centered. Outcomes should be observable and measurable, allowing for evaluation of the effectiveness of the care plan.
- Select appropriate nursing diagnoses based on the assessment data, using standardized nursing diagnosis taxonomies such as NANDA International.
- Ensure that nursing diagnoses are accurate and specific and reflect the patient’s actual or potential health problems.
Step 3: Setting Goals
Once nursing diagnoses are identified, establish realistic and patient-centered goals. Goals should be specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). Involve the patient in goal-setting to promote patient engagement and collaboration. Goals should address the patient’s identified needs and facilitate optimal outcomes.
- Establish realistic and measurable goals in collaboration with the patient, their family, and the healthcare team.
- Goals should be patient-centered, addressing the identified nursing diagnoses and promoting optimal health and well-being.
Step 4: Planning Interventions
After setting goals, determine appropriate nursing interventions. Interventions should be evidence-based, individualized, and aligned with the identified nursing diagnoses and goals. When selecting interventions, consider the patient’s preferences, cultural background, and available resources. Interventions can be categorized as independent (nurse-initiated), dependent (physician-initiated), or collaborative (interdisciplinary).
Based on the nursing diagnoses and desired outcomes, develop nursing interventions. These interventions should be evidence-based, considering current best practices and clinical guidelines. Interventions may include nursing actions, education, coordination with the healthcare team, and referrals to other healthcare professionals or services.
- Determine evidence-based nursing interventions that are relevant to each nursing diagnosis.
- Develop individualized interventions that are specific, measurable, achievable, realistic, and time-bound (SMART goals).
- Include both independent nursing interventions and collaborative interventions involving other healthcare team members.
Step 5: Implementing Interventions
Put the planned interventions into action. Communicate the care plan with the healthcare team, ensuring clear understanding and coordination. Provide patient education and involve the patient and family in the implementation process. Document all interventions, including the date, time, and response to treatment.
- Implement the identified nursing interventions, ensuring they are carried out effectively and safely.
- Continuously assess the patient’s response to interventions and make necessary adjustments.
- Provide education and support to the patient and their family to promote active participation in their care.
Step 6: Evaluation and Revision
Regularly assess and evaluate the patient’s response to interventions. Determine whether the goals were met, partially met, or not met. Modify the care plan as needed based on the patient’s progress or changes in their condition. Involve the patient, family, and healthcare team in the evaluation process and make adjustments accordingly.
- Regularly evaluate the patient’s progress toward achieving the established goals.
- Use objective data to determine the effectiveness of nursing interventions and whether adjustments or modifications are necessary.
- Document the outcomes and findings of the evaluation process.
Individualize the Care Plan:
Remember that each patient is unique, requiring an individualized approach to care. Tailor the care plan to meet the patient’s needs, preferences, cultural background, and health literacy level. Avoid copying and pasting generic care plans, as this can lead to plagiarism and compromise care quality.
Collaborate with the Healthcare Team:
Nursing care plans are most effective when they involve interdisciplinary collaboration. Communicate and collaborate with other healthcare professionals involved in the patient’s care to ensure seamless coordination and the integration of various perspectives.
Document and Review:
Thoroughly document the nursing care plan, ensuring clear, concise, and accurate documentation. This promotes continuity of care and provides a reference for future healthcare providers. Regularly review and update the care plan to reflect changes in the patient’s condition, goals achieved, or new diagnoses.
Conclusion:
Writing a nursing care plan is a crucial aspect of nursing practice promoting individualized and holistic patient care. Following a systematic approach, nurses can accurately identify patient needs, set goals, implement appropriate interventions, and evaluate outcomes. Effective nursing care plans enhance communication, coordination, and continuity of care, ultimately improving patient outcomes and satisfaction. Nursing professionals must continually refine and update our nursing care plans to provide the best possible care for our patients.
Note: This article is intended to provide a general guide on how to write a nursing care plan. It is important to consult institutional policies, nursing guidelines, and the healthcare team for specific requirements and recommendations in your practice setting.
Leave a Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- Aphthovirus Explained: The Virus Behind Foot-and-Mouth Disease
- Ebolavirus: Understanding the Deadly Virus and Its Impact on Global Health
- Mimivirus: The Discovery That Redefined the Boundaries Between Viruses and Life
- Megavirus: A Giant in the World of Viruses and What It Means for Science
- Pandoravirus: Unlocking the Secrets of One of the Largest Known Viruses
Very good. I thanks my teacher
THis was of tremendous help to me.
THANK YOU SO MUCH. MY WORK MADE EASY AND WELL EXPLAINED.
Very detailed information
MashaAllah well explained
TERMS OF SERVICE
PRIVACY POLICY
Made For Medical
Copyrights © 2024. All rights reserved.
🌟FREE CMEs/CEs – 75% DISCOUNT – ENDS TODAY 🩺✨
🚀 Supercharge your medical knowledge with our exclusive video lectures tailored for YOU !! 🚀 Unlock expert insights, earn FREE CME/CE credits, and learn quickly! 📚💡


How to Prepare a Nursing Care Plan: Guide for Nursing Students
- Jermaine Huey
- November 29, 2023
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on preparing a nursing care plan . As a nursing student, understanding the fundamentals of care planning is crucial for providing holistic care and effective communication within your nursing team. In this guide, we will provide step-by-step instructions, examples, and best practices for creating nursing care plans . Whether you need a care plan template or guidance on nursing interventions , diagnosis , patient care planning , documentation, or assessment , we have you covered. Read on to enhance your skills and excel in your nursing program.
Key Takeaways:
- A nursing care plan is essential in providing holistic care and facilitating communication within a nursing team.
- It involves a five-step framework: assessment , diagnosis , outcomes and planning , implementation , and evaluation.
- Having a care plan promotes patient-centered care , nursing team collaboration , and documentation compliance.
- SMART goals and effective communication are crucial components of a care plan.
- Care plans should be easily accessible, regularly updated, and tailored to individual patient needs .
What Is a Nursing Care Plan?
A nursing care plan is a documented process that identifies a patient’s needs and guides the delivery of holistic care . It ensures collaboration among nurses, patients, and other healthcare providers. By following a five-step framework, nurses can assess the patient, diagnose their needs, set goals, implement interventions, and evaluate the outcomes. This process promotes patient-centered care and facilitates effective communication within the healthcare team.
A nursing care plan is essential in addressing the unique needs of each patient. It takes into account the physical, emotional, social, and psychological aspects of care, providing a comprehensive approach to their well-being. By assessing the patient, nurses can gather data about their current health status, including any existing medical conditions, potential risks, and specific care requirements. This information forms the foundation for developing a care plan that is tailored to the individual patient’s needs.
“A nursing care plan is crucial for coordinating care among healthcare providers and ensuring that all aspects of the patient’s well-being are addressed.”
The collaborative nature of a nursing care plan is crucial in promoting effective teamwork among healthcare providers. By involving patients in the decision-making process, nurses can ensure patient-centered care and enhance overall patient satisfaction. Additionally, care plans facilitate communication and coordination among the healthcare team, ensuring that all providers are aware of the patient’s care goals, interventions, and progress. This collaborative approach fosters a more comprehensive and integrated approach to patient care.
In summary, a nursing care plan is a strategic approach that guides the delivery of holistic care and promotes effective communication within the healthcare team. By assessing patient needs , setting goals, implementing interventions, and evaluating outcomes, nurses can optimize patient care and ensure a patient-centered approach. The collaborative nature of care plans enhances teamwork among healthcare providers and promotes comprehensive and integrated care for patients.
Key Reasons to Have a Care Plan
A nursing care plan plays a crucial role in providing patient-centered care and promoting effective collaboration within the nursing team. It serves as a comprehensive guide that organizes and coordinates the various aspects of patient care, ensuring that healthcare professionals are working towards common goals. Here are the key reasons why having a care plan is essential:
Patient-Centered Care
A care plan puts the patient at the center of their own care by involving them in the decision-making process. It helps to identify their unique needs, preferences, and goals, ensuring that the care provided is tailored to their individual circumstances. By actively engaging patients in their treatment and recovery, care plans promote a sense of empowerment and enhance patient satisfaction.
Nursing Team Collaboration
A care plan serves as a shared document that facilitates collaboration among members of the nursing team. It allows for effective communication, ensuring that everyone is on the same page when it comes to the patient’s care. By providing a clear and structured framework, care plans enable nurses to work harmoniously, share responsibilities, and contribute to the overall well-being of the patient.
Documentation and Compliance
One of the key benefits of a care plan is its role in documentation and compliance. By documenting the care provided and the patient’s response to interventions, nurses can track the effectiveness of their care and make informed decisions. Care plans also serve as evidence of the care provided, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards and legal requirements.
In summary, a nursing care plan is vital for promoting patient-centered care, facilitating collaboration among the nursing team, and fulfilling documentation and compliance requirements. By implementing care plans, nurses can ensure that their patients receive individualized care that is based on their unique needs and goals.
What Are the Components of a Care Plan?
A care plan consists of five main components that guide the nursing process : assessment , diagnosis , outcomes and planning , implementation , and evaluation. Each component plays a crucial role in providing effective and holistic care to patients.
In the assessment phase, nurses collect subjective and objective data about the patient’s condition. This includes information about their medical history, current symptoms, vital signs, and physical examinations. By gathering comprehensive data, nurses can identify the patient’s needs and determine the appropriate interventions.
After the assessment, nurses make a clinical judgment known as a nursing diagnosis . A nursing diagnosis identifies the patient’s health problem and forms the basis for developing the care plan. It helps nurses prioritize the patient’s needs and tailor interventions to address specific issues.
Outcomes and Planning
Once the diagnosis is determined, nurses set specific goals and plan interventions to address the patient’s needs. Outcomes and planning involve collaboration between the nurse, patient, and other healthcare providers. By setting clear goals, nurses can measure the success of the care plan and ensure that it aligns with the patient’s expectations.
Implementation
The implementation phase is when the interventions outlined in the care plan are carried out. This includes administering medications, providing treatments, and delivering nursing care. Nurses must accurately and consistently implement the planned interventions to achieve the desired outcomes.
The final component of a care plan is evaluation. Nurses assess the effectiveness of the care plan by measuring the patient’s response to interventions and comparing it to the desired outcomes. Evaluation helps identify areas for improvement, adjust the care plan as needed, and ensure that the patient is receiving the best possible care.
Care Plan Fundamentals
Care plans are essential tools in nursing practice that require a combination of critical thinking , client-centered techniques , goal-oriented strategies , evidence-based practice , and nursing intuition. These fundamentals lay the groundwork for developing effective care plans that address the unique needs of each patient.
Firstly, critical thinking plays a crucial role in care planning. Nurses must assess the patient’s condition, analyze the collected data, and make informed decisions regarding nursing interventions . By applying critical thinking skills, nurses can prioritize interventions, identify potential risks, and anticipate the patient’s needs.
Client-centered techniques are another fundamental aspect of care planning. It involves actively involving the patient in the decision-making process and considering their preferences, values, and goals. By incorporating the patient’s input, nurses can develop care plans that are tailored to their individual needs, promoting a sense of empowerment and engagement in their healthcare journey.
“Nursing care should be based on scientific evidence and best practices.” – Anonymous
Goal-oriented strategies guide the development of care plans. Setting specific and measurable goals helps nurses track the progress of their interventions and determine the effectiveness of the care provided. These goals should be realistic, achievable , and aligned with the patient’s overall healthcare outcomes.
Evidence-based practice is a cornerstone of nursing care planning. It involves integrating the best available evidence, clinical expertise, and the patient’s preferences to guide nursing interventions . By relying on evidence-based practices, nurses can ensure that their care plans are rooted in the latest research and deliver the best possible outcomes for their patients.
SMART Goals in Care Planning
In care planning, setting goals that are specific, measurable , achievable , relevant , and time-bound (SMART) is essential for providing effective and focused care to patients. By following the SMART criteria, nurses can ensure that their goals are well-defined and contribute to the overall care plan.
Specific: SMART goals in care planning should be specific, clearly stating what is to be achieved. For example, instead of setting a general goal like “improve mobility,” a specific goal could be “increase patient’s ability to walk 100 meters without assistance.”
Measurable: Goals should be measurable so that progress can be tracked. Nurses should identify a way to measure the desired outcome, such as by using a specific tool or assessment. For instance, a measurable goal could be “patient will achieve a pain score of 4 or lower on a scale of 0-10 within two weeks.”
Achievable: Goals should be realistic and achievable within the capabilities of the patient. Nurses should consider the patient’s physical, emotional, and cognitive abilities when setting goals. It is important to ensure that the goals set are within reach and can be accomplished with the available resources and support.
Relevant: Goals should be relevant to the patient’s specific needs and align with the overall care plan. Nurses should prioritize goals that directly address the patient’s health concerns and contribute to their overall well-being. A relevant goal could be “patient will learn and demonstrate proper insulin administration techniques to manage their diabetes.”
Time-bound: Goals should have a specific timeframe within which they are expected to be achieved. Setting a deadline creates a sense of urgency and helps monitor progress. For example, a time-bound goal could be “patient will achieve 80% adherence to medication regimen within one month.”
By following the SMART criteria when setting goals in care planning, nurses can provide patient-centered care and effectively track the progress and outcomes of their interventions. SMART goals help ensure that care plans are focused, realistic, and tailored to the unique needs of each patient, ultimately leading to improved health outcomes.
Effective Communication in Care Planning
Effective communication is a vital aspect of care planning that plays a significant role in ensuring quality patient care. Accurate descriptions , timely documentation of dates and times , and strong writing skills are essential components for effective communication within healthcare teams.
When documenting care plans, nurses must provide accurate descriptions of the patient’s condition, interventions, and instructions. Clear and concise writing using terms understood by the entire healthcare team is crucial to ensure effective communication. This helps in conveying vital information, ensuring that everyone involved in the patient’s care has a comprehensive understanding of the plan.
“Accurate documentation is the backbone of effective care planning. It helps healthcare professionals provide consistent and evidence-based care,” emphasizes John Smith, a nurse with over 10 years of experience in the field.
Accurate documentation of dates and times is crucial in care planning. Including specific dates and times when recording interventions and assessments helps track the timing of actions and monitor the patient’s progress. This information is invaluable for evaluating the effectiveness of interventions and making necessary adjustments to the care plan if needed.
Benefits of Strong Writing Skills in Care Planning
Strong writing skills are essential for effective communication in care planning. Well-written care plans provide clarity and structure, allowing healthcare professionals to understand the plan easily and follow it accurately. Care plans with clear objectives, concise instructions, and well-organized sections promote efficient delivery of care and help prevent errors.
- Clear objectives: Strong writing skills enable nurses to clearly articulate the goals and objectives of the care plan, ensuring that all healthcare team members understand the desired outcomes.
- Concise instructions: Well-written care plans provide specific and concise instructions for interventions, allowing for easy implementation by healthcare providers.
- Organized sections: Care plans with well-organized sections facilitate efficient access to relevant information, making it easier for healthcare professionals to find the required details quickly.
In conclusion, effective communication in care planning requires accurate descriptions , timely documentation of dates and times, and strong writing skills. By ensuring clear and concise communication, healthcare teams can provide optimal care, promote patient safety, and facilitate collaboration among all stakeholders involved in the patient’s care.
Shareable and Easy to Access Care Plans
Care plans are an essential tool in healthcare, allowing nurses to provide individualized and comprehensive care to patients. To enhance communication and collaboration among healthcare providers, care plans should be easily shareable and accessible to all stakeholders. This is where electronic health records (EHRs) play a crucial role. EHRs enable nurses to create, store, and access care plans, ensuring that the most up-to-date information is readily available.
By utilizing EHRs, nurses can securely share care plans with relevant stakeholders, including patients, doctors, and other members of the healthcare team. This promotes effective communication and improves coordination of care. With easy access to care plans, healthcare providers can quickly review patient information, track interventions, and monitor progress. Electronic documentation also eliminates the need for physical copies, reducing the risk of loss or misplacement.
The documentation format may vary depending on the healthcare facility’s policy. However, it is essential to ensure that the format is user-friendly and intuitive for all stakeholders. Clear and concise documentation is key, providing essential information in a structured and organized manner. Incorporating headings (h3) and bullet points can further enhance readability and facilitate easy navigation within the care plan.
Benefits of Shareable and Accessible Care Plans:
- Improved communication and collaboration among healthcare providers
- Enhanced coordination of care
- Quick access to up-to-date patient information
- Efficient tracking of interventions and progress
- Reduced risk of loss or misplacement
Table: Comparison of Different Documentation Formats
Choosing the right documentation format is essential for efficient and effective care planning. By embracing electronic health records and ensuring easy access and sharing of care plans, nurses can optimize patient care, enhance communication, and improve overall healthcare outcomes.
Keeping Care Plans Up to Date
One of the key aspects of effective nursing care planning is keeping care plans up to date. This ensures that the care provided to patients is always tailored to their current needs and promotes positive outcomes. To achieve this, ongoing assessment plays a crucial role. Nurses need to regularly gather new data and evaluate the effectiveness of interventions.
By conducting ongoing assessments, nurses can identify any changes in the patient’s condition and make necessary adjustments to the care plan. This may involve updating the nursing diagnosis , modifying goals and interventions, or even considering alternative approaches. The goal is to ensure that the care plan remains relevant and responsive to the evolving needs of the patient.
Tracking the patient’s progress is another important aspect of keeping care plans up to date. By continuously monitoring and evaluating the outcomes of the care provided, nurses can determine if the desired goals are being met. This allows for timely adjustments and interventions as needed to optimize the patient’s health and well-being.
Benefits of Keeping Care Plans Up to Date
Maintaining up-to-date care plans offers several benefits. First and foremost, it improves the quality of care provided to patients. By regularly updating the care plan, nurses can ensure that it accurately reflects the patient’s current condition and needs. This helps prevent any potential gaps or inconsistencies in the care provided.
Keeping care plans up to date also promotes effective communication and collaboration within the healthcare team. When all team members have access to the most current care plan, they can work together seamlessly to provide holistic and coordinated care. This enhances patient safety and helps prevent any misunderstandings or errors in the delivery of care.
Furthermore, regularly updating care plans contributes to evidence-based practice. As new research and guidelines emerge, nurses can incorporate the latest evidence into their care plans. This ensures that the care provided is based on the best available evidence and aligns with current standards of practice.
Understanding Different Care Plan Formats
In the world of nursing, care plans play a crucial role in ensuring effective and holistic patient care. When it comes to documenting care plans, there are various formats that nurses can utilize. Two commonly used formats are the three-column format and the four-column format .
The Three-Column Format
The three-column format is a simple yet comprehensive way to structure a care plan. It typically includes three main columns: nursing diagnoses, outcomes and evaluation, and interventions. In the nursing diagnoses column, nurses identify the patient’s health problems and concerns. The outcomes and evaluation column is where nurses set specific goals for the patient and evaluate the effectiveness of the care provided. Finally, the interventions column outlines the actions and strategies that will be implemented to address the patient’s needs.
The Four-Column Format
The four-column format builds upon the three-column format and includes an additional column for goals and outcomes. This format allows nurses to provide more detailed information about the desired goals and expected outcomes. By including a separate column for goals, nurses can clearly define and track the progress of each goal, making it easier to monitor the patient’s overall progress and adjust interventions accordingly. The four-column format is particularly useful for complex care plans that require a more comprehensive approach.
Student Care Plans
Student care plans may have specific requirements or variations in format depending on the educational institution. It is important for nursing students to familiarize themselves with the specific guidelines provided by their school or program. These guidelines may include additional sections or columns that are unique to the educational setting. By adhering to the specific requirements, nursing students can develop well-structured and comprehensive care plans that meet the expectations of their instructors and future colleagues.
Overall, the choice of care plan format depends on the healthcare facility’s preferences and documentation system. Whether using the three-column format, the four-column format, or any other format specified by the institution, the main goal is to create clear and organized care plans that facilitate effective communication, collaboration, and continuity of care.
In conclusion, this nursing care plan guide serves as a comprehensive guide for nursing students , offering practical solutions for preparing effective care plans. By understanding the fundamentals and components of care planning, nurses can optimize patient care and enhance communication and collaboration within the healthcare team.
With a step-by-step approach and the utilization of evidence-based strategies, nursing students can develop comprehensive care plans that address the unique needs of their patients. This guide empowers busy nurses to excel in their BSN, MSN, and DNP programs by providing expert information and guidance on the different writing and comprehension challenges they may face.
Trust NursingWriters.net, a trusted nursing writing service, to provide you with the resources and support you need to succeed in your nursing career. With our comprehensive guide and expertise, you can confidently navigate the process of creating nursing care plans and deliver high-quality care to your patients.
What is a nursing care plan?
A nursing care plan is a strategic approach to the nursing process that helps nurses provide holistic care and facilitates effective communication within a nursing team.
Why is it important to have a nursing care plan?
Having a nursing care plan promotes patient-centered care, enables nursing team collaboration , and facilitates documentation and compliance.
What are the components of a care plan?
The components of a care plan include assessment, diagnosis, outcomes and planning, implementation, and evaluation.
What are the key reasons to follow a care plan?
Following a care plan promotes patient-centered care, enables nursing team collaboration , and facilitates documentation and compliance.
How do I set SMART goals in care planning?
SMART goals in care planning should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound.
Why is effective communication important in care planning?
Effective communication in care planning ensures accurate documentation, clear instructions, and efficient collaboration among healthcare team members.
How can I share and access care plans easily?
Care plans can be shared and accessed easily through electronic health records (EHRs) to ensure all stakeholders have the most up-to-date information.
How do I keep care plans up to date?
Care plans should be regularly updated through ongoing assessment and evaluation of interventions to reflect any changes in the patient’s condition or goals.
What are the different care plan formats?
Care plans can be structured in different formats, such as the three-column format or the four-column format, depending on the healthcare facility’s preferences and documentation system.
Have a subject expert Write for You Now
Have a subject expert finish your paper for you, edit my paper for me, have an expert write your dissertation's chapter, table of contents.
- Our Guarantees
- Client Reviews
- Privacy Policy
- Terms and Conditions
Knowledge Base
- All Writing Guides
- Nursing Essay Writing Guides
- Topics Ideas
- Nursing Guides
- Nursing Exemplar Papers
- DNP Nursing Paper Examples
- MSN Nursing Paper Writing
Nursing Writers Service
- Write My Nursing Paper
- Nursing Paper Writers
- Nursing Assignment Writers
- Nursing research paper writers
- Nursing Paper Writing Services
- Online Nursing Papers
- Personal Nursing Philosophy Paper
- Nursing Paper Writing Services reviews
- Nursing School Paper Writing Service
- Nursing Research Paper Writing Service
- Nursing Paper Writing Service
- Research Paper Writing Service nurses
- Paper Writing Service Nursing
- Paper Writing Service Reddit nursing
- Paper Writing Service chamberlain nursing
Writing Tools
- Citation Generator
- Topic Generator
- Thesis Generator
- Sentence Rewriter
- Title Page Generator
- Research Paper Title Generator
Use our resources and guides to write perfect papers. You can use our writing service and order customized sample papers without plagiarism!
Disclaimer
NursingWriters.net helps students cope with college assignments and write papers on various topics. We deal with academic writing, creative writing, and non-word assignments.
All the materials from our website should be used with proper references. All the work should be used per the appropriate policies and applicable laws.
Our samples and other types of content are meant for research and reference purposes only. We are strongly against plagiarism and academic dishonesty.

✍️ Nursing Writers
Typically replies within minutes
Hey! 👋 Need help with an assignment?
WhatsApp Us
🟢 Online | Privacy policy
WhatsApp us

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Learn how to write a nursing care plan with a step-by-step approach and a database of free samples. Find out the types, purposes, components, formats, and examples of nursing care plans for various conditions and situations.
How to Write a Nursing Care Plan. Before writing a nursing care plan, determine the most significant problems affecting the patient. Think about medical problems but also psychosocial problems. At times, a patient's psychosocial concerns might be more pressing or even holding up discharge instead of the actual medical issues.
Learn how to write a nursing care plan based on the nursing process, which includes assessment, diagnosis, planning, implementation, and evaluation. Find out the benefits, types, and examples of nursing care plans for different patient conditions and settings.
Learn the fundamentals of nursing care plans and how to create them, step by step. This guide covers the five-step framework, the components of a care plan, and a sample care plan that you can download and print.
Given the understanding of the five main components of a nursing care plan, we also say that nursing care plans follow a five-step framework. 1. Assessment. The first step of writing a nursing care plan is to practice critical thinking skills and perform data collection. During this phase, you collect subjective and objective data.
Components of a Nursing Care Plan. Regardless of the format chosen, an effective NCP should include these key components. Follow these steps to write an effective nursing care plan: Patient Information Client Information. This includes the client's name, date of birth, age, and gender.
Pro Tips for Writing Nursing Care Plans. Prioritize diagnoses based on the severity of the patient's condition.; Use evidence-based interventions to improve care outcomes.; Collaborate with other healthcare providers to enhance patient care.; Review and revise care plans regularly to ensure they meet the patient's evolving needs.; Practice writing care plans to improve critical thinking ...
A well-constructed care plan promotes efficient communication among healthcare professionals and enhances patient outcomes. This article will guide you through the step-by-step process of writing a nursing care plan, equipping you with the knowledge and skills necessary to deliver holistic and individualized care. 1. Understanding the Purpose ...
In this article, we will provide a step-by-step guide on how to write a nursing care plan. Step 1: Assessment . A thorough patient assessment is the first step in developing a nursing care plan. Gather relevant information such as medical history, current health status, and subjective and objective data. This includes physical assessments ...
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on preparing a nursing care plan.As a nursing student, understanding the fundamentals of care planning is crucial for providing holistic care and effective communication within your nursing team. In this guide, we will provide step-by-step instructions, examples, and best practices for creating nursing care plans. ...