How to write a research question
Last updated
7 February 2023
Reviewed by
Miroslav Damyanov
In this article, we take an in-depth look at what a research question is, the different types of research questions, and how to write one (with examples). Read on to get started with your thesis, dissertation, or research paper .

Make research less tedious
Dovetail streamlines research to help you uncover and share actionable insights
- What is a research question?
A research question articulates exactly what you want to learn from your research. It stems directly from your research objectives, and you will arrive at an answer through data analysis and interpretation.
However, it is not that simple to write a research question—even when you know the question you intend to answer with your study. The main characteristics of a good research question are:
Feasible. You need to have the resources and abilities to examine the question, collect the data, and give answers.
Interesting. Create research questions that offer fascinating insights into your industry.
Novel. Research questions have to offer something new within your field of study.
Ethical. The research question topic should be approved by the relevant authorities and review boards.
Relevant. Your research question should lead to visible changes in society or your industry.
Usually, you write one single research question to guide your entire research paper. The answer becomes the thesis statement—the central position of your argument. A dissertation or thesis, on the other hand, may require multiple problem statements and research questions. However, they should be connected and focused on a specific problem.
- Importance of the research question
A research question acts as a guide for your entire study. It serves two vital purposes:
to determine the specific issue your research paper addresses
to identify clear objectives
Therefore, it helps split your research into small steps that you need to complete to provide answers.
Your research question will also provide boundaries for your study, which help set limits and ensure cohesion.
Finally, it acts as a frame of reference for assessing your work. Bear in mind that research questions can evolve, shift, and change during the early stages of your study or project.
- Types of research questions
The type of research you are conducting will dictate the type of research question to use. Primarily, research questions are grouped into three distinct categories of study:
qualitative
quantitative
mixed-method
Let’s look at each of these in turn:
Quantitative research questions
The number-one rule of quantitative research questions is that they are precise. They mainly include:
independent and dependent variables
the exact population being studied
the research design to be used
Therefore, you must frame and finalize quantitative research questions before starting the study.
Equally, a quantitative research question creates a link between itself and the research design. These questions cannot be answered with simple 'yes' or' no' responses, so they begin with words like 'does', 'do', 'are', and 'is'.
Quantitative research questions can be divided into three categories:
Relationship research questions usually leverage words such as 'trends' and 'association' because they include independent and dependent variables. They seek to define or explore trends and interactions between multiple variables.
Comparative research questions tend to analyze the differences between different groups to find an outcome variable. For instance, you may decide to compare two distinct groups where a specific variable is present in one and absent in the other.
Descriptive research questions usually start with the word 'what' and aim to measure how a population will respond to one or more variables.
Qualitative research questions
Like quantitative research questions, these questions are linked to the research design. However, qualitative research questions may deal with a specific or broad study area. This makes them more flexible, very adaptable, and usually non-directional.
Use qualitative research questions when your primary aim is to explain, discover, or explore.
There are seven types of qualitative research questions:
Explanatory research questions investigate particular topic areas that aren't well known.
Contextual research questions describe the workings of what is already in existence.
Evaluative research questions examine the effectiveness of specific paradigms or methods.
Ideological research questions aim to advance existing ideologies.
Descriptive research questions describe an event.
Generative research questions help develop actions and theories by providing new ideas.
Emancipatory research questions increase social action engagement, usually to benefit disadvantaged people.
Mixed-methods studies
With mixed-methods studies, you combine qualitative and quantitative research elements to get answers to your research question. This approach is ideal when you need a more complete picture. through a blend of the two approaches.
Mixed-methods research is excellent in multidisciplinary settings, societal analysis, and complex situations. Consider the following research question examples, which would be ideal candidates for a mixed-methods approach
How can non-voter and voter beliefs about democracy (qualitative) help explain Town X election turnout patterns (quantitative)?
How does students’ perception of their study environment (quantitative) relate to their test score differences (qualitative)?
- Developing a strong research question—a step-by-step guide
Research questions help break up your study into simple steps so you can quickly achieve your objectives and find answers. However, how do you develop a good research question? Here is our step-by-step guide:
1. Choose a topic
The first step is to select a broad research topic for your study. Pick something within your expertise and field that interests you. After all, the research itself will stem from the initial research question.
2. Conduct preliminary research
Once you have a broad topic, dig deeper into the problem by researching past studies in the field and gathering requirements from stakeholders if you work in a business setting.
Through this process, you will discover articles that mention areas not explored in that field or products that didn’t resonate with people’s expectations in a particular industry. For instance, you could explore specific topics that earlier research failed to study or products that failed to meet user needs.
3. Keep your audience in mind
Is your audience interested in the particular field you want to study? Are the research questions in your mind appealing and interesting to the audience? Defining your audience will help you refine your research question and ensure you pick a question that is relatable to your audience.
4. Generate a list of potential questions
Ask yourself numerous open-ended questions on the topic to create a potential list of research questions. You could start with broader questions and narrow them down to more specific ones. Don’t forget that you can challenge existing assumptions or use personal experiences to redefine research issues.
5. Review the questions
Evaluate your list of potential questions to determine which seems most effective. Ensure you consider the finer details of every question and possible outcomes. Doing this helps you determine if the questions meet the requirements of a research question.
6. Construct and evaluate your research question
Consider these two frameworks when constructing a good research question: PICOT and PEO.
PICOT stands for:
P: Problem or population
I: Indicator or intervention to be studied
C: Comparison groups
O: Outcome of interest
T: Time frame
PEO stands for:
P: Population being studied
E: Exposure to any preexisting conditions
To evaluate your research question once you’ve constructed it, ask yourself the following questions:
Is it clear?
Your study should produce precise data and observations. For qualitative studies, the observations need to be delineable across categories. Quantitative studies must have measurable and empirical data.
Is it specific and focused?
An excellent research question must be specific enough to ensure your testing yields objective results. General or open-ended research questions are often ambiguous and subject to different kinds of interpretation.
Is it sufficiently complex?
Your research needs to yield substantial and consequential results to warrant the study. Merely supporting or reinforcing an existing paper is not good enough.
- Examples of good research questions
A robust research question actively contributes to a specific body of knowledge; it is a question that hasn’t been answered before within your research field.
Here are some examples of good and bad research questions :
Good: How effective are A and B policies at reducing the rates of Z?
Bad: Is A or B a better policy?
The first is more focused and researchable because it isn't based on value judgment. The second fails to give clear criteria for answering the question.
Good: What is the effect of daily Twitter use on the attention span of college students?
Bad: What is the effect of social media use on people's minds?
The first includes specific and well-defined concepts, which the second lacks.
Ensure all terms within your research question have precise meanings. Avoid vague or general language that makes the topic too broad.
- The bottom line
The success of any research starts with formulating the right questions that ensure you collect the most insightful data. A good research question will showcase the objectives of your systematic investigation and emphasize specific contexts.
Should you be using a customer insights hub?
Do you want to discover previous research faster?
Do you share your research findings with others?
Do you analyze research data?
Start for free today, add your research, and get to key insights faster
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 18 April 2023
Last updated: 27 February 2023
Last updated: 6 February 2023
Last updated: 15 January 2024
Last updated: 6 October 2023
Last updated: 5 February 2023
Last updated: 16 April 2023
Last updated: 7 March 2023
Last updated: 16 August 2024
Last updated: 9 March 2023
Last updated: 11 March 2024
Last updated: 13 May 2024
Latest articles
Related topics, decide what to build next, log in or sign up.
Get started for free

How to Write a Research Question: Types and Examples

The first step in any research project is framing the research question. It can be considered the core of any systematic investigation as the research outcomes are tied to asking the right questions. Thus, this primary interrogation point sets the pace for your research as it helps collect relevant and insightful information that ultimately influences your work.
Typically, the research question guides the stages of inquiry, analysis, and reporting. Depending on the use of quantifiable or quantitative data, research questions are broadly categorized into quantitative or qualitative research questions. Both types of research questions can be used independently or together, considering the overall focus and objectives of your research.
What is a research question?
A research question is a clear, focused, concise, and arguable question on which your research and writing are centered. 1 It states various aspects of the study, including the population and variables to be studied and the problem the study addresses. These questions also set the boundaries of the study, ensuring cohesion.
Designing the research question is a dynamic process where the researcher can change or refine the research question as they review related literature and develop a framework for the study. Depending on the scale of your research, the study can include single or multiple research questions.
A good research question has the following features:
- It is relevant to the chosen field of study.
- The question posed is arguable and open for debate, requiring synthesizing and analysis of ideas.
- It is focused and concisely framed.
- A feasible solution is possible within the given practical constraint and timeframe.
A poorly formulated research question poses several risks. 1
- Researchers can adopt an erroneous design.
- It can create confusion and hinder the thought process, including developing a clear protocol.
- It can jeopardize publication efforts.
- It causes difficulty in determining the relevance of the study findings.
- It causes difficulty in whether the study fulfils the inclusion criteria for systematic review and meta-analysis. This creates challenges in determining whether additional studies or data collection is needed to answer the question.
- Readers may fail to understand the objective of the study. This reduces the likelihood of the study being cited by others.
Now that you know “What is a research question?”, let’s look at the different types of research questions.
Types of research questions
Depending on the type of research to be done, research questions can be classified broadly into quantitative, qualitative, or mixed-methods studies. Knowing the type of research helps determine the best type of research question that reflects the direction and epistemological underpinnings of your research.
The structure and wording of quantitative 2 and qualitative research 3 questions differ significantly. The quantitative study looks at causal relationships, whereas the qualitative study aims at exploring a phenomenon.
- Quantitative research questions:
- Seeks to investigate social, familial, or educational experiences or processes in a particular context and/or location.
- Answers ‘how,’ ‘what,’ or ‘why’ questions.
- Investigates connections, relations, or comparisons between independent and dependent variables.
Quantitative research questions can be further categorized into descriptive, comparative, and relationship, as explained in the Table below.
| Descriptive research questions | These measure the responses of a study’s population toward a particular question or variable. Common descriptive research questions will begin with “How much?”, “How regularly?”, “What percentage?”, “What time?”, “What is?” Research question example: How often do you buy mobile apps for learning purposes? |
| Comparative research questions | These investigate differences between two or more groups for an outcome variable. For instance, the researcher may compare groups with and without a certain variable. Research question example: What are the differences in attitudes towards online learning between visual and Kinaesthetic learners? |
| Relationship research questions | These explore and define trends and interactions between two or more variables. These investigate relationships between dependent and independent variables and use words such as “association” or “trends. Research question example: What is the relationship between disposable income and job satisfaction amongst US residents? |
- Qualitative research questions
Qualitative research questions are adaptable, non-directional, and more flexible. It concerns broad areas of research or more specific areas of study to discover, explain, or explore a phenomenon. These are further classified as follows:
| Exploratory Questions | These question looks to understand something without influencing the results. The aim is to learn more about a topic without attributing bias or preconceived notions. Research question example: What are people’s thoughts on the new government? |
| Experiential questions | These questions focus on understanding individuals’ experiences, perspectives, and subjective meanings related to a particular phenomenon. They aim to capture personal experiences and emotions. Research question example: What are the challenges students face during their transition from school to college? |
| Interpretive Questions | These questions investigate people in their natural settings to help understand how a group makes sense of shared experiences of a phenomenon. Research question example: How do you feel about ChatGPT assisting student learning? |
- Mixed-methods studies
Mixed-methods studies use both quantitative and qualitative research questions to answer your research question. Mixed methods provide a complete picture than standalone quantitative or qualitative research, as it integrates the benefits of both methods. Mixed methods research is often used in multidisciplinary settings and complex situational or societal research, especially in the behavioral, health, and social science fields.
What makes a good research question
A good research question should be clear and focused to guide your research. It should synthesize multiple sources to present your unique argument, and should ideally be something that you are interested in. But avoid questions that can be answered in a few factual statements. The following are the main attributes of a good research question.
- Specific: The research question should not be a fishing expedition performed in the hopes that some new information will be found that will benefit the researcher. The central research question should work with your research problem to keep your work focused. If using multiple questions, they should all tie back to the central aim.
- Measurable: The research question must be answerable using quantitative and/or qualitative data or from scholarly sources to develop your research question. If such data is impossible to access, it is better to rethink your question.
- Attainable: Ensure you have enough time and resources to do all research required to answer your question. If it seems you will not be able to gain access to the data you need, consider narrowing down your question to be more specific.
- You have the expertise
- You have the equipment and resources
- Realistic: Developing your research question should be based on initial reading about your topic. It should focus on addressing a problem or gap in the existing knowledge in your field or discipline.
- Based on some sort of rational physics
- Can be done in a reasonable time frame
- Timely: The research question should contribute to an existing and current debate in your field or in society at large. It should produce knowledge that future researchers or practitioners can later build on.
- Novel
- Based on current technologies.
- Important to answer current problems or concerns.
- Lead to new directions.
- Important: Your question should have some aspect of originality. Incremental research is as important as exploring disruptive technologies. For example, you can focus on a specific location or explore a new angle.
- Meaningful whether the answer is “Yes” or “No.” Closed-ended, yes/no questions are too simple to work as good research questions. Such questions do not provide enough scope for robust investigation and discussion. A good research question requires original data, synthesis of multiple sources, and original interpretation and argumentation before providing an answer.
Steps for developing a good research question
The importance of research questions cannot be understated. When drafting a research question, use the following frameworks to guide the components of your question to ease the process. 4
- Determine the requirements: Before constructing a good research question, set your research requirements. What is the purpose? Is it descriptive, comparative, or explorative research? Determining the research aim will help you choose the most appropriate topic and word your question appropriately.
- Select a broad research topic: Identify a broader subject area of interest that requires investigation. Techniques such as brainstorming or concept mapping can help identify relevant connections and themes within a broad research topic. For example, how to learn and help students learn.
- Perform preliminary investigation: Preliminary research is needed to obtain up-to-date and relevant knowledge on your topic. It also helps identify issues currently being discussed from which information gaps can be identified.
- Narrow your focus: Narrow the scope and focus of your research to a specific niche. This involves focusing on gaps in existing knowledge or recent literature or extending or complementing the findings of existing literature. Another approach involves constructing strong research questions that challenge your views or knowledge of the area of study (Example: Is learning consistent with the existing learning theory and research).
- Identify the research problem: Once the research question has been framed, one should evaluate it. This is to realize the importance of the research questions and if there is a need for more revising (Example: How do your beliefs on learning theory and research impact your instructional practices).
How to write a research question
Those struggling to understand how to write a research question, these simple steps can help you simplify the process of writing a research question.
| Topic selection | Choose a broad topic, such as “learner support” or “social media influence” for your study. Select topics of interest to make research more enjoyable and stay motivated. |
| Preliminary research | The goal is to refine and focus your research question. The following strategies can help: Skim various scholarly articles. List subtopics under the main topic. List possible research questions for each subtopic. Consider the scope of research for each of the research questions. Select research questions that are answerable within a specific time and with available resources. If the scope is too large, repeat looking for sub-subtopics. |
| Audience | When choosing what to base your research on, consider your readers. For college papers, the audience is academic. Ask yourself if your audience may be interested in the topic you are thinking about pursuing. Determining your audience can also help refine the importance of your research question and focus on items related to your defined group. |
| Generate potential questions | Ask open-ended “how?” and “why?” questions to find a more specific research question. Gap-spotting to identify research limitations, problematization to challenge assumptions made by others, or using personal experiences to draw on issues in your industry can be used to generate questions. |
| Review brainstormed questions | Evaluate each question to check their effectiveness. Use the FINER model to see if the question meets all the research question criteria. |
| Construct the research question | Multiple frameworks, such as PICOT and PEA, are available to help structure your research question. The frameworks listed below can help you with the necessary information for generating your research question. |
| Framework | Attributes of each framework |
| FINER | Feasible Interesting Novel Ethical Relevant |
| PICOT | Population or problem Intervention or indicator being studied Comparison group Outcome of interest Time frame of the study |
| PEO | Population being studied Exposure to preexisting conditions Outcome of interest |
Sample Research Questions
The following are some bad and good research question examples
- Example 1
| Unclear: How does social media affect student growth? |
| Clear: What effect does the daily use of Twitter and Facebook have on the career development goals of students? |
| Explanation: The first research question is unclear because of the vagueness of “social media” as a concept and the lack of specificity. The second question is specific and focused, and its answer can be discovered through data collection and analysis. |
- Example 2
| Simple: Has there been an increase in the number of gifted children identified? |
| Complex: What practical techniques can teachers use to identify and guide gifted children better? |
| Explanation: A simple “yes” or “no” statement easily answers the first research question. The second research question is more complicated and requires the researcher to collect data, perform in-depth data analysis, and form an argument that leads to further discussion. |
References:
- Thabane, L., Thomas, T., Ye, C., & Paul, J. (2009). Posing the research question: not so simple. Canadian Journal of Anesthesia/Journal canadien d’anesthésie , 56 (1), 71-79.
- Rutberg, S., & Bouikidis, C. D. (2018). Focusing on the fundamentals: A simplistic differentiation between qualitative and quantitative research. Nephrology Nursing Journal , 45 (2), 209-213.
- Kyngäs, H. (2020). Qualitative research and content analysis. The application of content analysis in nursing science research , 3-11.
- Mattick, K., Johnston, J., & de la Croix, A. (2018). How to… write a good research question. The clinical teacher , 15 (2), 104-108.
- Fandino, W. (2019). Formulating a good research question: Pearls and pitfalls. Indian Journal of Anaesthesia , 63 (8), 611.
- Richardson, W. S., Wilson, M. C., Nishikawa, J., & Hayward, R. S. (1995). The well-built clinical question: a key to evidence-based decisions. ACP journal club , 123 (3), A12-A13
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- Scientific Writing Style Guides Explained
- Ethical Research Practices For Research with Human Subjects
- 8 Most Effective Ways to Increase Motivation for Thesis Writing
- 6 Tips for Post-Doc Researchers to Take Their Career to the Next Level
Transitive and Intransitive Verbs in the World of Research
Language and grammar rules for academic writing, you may also like, how to cite in apa format (7th edition):..., how to write your research paper in apa..., how to choose a dissertation topic, how to write a phd research proposal, how to write an academic paragraph (step-by-step guide), research funding basics: what should a grant proposal..., how to write the first draft of a..., mla works cited page: format, template & examples, academic editing: how to self-edit academic text with..., measuring academic success: definition & strategies for excellence.
- News & Highlights
- Publications and Documents
- Education in C/T Science
- Browse Our Courses
- C/T Research Academy
- K12 Investigator Training
- Harvard Catalyst On-Demand
- SMART IRB Reliance Request
- Biostatistics Consulting
- Regulatory Support
- Pilot Funding
- Informatics Program
- Community Engagement
- Diversity Inclusion
- Research Enrollment and Diversity
- Harvard Catalyst Profiles

Creating a Good Research Question
- Advice & Growth
- Process in Practice
Successful translation of research begins with a strong question. How do you get started? How do good research questions evolve? And where do you find inspiration to generate good questions in the first place? It’s helpful to understand existing frameworks, guidelines, and standards, as well as hear from researchers who utilize these strategies in their own work.
In the fall and winter of 2020, Naomi Fisher, MD, conducted 10 interviews with clinical and translational researchers at Harvard University and affiliated academic healthcare centers, with the purpose of capturing their experiences developing good research questions. The researchers featured in this project represent various specialties, drawn from every stage of their careers. Below you will find clips from their interviews and additional resources that highlight how to get started, as well as helpful frameworks and factors to consider. Additionally, visit the Advice & Growth section to hear candid advice and explore the Process in Practice section to hear how researchers have applied these recommendations to their published research.
- Naomi Fisher, MD , is associate professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School (HMS), and clinical staff at Brigham and Women’s Hospital (BWH). Fisher is founder and director of Hypertension Services and the Hypertension Specialty Clinic at the BWH, where she is a renowned endocrinologist. She serves as a faculty director for communication-related Boundary-Crossing Skills for Research Careers webinar sessions and the Writing and Communication Center .
- Christopher Gibbons, MD , is associate professor of neurology at HMS, and clinical staff at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC) and Joslin Diabetes Center. Gibbons’ research focus is on peripheral and autonomic neuropathies.
- Clare Tempany-Afdhal, MD , is professor of radiology at HMS and the Ferenc Jolesz Chair of Research, Radiology at BWH. Her major areas of research are MR imaging of the pelvis and image- guided therapy.
- David Sykes, MD, PhD , is assistant professor of medicine at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH), he is also principal investigator at the Sykes Lab at MGH. His special interest area is rare hematologic conditions.
- Elliot Israel, MD , is professor of medicine at HMS, director of the Respiratory Therapy Department, the director of clinical research in the Pulmonary and Critical Care Medical Division and associate physician at BWH. Israel’s research interests include therapeutic interventions to alter asthmatic airway hyperactivity and the role of arachidonic acid metabolites in airway narrowing.
- Jonathan Williams, MD, MMSc , is assistant professor of medicine at HMS, and associate physician at BWH. He focuses on endocrinology, specifically unravelling the intricate relationship between genetics and environment with respect to susceptibility to cardiometabolic disease.
- Junichi Tokuda, PhD , is associate professor of radiology at HMS, and is a research scientist at the Department of Radiology, BWH. Tokuda is particularly interested in technologies to support image-guided “closed-loop” interventions. He also serves as a principal investigator leading several projects funded by the National Institutes of Health and industry.
- Osama Rahma, MD , is assistant professor of medicine at HMS and clinical staff member in medical oncology at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute (DFCI). Rhama is currently a principal investigator at the Center for Immuno-Oncology and Gastroenterology Cancer Center at DFCI. His research focus is on drug development of combinational immune therapeutics.
- Sharmila Dorbala, MD, MPH , is professor of radiology at HMS and clinical staff at BWH in cardiovascular medicine and radiology. She is also the president of the American Society of Nuclear Medicine. Dorbala’s specialty is using nuclear medicine for cardiovascular discoveries.
- Subha Ramani, PhD, MBBS, MMed , is associate professor of medicine at HMS, as well as associate physician in the Division of General Internal Medicine and Primary Care at BWH. Ramani’s scholarly interests focus on innovative approaches to teaching, learning and assessment of clinical trainees, faculty development in teaching, and qualitative research methods in medical education.
- Ursula Kaiser, MD , is professor at HMS and chief of the Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes and Hypertension, and senior physician at BWH. Kaiser’s research focuses on understanding the molecular mechanisms by which pulsatile gonadotropin-releasing hormone regulates the expression of luteinizing hormone and follicle-stimulating hormone genes.
Insights on Creating a Good Research Question

Play Junichi Tokuda video

Play Ursula Kaiser video
Start Successfully: Build the Foundation of a Good Research Question

Start Successfully Resources
Ideation in Device Development: Finding Clinical Need Josh Tolkoff, MS A lecture explaining the critical importance of identifying a compelling clinical need before embarking on a research project. Play Ideation in Device Development video .
Radical Innovation Jeff Karp, PhD This ThinkResearch podcast episode focuses on one researcher’s approach using radical simplicity to break down big problems and questions. Play Radical Innovation .
Using Healthcare Data: How can Researchers Come up with Interesting Questions? Anupam Jena, MD, PhD Another ThinkResearch podcast episode addresses how to discover good research questions by using a backward design approach which involves analyzing big data and allowing the research question to unfold from findings. Play Using Healthcare Data .
Important Factors: Consider Feasibility and Novelty

Refining Your Research Question
Play video of Clare Tempany-Afdhal

Play Elliott Israel video
Frameworks and Structure: Evaluate Research Questions Using Tools and Techniques
Frameworks and Structure Resources
Designing Clinical Research Hulley et al. A comprehensive and practical guide to clinical research, including the FINER framework for evaluating research questions. Learn more about the book .
Translational Medicine Library Guide Queens University Library An introduction to popular frameworks for research questions, including FINER and PICO. Review translational medicine guide .
Asking a Good T3/T4 Question Niteesh K. Choudhry, MD, PhD This video explains the PICO framework in practice as participants in a workshop propose research questions that compare interventions. Play Asking a Good T3/T4 Question video
Introduction to Designing & Conducting Mixed Methods Research An online course that provides a deeper dive into mixed methods’ research questions and methodologies. Learn more about the course
Network and Support: Find the Collaborators and Stakeholders to Help Evaluate Research Questions

Network & Support Resource
Bench-to-bedside, Bedside-to-bench Christopher Gibbons, MD In this lecture, Gibbons shares his experience of bringing research from bench to bedside, and from bedside to bench. His talk highlights the formation and evolution of research questions based on clinical need. Play Bench-to-bedside.

Research Question 101 📖
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Reviewed By: Dr. Eunice Rautenbach | October 2023

I f you’ve landed on this page, you’re probably asking yourself, “ What is a research question? ”. Well, you’ve come to the right place. In this post, we’ll explain what a research question is , how it’s differen t from a research aim, and how to craft a high-quality research question that sets you up for success.
Research Question 101
What is a research question.
- Research questions vs research aims
- The 4 types of research questions
- How to write a research question
- Frequently asked questions
- Examples of research questions
As the name suggests, the research question is the core question (or set of questions) that your study will (attempt to) answer .
In many ways, a research question is akin to a target in archery . Without a clear target, you won’t know where to concentrate your efforts and focus. Essentially, your research question acts as the guiding light throughout your project and informs every choice you make along the way.
Let’s look at some examples:
What impact does social media usage have on the mental health of teenagers in New York?
How does the introduction of a minimum wage affect employment levels in small businesses in outer London?
How does the portrayal of women in 19th-century American literature reflect the societal attitudes of the time?
What are the long-term effects of intermittent fasting on heart health in adults?
As you can see in these examples, research questions are clear, specific questions that can be feasibly answered within a study. These are important attributes and we’ll discuss each of them in more detail a little later . If you’d like to see more examples of research questions, you can find our RQ mega-list here .

Research Questions vs Research Aims
At this point, you might be asking yourself, “ How is a research question different from a research aim? ”. Within any given study, the research aim and research question (or questions) are tightly intertwined , but they are separate things . Let’s unpack that a little.
A research aim is typically broader in nature and outlines what you hope to achieve with your research. It doesn’t ask a specific question but rather gives a summary of what you intend to explore.
The research question, on the other hand, is much more focused . It’s the specific query you’re setting out to answer. It narrows down the research aim into a detailed, researchable question that will guide your study’s methods and analysis.
Let’s look at an example:
Research Aim: To explore the effects of climate change on marine life in Southern Africa.
Research Question: How does ocean acidification caused by climate change affect the reproduction rates of coral reefs?
As you can see, the research aim gives you a general focus , while the research question details exactly what you want to find out.
Need a helping hand?
Types of research questions
Now that we’ve defined what a research question is, let’s look at the different types of research questions that you might come across. Broadly speaking, there are (at least) four different types of research questions – descriptive , comparative , relational , and explanatory .
Descriptive questions ask what is happening. In other words, they seek to describe a phenomena or situation . An example of a descriptive research question could be something like “What types of exercise do high-performing UK executives engage in?”. This would likely be a bit too basic to form an interesting study, but as you can see, the research question is just focused on the what – in other words, it just describes the situation.
Comparative research questions , on the other hand, look to understand the way in which two or more things differ , or how they’re similar. An example of a comparative research question might be something like “How do exercise preferences vary between middle-aged men across three American cities?”. As you can see, this question seeks to compare the differences (or similarities) in behaviour between different groups.
Next up, we’ve got exploratory research questions , which ask why or how is something happening. While the other types of questions we looked at focused on the what, exploratory research questions are interested in the why and how . As an example, an exploratory research question might ask something like “Why have bee populations declined in Germany over the last 5 years?”. As you can, this question is aimed squarely at the why, rather than the what.
Last but not least, we have relational research questions . As the name suggests, these types of research questions seek to explore the relationships between variables . Here, an example could be something like “What is the relationship between X and Y” or “Does A have an impact on B”. As you can see, these types of research questions are interested in understanding how constructs or variables are connected , and perhaps, whether one thing causes another.
Of course, depending on how fine-grained you want to get, you can argue that there are many more types of research questions , but these four categories give you a broad idea of the different flavours that exist out there. It’s also worth pointing out that a research question doesn’t need to fit perfectly into one category – in many cases, a research question might overlap into more than just one category and that’s okay.
The key takeaway here is that research questions can take many different forms , and it’s useful to understand the nature of your research question so that you can align your research methodology accordingly.

How To Write A Research Question
As we alluded earlier, a well-crafted research question needs to possess very specific attributes, including focus , clarity and feasibility . But that’s not all – a rock-solid research question also needs to be rooted and aligned . Let’s look at each of these.
A strong research question typically has a single focus. So, don’t try to cram multiple questions into one research question; rather split them up into separate questions (or even subquestions), each with their own specific focus. As a rule of thumb, narrow beats broad when it comes to research questions.
Clear and specific
A good research question is clear and specific, not vague and broad. State clearly exactly what you want to find out so that any reader can quickly understand what you’re looking to achieve with your study. Along the same vein, try to avoid using bulky language and jargon – aim for clarity.
Unfortunately, even a super tantalising and thought-provoking research question has little value if you cannot feasibly answer it. So, think about the methodological implications of your research question while you’re crafting it. Most importantly, make sure that you know exactly what data you’ll need (primary or secondary) and how you’ll analyse that data.
A good research question (and a research topic, more broadly) should be rooted in a clear research gap and research problem . Without a well-defined research gap, you risk wasting your effort pursuing a question that’s already been adequately answered (and agreed upon) by the research community. A well-argued research gap lays at the heart of a valuable study, so make sure you have your gap clearly articulated and that your research question directly links to it.
As we mentioned earlier, your research aim and research question are (or at least, should be) tightly linked. So, make sure that your research question (or set of questions) aligns with your research aim . If not, you’ll need to revise one of the two to achieve this.
FAQ: Research Questions
Research question faqs, how many research questions should i have, what should i avoid when writing a research question, can a research question be a statement.
Typically, a research question is phrased as a question, not a statement. A question clearly indicates what you’re setting out to discover.
Can a research question be too broad or too narrow?
Yes. A question that’s too broad makes your research unfocused, while a question that’s too narrow limits the scope of your study.
Here’s an example of a research question that’s too broad:
“Why is mental health important?”
Conversely, here’s an example of a research question that’s likely too narrow:
“What is the impact of sleep deprivation on the exam scores of 19-year-old males in London studying maths at The Open University?”
Can I change my research question during the research process?
How do i know if my research question is good.
A good research question is focused, specific, practical, rooted in a research gap, and aligned with the research aim. If your question meets these criteria, it’s likely a strong question.
Is a research question similar to a hypothesis?
Not quite. A hypothesis is a testable statement that predicts an outcome, while a research question is a query that you’re trying to answer through your study. Naturally, there can be linkages between a study’s research questions and hypothesis, but they serve different functions.
How are research questions and research objectives related?
The research question is a focused and specific query that your study aims to answer. It’s the central issue you’re investigating. The research objective, on the other hand, outlines the steps you’ll take to answer your research question. Research objectives are often more action-oriented and can be broken down into smaller tasks that guide your research process. In a sense, they’re something of a roadmap that helps you answer your research question.
Need some inspiration?
If you’d like to see more examples of research questions, check out our research question mega list here . Alternatively, if you’d like 1-on-1 help developing a high-quality research question, consider our private coaching service .

You Might Also Like:

How To Choose A Tutor For Your Dissertation
Hiring the right tutor for your dissertation or thesis can make the difference between passing and failing. Here’s what you need to consider.

5 Signs You Need A Dissertation Helper
Discover the 5 signs that suggest you need a dissertation helper to get unstuck, finish your degree and get your life back.

Writing A Dissertation While Working: A How-To Guide
Struggling to balance your dissertation with a full-time job and family? Learn practical strategies to achieve success.

How To Review & Understand Academic Literature Quickly
Learn how to fast-track your literature review by reading with intention and clarity. Dr E and Amy Murdock explain how.

Dissertation Writing Services: Far Worse Than You Think
Thinking about using a dissertation or thesis writing service? You might want to reconsider that move. Here’s what you need to know.
📄 FREE TEMPLATES
Research Topic Ideation
Proposal Writing
Literature Review
Methodology & Analysis
Academic Writing
Referencing & Citing
Apps, Tools & Tricks
The Grad Coach Podcast
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Submit Comment
- Print Friendly
Educational resources and simple solutions for your research journey

How to Craft a Strong Research Question (With Research Question Examples)
A sound and effective research question is a key element that must be identified and pinned down before researchers can even begin their research study or work. A strong research question lays the foundation for your entire study, guiding your investigation and shaping your findings. Hence, it is critical that researchers spend considerable time assessing and refining the research question based on in-depth reading and comprehensive literature review. In this article, we will discuss how to write a strong research question and provide you with some good examples of research questions across various disciplines.
Table of Contents
The importance of a research question
A research question plays a crucial role in driving scientific inquiry, setting the direction and purpose of your study, and guiding your entire research process. By formulating a clear and focused research question, you lay the foundation for your investigation, ensuring that your research remains on track and aligned with your objectives so you can make meaningful contribution to the existing body of knowledge. A well-crafted research question also helps you define the scope of your study and identify the appropriate methodologies and data collection techniques to employ.
Key components of a strong research question
A good research question possesses several key components that contribute to the quality and impact of your study. Apart from providing a clear framework to generate meaningful results, a well-defined research question allows other researchers to understand the purpose and significance of your work. So, when working on your research question, incorporate the following elements:
- Specificity : A strong research question should be specific about the main focus of your study, enabling you to gather precise data and draw accurate conclusions. It clearly defines the variables, participants, and context involved, leaving no room for ambiguity.
- Clarity : A good research question is clear and easily understood, so articulate the purpose and intent of your study concisely without being generic or vague. Ensuring clarity in your research question helps both you and your readers grasp the research objective.
- Feasibility : While crafting a research question, consider the practicality of conducting the research and availability of necessary data or access to participants. Think whether your study is realistic and achievable within the constraints of time, resources, and ethical considerations.
How to craft a well-defined research question
A first step that will help save time and effort is knowing what your aims are and thinking about a few problem statements on the area or aspect one wants to study or do research on. Contemplating these statements as one undertakes more progressive reading can help the researcher in reassessing and fine-tuning the research question. This can be done over time as they read and learn more about the research topic, along with a broad literature review and parallel discussions with peer researchers and supervisors. In some cases, a researcher can have more than one research question if the research being undertaken is a PhD thesis or dissertation, but try not to cover multiple concerns on a topic.
A strong research question must be researchable, original, complex, and relevant. Here are five simple steps that can make the entire process easier.
- Identify a broad topic from your areas of interest, something that is relevant, and you are passionate about since you’ll be spending a lot of time conducting your research.
- Do a thorough literature review to weed out potential gaps in research and stay updated on what’s currently being done in your chosen topic and subject area.
- Shortlist possible research questions based on the research gaps or see how you can build on or refute previously published ideas and concepts.
- Assess your chosen research question using the FINER criteria that helps you evaluate whether the research is Feasible, Interesting, Novel, Ethical, and Relevant. 1
- Formulate the final research question, while ensuring it is clear, well-written, and addresses all the key elements of a strong research question.
Examples of research questions
Remember to adapt your research question to suit your purpose, whether it’s exploratory, descriptive, comparative, experimental, qualitative, or quantitative. Embrace the iterative nature of the research process, continually evaluating and refining your question as you progress. Here are some good examples of research questions across various disciplines.
Exploratory research question examples
- How does social media impact interpersonal relationships among teenagers?
- What are the potential benefits of incorporating mindfulness practices in the workplace?
Descriptive research question examples
- What factors influence customer loyalty in the e-commerce industry?
- Is there a relationship between socioeconomic status and academic performance among elementary school students?
Comparative research question examples
- How does the effectiveness of traditional teaching methods compare to online learning platforms in mathematics education?
- What is the impact of different healthcare policies on patient outcomes in various countries?
Experimental research question examples
- What are the effects of a new drug on reducing symptoms of a specific medical condition?
- Does a dietary intervention have an impact on weight loss among individuals with obesity?
Qualitative research question examples
- What are the lived experiences of immigrants adapting to a new culture?
- What factors influence job satisfaction among healthcare professionals?
Quantitative research question examples
- Is there a relationship between sleep duration and academic performance among college students?
- How effective is a specific intervention in reducing anxiety levels among individuals with phobias?
With these simple guidelines and inspiring examples of research questions, you are equipped to embark on your research journey with confidence and purpose. Here’s wishing you all the best for your future endeavors!
References:
- How to write a research question: Steps and examples. Indeed Career Guide. Available online at https://www.indeed.com/career-advice/career-development/how-to-write-research-questions
R Discovery is a literature search and research reading platform that accelerates your research discovery journey by keeping you updated on the latest, most relevant scholarly content. With 250M+ research articles sourced from trusted aggregators like CrossRef, Unpaywall, PubMed, PubMed Central, Open Alex and top publishing houses like Springer Nature, JAMA, IOP, Taylor & Francis, NEJM, BMJ, Karger, SAGE, Emerald Publishing and more, R Discovery puts a world of research at your fingertips.
Try R Discovery Prime FREE for 1 week or upgrade at just US$72 a year to access premium features that let you listen to research on the go, read in your language, collaborate with peers, auto sync with reference managers, and much more. Choose a simpler, smarter way to find and read research – Download the app and start your free 7-day trial today !
Related Posts

What Constitutes Good Research in Academia?

Is Google Scholar a Database or Search Engine?
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
5 Steps to Creating Better Research Questions

5-minute read
- 14th December 2021
Research questions are central to scientific inquiry . Well-formulated research questions identify the specific issues your study will address and help you plan your investigation.
In this post, we’ll show you how to formulate strong research questions in five steps:
- Start with a broad topic that you’re interested in.
- Familiarize yourself with current work in your chosen area.
- Identify the specific issue you want to focus on.
- Develop a suitably complex question.
- Refine your question by examining each word.
Read on to learn more about each of these points.
1. Choose a Subject That You Are Genuinely Curious About
You’ll spend a lot of time researching your chosen topic. That’s why you should choose a topic that interests you and that you’d like to learn about. Also, you should choose a topic that’s exciting and relevant to your audience, especially if you hope to have your work published .
Instead of choosing a completely new area of study, choose a topic that you already know a little bit about. If you’ve read even just a few articles about something, that’s better than tackling something completely new.
Your topic should be broad but not too broad. For example, if you choose “mental health,” you need to narrow it down right away so that step 2 is doable. A more realistic broad topic would be “mental health in teenagers.” You won’t have to complete as much research, but you’ll still have plenty of room to find a niche topic within the larger area.
2. Carry Out Preliminary Research
The next step is to research your chosen topic. By looking at recent journal articles and review papers , you can find out what other researchers are exploring and what questions arise from existing studies.
The aim here is to identify possible subtopics and/or find gaps in current research. So, as you read, jot down questions you’d like to answer and areas you’d like to explore further.
3. Focus on a Precise Issue Within the Broader Topic
Now that you’ve familiarized yourself with the current state of research on your chosen topic, you can focus on a niche area.
In our example above, “mental health in teenagers,” this could mean focusing on a specific group (e.g., 7th–9 th -grade students). We could look at a single area of mental health (e.g., anxiety) or a specific time or place.
Maybe in your initial reading, you discovered a gap in existing research that could form the basis of your research question, or you may be interested in exploring the relationship between different variables (e.g., gender and anxiety level).
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
Another idea is to consider how current events might affect the broader topic. For example, you might choose to study the impact of the pandemic on the mental wellbeing of 11–16-year-old children.
4. Create an Interesting, Researchable Question
The next step is to turn your idea into a well-balanced question. The best research questions will tick all the boxes below:
● Original: This simply means that your question shouldn’t have already been answered. It doesn’t mean you must have an idea that nobody has come up with yet, but your approach should bring new insight. This could mean that you focus on a specific age group or geographic area.
● Focused: Your question should identify a single problem that you want your research to address.
● Complex: If someone could answer your question by searching the Internet for five minutes, it’s not complex enough. Research questions should ask “how” and “why” rather than “is” or “does.” In other words, they shouldn’t be easily answered with “yes” or “no.” Rather, answering the question means bringing together ideas and data from different sources.
● Achievable: Even if your question is complex enough to turn into a research paper, you still need to keep in mind constraints like word count, time frame, availability of resources, and your ability to complete the necessary research.
● Debatable: When answering your research question, keep in mind that you don’t want to reach a definitive conclusion. A strong question leaves room for further discussion.
5. Make Every Word Count
The final step is to formulate the precise wording of your question. You may need to follow a defined format (e.g., PICO or PEO ), or you can phrase the question in your own way.
In either case, your research question must clearly state what the paper is about. It should be as concise as possible but not open to misinterpretation. This includes defining ambiguous terms (e.g., “young people”) and detailing how you’ll evaluate any relevant variables.
Hopefully, you can now formulate effective research questions. Don’t forget to have your paper proofread by an expert when you’re done. At Proofed, we’ll check your writing for errors in grammar, spelling, and punctuation and give you feedback on clarity and conciseness. You can even try our proofreading service for free .
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
Free email newsletter template.
Promoting a brand means sharing valuable insights to connect more deeply with your audience, and...
6-minute read
How to Write a Nonprofit Grant Proposal
If you’re seeking funding to support your charitable endeavors as a nonprofit organization, you’ll need...
9-minute read
How to Use Infographics to Boost Your Presentation
Is your content getting noticed? Capturing and maintaining an audience’s attention is a challenge when...
8-minute read
Why Interactive PDFs Are Better for Engagement
Are you looking to enhance engagement and captivate your audience through your professional documents? Interactive...
7-minute read
Seven Key Strategies for Voice Search Optimization
Voice search optimization is rapidly shaping the digital landscape, requiring content professionals to adapt their...
4-minute read
Five Creative Ways to Showcase Your Digital Portfolio
Are you a creative freelancer looking to make a lasting impression on potential clients or...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
Writing Studio
Formulating your research question (rq).
In an effort to make our handouts more accessible, we have begun converting our PDF handouts to web pages. Download this page as a PDF: Formulating Your Research Question Return to Writing Studio Handouts
In a research paper, the emphasis is on generating a unique question and then synthesizing diverse sources into a coherent essay that supports your argument about the topic. In other words, you integrate information from publications with your own thoughts in order to formulate an argument. Your topic is your starting place: from here, you will develop an engaging research question. Merely presenting a topic in the form of a question does not transform it into a good research question.
Research Topic Versus Research Question Examples
1. broad topic versus narrow question, 1a. broad topic.
“What forces affect race relations in America?”
1b. NARROWER QUESTION
“How do corporate hiring practices affect race relations in Nashville?”
The question “What is the percentage of racial minorities holding management positions in corporate offices in Nashville?” is much too specific and would yield, at best, a statistic that could become part of a larger argument.

2. Neutral Topic Versus Argumentative Question
2a. neutral topic.
“How does KFC market its low-fat food offerings?”
2b. Argumentative question
“Does KFC put more money into marketing its high-fat food offerings than its lower-fat ones?”
The latter question is somewhat better, since it may lead you to take a stance or formulate an argument about consumer awareness or benefit.
3. Objective Topic Versus Subjective Question
Objective subjects are factual and do not have sides to be argued. Subjective subjects are those about which you can take a side.
3a. Objective topic
“How much time do youth between the ages of 10 and 15 spend playing video games?”
3b. Subjective Question
“What are the effects of video-gaming on the attention spans of youth between the ages of 10 and 15?”
The first question is likely to lead to some data, though not necessarily to an argument or issue. The second question is somewhat better, since it might lead you to formulate an argument for or against time spent playing video games.
4. Open-Ended Topic Versus Direct Question
4a. open-ended topic.
“Does the author of this text use allusion?”
4b. Direct question (gives direction to research)
“Does the ironic use of allusion in this text reveal anything about the author’s unwillingness to divulge his political commitments?”
The second question gives focus by putting the use of allusion into the specific context of a question about the author’s political commitments and perhaps also about the circumstances under which the text was produced.
Research Question (RQ) Checklist
- Is my RQ something that I am curious about and that others might care about? Does it present an issue on which I can take a stand?
- Does my RQ put a new spin on an old issue, or does it try to solve a problem?
- Is my RQ too broad, too narrow, or OK?
- within the time frame of the assignment?
- given the resources available at my location?
- Is my RQ measurable? What type of information do I need? Can I find actual data to support or contradict a position?
- What sources will have the type of information that I need to answer my RQ (journals, books, internet resources, government documents, interviews with people)?
Final Thoughts
The answer to a good research question will often be the THESIS of your research paper! And the results of your research may not always be what you expected them to be. Not only is this ok, it can be an indication that you are doing careful work!
Adapted from an online tutorial at Empire State College: http://www.esc.edu/htmlpages/writerold/menus.htm#develop (broken link)
Last revised: November 2022 | Adapted for web delivery: November 2022
In order to access certain content on this page, you may need to download Adobe Acrobat Reader or an equivalent PDF viewer software.

Starting your research
- Starting Your Research
- Refine your topic
- Background information & facts
What Is a research question?
Steps to developing a research question, sample research questions.
- Other information sources
- What databases should I use?
- Boolean: AND & OR
- Truncation (stemming & wildcards)
- Phrases (quotation marks)
- Database limiters
- Subjects vs. Keywords
- I found a good source. How do I get to it?
- What do I cite? (avoiding plagiarism)
- Citation style guides
- Citation Tools
- Research checklist
A research question is the question around which you center your inquiry and write your paper. It helps focus your research by providing a path through the research and writing process, and also helps you create a paper that supports a single, arguable thesis. Your research question should be:
- Clear: providing enough specifics that your audience can easily understand its purpose without needing additional explanation.
- Focused: narrow enough that it can be answered thoroughly within the length of your paper.
- Concise: expressed in the fewest possible words.
- Complex: cannot be answered through just a "yes" or "no," but requires synthesis and analysis of ideas and sources prior to the composition of an answer.
- Arguable : potential answers are open to debate rather than simple statement of facts.
As mentioned in the previous tab, it's important to select a topic you are passionate about or interested in. You will spend a lot of time with this topic, including hours of research, reading, and writing, so make sure it's something that speaks to you.
1. Choose an interesting general topic: Start with a broad topic about which you're genuinely interested. An example of a general topic might be "the Underground Railroad" or "Films of the 1930s."
2. Do some preliminary research on that general topic: Conduct quick searches in current periodicals or journals, reference books like encyclopedias (which can be found in the library's first floor reference section), or even Wikipedia, to see what's already been done and to help you narrow your focus. What issues are scholars and researchers discussing when it comes to your topic? What questions occurred to you as you've read these sources?
3. Consider your audience: For most of your papers, your audience will be academic (specifically, the professor who assigned this project), but always keep your audience in mind when narrowing your topic and devising your research question. Would that particular audience be interested in the question you've come up with?
4. Start asking questions: Now that you have a bit of a foundation laid, start asking some open-ended "how" and "why" questions about your general topic. For example, "Why was New York's Hudson Valley such a center of the Underground Railroad?" or "How was the Great Depression reflected in Hollywood films of the 1930s?"
5. Evaluate your question: Once you've come up with some possible research questions, evaluate them to determine whether they would be effective for your project, or whether they require additional revising and refining.
- Is your research question clear? Having a clear research question will help guide and direct your research, and will make it easier for you to develop your argument as you write your paper.
- Is your research question focused? You want to be sure your question is focused enough that you can deal with the topic within the length and confines of your paper. Choose too broad a topic, and you won't be able to answer it completely before you run out of room.
- Is your research question complex? Your question shouldn't be answerable with just a simple "yes" or "no," or by easily-found facts. Instead, it should require both research and analysis on your part. Often, research questions begin with "how" or "why."
- Begin your research. After you've come up with your research question, think about the possible paths your research might take you. What sources should you look for? What research process will ensure that you find a variety of perspectives and responses to your question? Lucky for you, the following tabs on this guide will help you through this process.
Unclear: How should social media sites address the harm they cause?
Clear: What action should social media sites like Twitter and Facebook take to reduce the spread of disinformation in users' newsfeeds?
The unclear version of this question doesn't specify which social media sites the writer is focusing on, or suggest what kind of harm they might be causing. It also assumes that this "harm" is proven and/or accepted. The clearer version specifies sites (Twitter and Facebook), the type of potential harm (the spread of disinformation), and who might be experiencing that harm (users). A strong research question should never leave room for ambiguity or confusion.
Unfocused: What is the effect on the environment from global warming?
Focused: What is the most significant effect of the melting of polar ice caps on the lives of polar bears in the Arctic?
The unfocused research question is so broad that it could never be properly addressed in an entire book, much less a standard college-level research paper. The focused version narrows down to a specific effect of global warming (the melting of polar ice caps), a specific place (the Arctic), and a specific population that is affected (polar bears). It also requires the writer to take a stance on which effect has the greatest impact on the affected animal. When in doubt, make a research question as narrow and focused as possible.
Too simple: How are doctors addressing diabetes in the U.S.?
Appropriately complex: What main environmental, behavioral, and genetic factors predict whether Americans will develop diabetes, and how can these commonalities be used to aid the medical community in prevention of the disease?
The simple version of this question can be looked up online and answered in a few factual sentences; it leaves no room for analysis. The more complex version is written in two parts; it is thought provoking and requires both significant investigation and evaluation from the writer. As a general rule, if a quick Google search can answer a research question, it's likely not very effective. This guide is based upon How to Write a Research Question by George Mason University's Writing Center.
- << Previous: Background information & facts
- Next: What types of sources do I need? >>
- Last Updated: Aug 28, 2024 3:05 PM
- URL: https://library.potsdam.edu/start
Crumb Library: 315-267-2485 Crane Library: 315-267-2451 [email protected] Text Us!: 315-277-3730
Accessibility
Social media, college libraries.
SUNY Potsdam College Libraries 44 Pierrepont Ave Potsdam, NY 13676
How to Develop a Research Problem/Question
The goal of this guide is to recommend an approach to developing a research problem and help writers to avoid common mistakes.
A good research question or problem is a vital part of the research process. It directs the project and helps the writer to build a solid argument. A well-developed research question helps an individual to develop a practical thesis. Thus, it is crucial to understand its purpose and features.
Purpose of a Research Problem/Question
Academic writers should center their research on a research question. This means that the research question should be clear, narrow, concise, and arguable as well as require analysis and evaluation before being answered. The purpose of a problem statement is to show the reader that the topic is significant and demands study, presents the research questions and discusses the goals of the paper, and defines the context of the topic. It is also necessary to ensure that the selected problem answers the question “so what?”. In other words, an individual is expected to show proof of having conveyed the central idea of the paper, proven its significance, and presented the implications of the research. Thus, a writer should ensure that the topic is identified clearly, the main concepts and terms are outlined, and the justification for the study is presented.
Structure and Writing Style
Types of research problems.
Several types of research problems are available to assist individuals in narrowing their topic of investigation:
- A descriptive research problem aims to present the analysis of a phenomenon and may be used for an understudied topic.
- A relational research problem underlines that the research will identify a potential link between multiple variables.
- A difference research problem is used when the study compares various phenomena and is appropriate for behavioral and clinical social sciences.
- A casuist research problem aims to identify right and wrong statements or beliefs in questions that apply general rules to moral dilemmas.
A problem statement should be authentically motivated by a gap in the existing knowledge on the topic, indicate the focus of the research, and ensure that a study is worth the reader’s attention.
Selecting a Problem
Selecting a unique, researchable, and academically relevant problem may be challenging. To do so, individuals may formulate a question from an existing theory, review the literature on the topic and note issues that have not been analyzed in detail, use personal experience, or interview experts in the field. For example, a writer may collect social workers’ opinions on the limitations of the social support system and review the literature to analyze whether the reported issues have already been addressed.
Features of a Research Statement
The writer should incorporate three main features in the research problem:
- A compelling topic followed by a convincing argument is vital; the chosen problem should be significant to both the writer and intended readers. Moreover, the study should contribute to existing knowledge and offer benefit to academic and social communities.
- A research problem should be researchable, which means that it is necessary to choose an issue that is supported by other sources. Thus, an individual should conduct a thorough prior investigation before developing a research statement.
- It is essential for the study to present various viewpoints and avoid ambivalence.
Asking Critical Questions
Research should be based on the critical questions to be analyzed. It may be feasible to list these questions at the end of the introductory paragraph to create a clear plan for the study. The number of questions depends on the aims and complexity of the research. Well-developed critical questions can:
- present a dilemma or a topic for interpretation
- provoke thought
- reveal the need for analysis
- increase the readers’ awareness of the concept or an idea
- provide an unexpected answer or solution to an issue
Avoiding Mistakes
The primary error that individuals should avoid while developing a research question is circular reasoning. The research problem should show the relevance of the investigation, present its significance, clarify existing knowledge, and suggest implications or recommendations for future studies. For example, “The research problem can be determined by the lack of relevant studies” is a weak research problem because it does not answer the “so what?” question or offer meaningful findings. It is necessary to develop a complex problem that will address the issues related to the topic, provide a comprehensive understanding of the issue, and, if possible, offer practical knowledge that readers can use.
This guide shows that the development of a research question is a crucial step for a study. An individual should aim to make a strong argument, prove that the problem is significant, and provide a detailed analysis of the topic. It is vital to consider the complexity and specificity of a research question to ensure the study presents reliable and important data that contributes to the existing knowledge on the issue.
- Types of Assignment
- Scholarly VS Popular Sources
- 4 Useful Tips to Make a Great Presentation
- How to Write Research Methodology like a Pro
- Everything You Need to Know about Quantitative Research
- Everything You Need to Know about Qualitative Research
- Evaluating Sources
- How to Write a Literature Review like a Pro
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Research process
- Writing Strong Research Questions | Criteria & Examples
Writing Strong Research Questions | Criteria & Examples
Published on 30 October 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 12 December 2023.
A research question pinpoints exactly what you want to find out in your work. A good research question is essential to guide your research paper , dissertation , or thesis .
All research questions should be:
- Focused on a single problem or issue
- Researchable using primary and/or secondary sources
- Feasible to answer within the timeframe and practical constraints
- Specific enough to answer thoroughly
- Complex enough to develop the answer over the space of a paper or thesis
- Relevant to your field of study and/or society more broadly
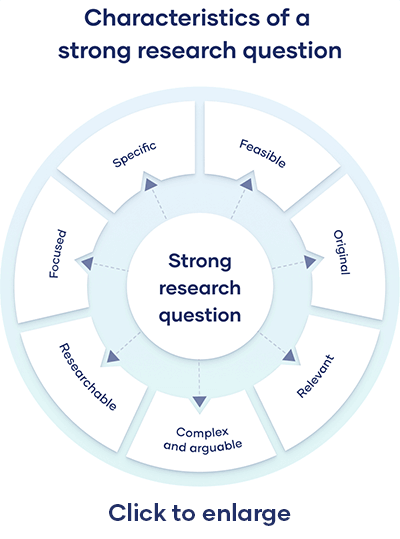
Table of contents
How to write a research question, what makes a strong research question, research questions quiz, frequently asked questions.
You can follow these steps to develop a strong research question:
- Choose your topic
- Do some preliminary reading about the current state of the field
- Narrow your focus to a specific niche
- Identify the research problem that you will address
The way you frame your question depends on what your research aims to achieve. The table below shows some examples of how you might formulate questions for different purposes.
| Research question formulations | |
|---|---|
| Describing and exploring | |
| Explaining and testing | |
| Evaluating and acting |
Using your research problem to develop your research question
| Example research problem | Example research question(s) |
|---|---|
| Teachers at the school do not have the skills to recognize or properly guide gifted children in the classroom. | What practical techniques can teachers use to better identify and guide gifted children? |
| Young people increasingly engage in the ‘gig economy’, rather than traditional full-time employment. However, it is unclear why they choose to do so. | What are the main factors influencing young people’s decisions to engage in the gig economy? |
Note that while most research questions can be answered with various types of research , the way you frame your question should help determine your choices.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Research questions anchor your whole project, so it’s important to spend some time refining them. The criteria below can help you evaluate the strength of your research question.
Focused and researchable
| Criteria | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Focused on a single topic | Your central research question should work together with your research problem to keep your work focused. If you have multiple questions, they should all clearly tie back to your central aim. |
| Answerable using | Your question must be answerable using and/or , or by reading scholarly sources on the topic to develop your argument. If such data is impossible to access, you likely need to rethink your question. |
| Not based on value judgements | Avoid subjective words like , , and . These do not give clear criteria for answering the question. |
Feasible and specific
| Criteria | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Answerable within practical constraints | Make sure you have enough time and resources to do all research required to answer your question. If it seems you will not be able to gain access to the data you need, consider narrowing down your question to be more specific. |
| Uses specific, well-defined concepts | All the terms you use in the research question should have clear meanings. Avoid vague language, jargon, and too-broad ideas. |
| Does not demand a conclusive solution, policy, or course of action | Research is about informing, not instructing. Even if your project is focused on a practical problem, it should aim to improve understanding rather than demand a ready-made solution. |
Complex and arguable
| Criteria | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Cannot be answered with or | Closed-ended, / questions are too simple to work as good research questions—they don’t provide enough scope for robust investigation and discussion. |
| Cannot be answered with easily-found facts | If you can answer the question through a single Google search, book, or article, it is probably not complex enough. A good research question requires original data, synthesis of multiple sources, and original interpretation and argumentation prior to providing an answer. |
Relevant and original
| Criteria | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Addresses a relevant problem | Your research question should be developed based on initial reading around your . It should focus on addressing a problem or gap in the existing knowledge in your field or discipline. |
| Contributes to a timely social or academic debate | The question should aim to contribute to an existing and current debate in your field or in society at large. It should produce knowledge that future researchers or practitioners can later build on. |
| Has not already been answered | You don’t have to ask something that nobody has ever thought of before, but your question should have some aspect of originality. For example, you can focus on a specific location, or explore a new angle. |
The way you present your research problem in your introduction varies depending on the nature of your research paper . A research paper that presents a sustained argument will usually encapsulate this argument in a thesis statement .
A research paper designed to present the results of empirical research tends to present a research question that it seeks to answer. It may also include a hypothesis – a prediction that will be confirmed or disproved by your research.
As you cannot possibly read every source related to your topic, it’s important to evaluate sources to assess their relevance. Use preliminary evaluation to determine whether a source is worth examining in more depth.
This involves:
- Reading abstracts , prefaces, introductions , and conclusions
- Looking at the table of contents to determine the scope of the work
- Consulting the index for key terms or the names of important scholars
An essay isn’t just a loose collection of facts and ideas. Instead, it should be centered on an overarching argument (summarised in your thesis statement ) that every part of the essay relates to.
The way you structure your essay is crucial to presenting your argument coherently. A well-structured essay helps your reader follow the logic of your ideas and understand your overall point.
A research hypothesis is your proposed answer to your research question. The research hypothesis usually includes an explanation (‘ x affects y because …’).
A statistical hypothesis, on the other hand, is a mathematical statement about a population parameter. Statistical hypotheses always come in pairs: the null and alternative hypotheses. In a well-designed study , the statistical hypotheses correspond logically to the research hypothesis.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, December 12). Writing Strong Research Questions | Criteria & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 15 October 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/the-research-process/research-question/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a research proposal | examples & templates, how to write a results section | tips & examples, what is a research methodology | steps & tips.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Research paper
Writing a Research Paper Introduction | Step-by-Step Guide
Published on September 24, 2022 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on September 5, 2024.

The introduction to a research paper is where you set up your topic and approach for the reader. It has several key goals:
- Present your topic and get the reader interested
- Provide background or summarize existing research
- Position your own approach
- Detail your specific research problem and problem statement
- Give an overview of the paper’s structure
The introduction looks slightly different depending on whether your paper presents the results of original empirical research or constructs an argument by engaging with a variety of sources.
The five steps in this article will help you put together an effective introduction for either type of research paper.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Step 1: introduce your topic, step 2: describe the background, step 3: establish your research problem, step 4: specify your objective(s), step 5: map out your paper, research paper introduction examples, frequently asked questions about the research paper introduction.
The first job of the introduction is to tell the reader what your topic is and why it’s interesting or important. This is generally accomplished with a strong opening hook.
The hook is a striking opening sentence that clearly conveys the relevance of your topic. Think of an interesting fact or statistic, a strong statement, a question, or a brief anecdote that will get the reader wondering about your topic.
For example, the following could be an effective hook for an argumentative paper about the environmental impact of cattle farming:
A more empirical paper investigating the relationship of Instagram use with body image issues in adolescent girls might use the following hook:
Don’t feel that your hook necessarily has to be deeply impressive or creative. Clarity and relevance are still more important than catchiness. The key thing is to guide the reader into your topic and situate your ideas.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

This part of the introduction differs depending on what approach your paper is taking.
In a more argumentative paper, you’ll explore some general background here. In a more empirical paper, this is the place to review previous research and establish how yours fits in.
Argumentative paper: Background information
After you’ve caught your reader’s attention, specify a bit more, providing context and narrowing down your topic.
Provide only the most relevant background information. The introduction isn’t the place to get too in-depth; if more background is essential to your paper, it can appear in the body .
Empirical paper: Describing previous research
For a paper describing original research, you’ll instead provide an overview of the most relevant research that has already been conducted. This is a sort of miniature literature review —a sketch of the current state of research into your topic, boiled down to a few sentences.
This should be informed by genuine engagement with the literature. Your search can be less extensive than in a full literature review, but a clear sense of the relevant research is crucial to inform your own work.
Begin by establishing the kinds of research that have been done, and end with limitations or gaps in the research that you intend to respond to.
The next step is to clarify how your own research fits in and what problem it addresses.
Argumentative paper: Emphasize importance
In an argumentative research paper, you can simply state the problem you intend to discuss, and what is original or important about your argument.
Empirical paper: Relate to the literature
In an empirical research paper, try to lead into the problem on the basis of your discussion of the literature. Think in terms of these questions:
- What research gap is your work intended to fill?
- What limitations in previous work does it address?
- What contribution to knowledge does it make?
You can make the connection between your problem and the existing research using phrases like the following.
| Although has been studied in detail, insufficient attention has been paid to . | You will address a previously overlooked aspect of your topic. |
| The implications of study deserve to be explored further. | You will build on something suggested by a previous study, exploring it in greater depth. |
| It is generally assumed that . However, this paper suggests that … | You will depart from the consensus on your topic, establishing a new position. |
Now you’ll get into the specifics of what you intend to find out or express in your research paper.
The way you frame your research objectives varies. An argumentative paper presents a thesis statement, while an empirical paper generally poses a research question (sometimes with a hypothesis as to the answer).
Argumentative paper: Thesis statement
The thesis statement expresses the position that the rest of the paper will present evidence and arguments for. It can be presented in one or two sentences, and should state your position clearly and directly, without providing specific arguments for it at this point.
Empirical paper: Research question and hypothesis
The research question is the question you want to answer in an empirical research paper.
Present your research question clearly and directly, with a minimum of discussion at this point. The rest of the paper will be taken up with discussing and investigating this question; here you just need to express it.
A research question can be framed either directly or indirectly.
- This study set out to answer the following question: What effects does daily use of Instagram have on the prevalence of body image issues among adolescent girls?
- We investigated the effects of daily Instagram use on the prevalence of body image issues among adolescent girls.
If your research involved testing hypotheses , these should be stated along with your research question. They are usually presented in the past tense, since the hypothesis will already have been tested by the time you are writing up your paper.
For example, the following hypothesis might respond to the research question above:
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
The final part of the introduction is often dedicated to a brief overview of the rest of the paper.
In a paper structured using the standard scientific “introduction, methods, results, discussion” format, this isn’t always necessary. But if your paper is structured in a less predictable way, it’s important to describe the shape of it for the reader.
If included, the overview should be concise, direct, and written in the present tense.
- This paper will first discuss several examples of survey-based research into adolescent social media use, then will go on to …
- This paper first discusses several examples of survey-based research into adolescent social media use, then goes on to …
Scribbr’s paraphrasing tool can help you rephrase sentences to give a clear overview of your arguments.
Full examples of research paper introductions are shown in the tabs below: one for an argumentative paper, the other for an empirical paper.
- Argumentative paper
- Empirical paper
Are cows responsible for climate change? A recent study (RIVM, 2019) shows that cattle farmers account for two thirds of agricultural nitrogen emissions in the Netherlands. These emissions result from nitrogen in manure, which can degrade into ammonia and enter the atmosphere. The study’s calculations show that agriculture is the main source of nitrogen pollution, accounting for 46% of the country’s total emissions. By comparison, road traffic and households are responsible for 6.1% each, the industrial sector for 1%. While efforts are being made to mitigate these emissions, policymakers are reluctant to reckon with the scale of the problem. The approach presented here is a radical one, but commensurate with the issue. This paper argues that the Dutch government must stimulate and subsidize livestock farmers, especially cattle farmers, to transition to sustainable vegetable farming. It first establishes the inadequacy of current mitigation measures, then discusses the various advantages of the results proposed, and finally addresses potential objections to the plan on economic grounds.
The rise of social media has been accompanied by a sharp increase in the prevalence of body image issues among women and girls. This correlation has received significant academic attention: Various empirical studies have been conducted into Facebook usage among adolescent girls (Tiggermann & Slater, 2013; Meier & Gray, 2014). These studies have consistently found that the visual and interactive aspects of the platform have the greatest influence on body image issues. Despite this, highly visual social media (HVSM) such as Instagram have yet to be robustly researched. This paper sets out to address this research gap. We investigated the effects of daily Instagram use on the prevalence of body image issues among adolescent girls. It was hypothesized that daily Instagram use would be associated with an increase in body image concerns and a decrease in self-esteem ratings.
The introduction of a research paper includes several key elements:
- A hook to catch the reader’s interest
- Relevant background on the topic
- Details of your research problem
and your problem statement
- A thesis statement or research question
- Sometimes an overview of the paper
Don’t feel that you have to write the introduction first. The introduction is often one of the last parts of the research paper you’ll write, along with the conclusion.
This is because it can be easier to introduce your paper once you’ve already written the body ; you may not have the clearest idea of your arguments until you’ve written them, and things can change during the writing process .
The way you present your research problem in your introduction varies depending on the nature of your research paper . A research paper that presents a sustained argument will usually encapsulate this argument in a thesis statement .
A research paper designed to present the results of empirical research tends to present a research question that it seeks to answer. It may also include a hypothesis —a prediction that will be confirmed or disproved by your research.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2024, September 05). Writing a Research Paper Introduction | Step-by-Step Guide. Scribbr. Retrieved October 18, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/research-paper/research-paper-introduction/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, writing strong research questions | criteria & examples, writing a research paper conclusion | step-by-step guide, research paper format | apa, mla, & chicago templates, what is your plagiarism score.
Research Skills
Creating a research question, mapping your research ideas.
For many students, having to start with a research question is the biggest difference between how they did research in high school and how they are required to carry out their college research projects. Developing a research question is a process of working from the outside in: you start with the world of all possible topics (or your assigned topic) and narrow your ideas down until you’ve focused your interest enough to be able to tell precisely what you want to find out instead of only what you want to “write about.”

All Possible Topics – You’ll need to narrow your topic in order to do research effectively. Without specific areas of focus, it will be hard to even know where to begin.
Assigned Topics – Ideas about a narrower topic can come from anywhere, and even when you are assigned a topic you typically will need to further define the focus for your project. Often, a narrower topic boils down to deciding what’s interesting to you (e.g., why do you care about the topic, how does it affect you now and/or how may it affect you in the future, etc.). One way to get ideas is to read background information in a source like Wikipedia.
Topic Narrowed by Initial Exploration – It’s helpful to do some more reading about that narrower topic to both learn more about it and learn specialized terms used by professionals and scholars who study it. You may be able to use those specialized terms to help you look for further source material to use in your project.
Topic Narrowed to Research Question(s) – A research question defines exactly what you are trying to find out. It will influence most of the steps you take to conduct the research.
Most of us look for information to answer questions every day, and we often act on the answers to those questions. You may be wondering then, are research questions any different from most of the questions for which we seek information? Yes.
See the chart below for examples of regular questions and research questions that are based on them.
| What time is my movie showing at Lennox on Friday? | How do sleeper films end up having outstanding attendance figures? |
| What can I do about my insomnia? | How do flights more than 16 hours long affect the reflexes of commercial jet pilots? |
| How many children in the U.S. have allergies? | How does his or her country of birth affect a child’s chances of developing asthma? |
| What new medicines for diabetes are under development? | Why are nanomedicines, such as doxorubicin, worth developing? |
| Could citizens register to vote at branches of the Columbus Public Library in 2012? | How do public libraries in the United States support democracy? |
| What is the Whorfian Hypothesis? | Why have linguists cared about the Whorfian hypothesis? |
| Where is the Apple, Inc. home office? | Why are Apple’s marketing efforts so successful? |
| What is Mers? | How could decision making about whether to declare a pandemic be improved? |
| Does MLA style recommend the use of generic male pronouns intended to refer to both males and females? | How do age, gender, IQ, and socioeconomic status affect whether students interpret generic male pronouns as referring to both males and females? |
Research questions cannot be answered by a quick web search. Answering them involves using more critical thinking than answering everyday questions because they seem more debatable. Research questions require more sources of information to answer and, consequently, take more time to answer. They, more often than regular questions, start with the word “How” or “Why.”
Check your understanding
- Choosing & Using Sources: A Guide to Academic Research: Narrowing your Sources. Provided by : Ohio State University Libraries. Located at : https://osu.pb.unizin.org/choosingsources/chapter/narrowing-a-topic/ . Project : Ohio State University Libraries Teaching and Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution
- Mapping your Research Ideas. Provided by : UCLA Library. Located at : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jj-F6YVtsxI . License : CC BY: Attribution

Privacy Policy
- How it works

How to Write the Research Questions – Tips & Examples
Published by Owen Ingram at August 13th, 2021 , Revised On October 3, 2023
Conducting research and writing an academic paper requires a clear direction and focus.
A good research question provides purpose to your research and clarifies the direction. It further helps your readers to understand what issue your research aims to explore and address.
If you are unsure about how to write research questions, here is a list of the attributes of a good research question;
- The research question should contain only a single problem
- You should be able to find the answer to it using primary and secondary data sources
- You should be able to address it within the time limit and other constraints
- Can attain in-depth and detailed results
- Relevant and applicable
- Should relate to your chosen field of research
Whenever you want to discover something new about a topic , you will ask a question about it. Therefore, the research question is important in the overall research process and provides the author with the reading and writing guidelines.
In a research paper or an essay, you will need to create a single research question that highlights just one problem or issue. The thesis statement should include the specific problem you aim to investigate to establish your argument’s central position or claim.
A larger project such as a dissertation or thesis , on the other hand, can have multiple research questions, but every question should focus on your main research problem . Different types of research will help you answer different research questions, but they should all be relevant to the research scope.
How to Write a Research Question
Steps to develop your research question.
- Choose a topic with a wide range of published literature
- Read and skim relevant articles to find out different problems and issues
- Specify a theoretical or practical research problem that your research question will address
- Narrow down the focus of your selected core niche

Example Research Question (s)
Here are examples of research problems and research questions to help you understand how to create a research question for a given research problem.
| Example Research Problem | Example Research Question (s) |
|---|---|
| A small-scale company, ‘A’ in the UK, cannot allocate a marketing budget for next year due to their poor revenue collection in the running year. | What practical steps can the company take to improve its revenue? |
| Many fresh graduates in the UK are working as freelancers despite having attained degrees well known academic institutes, but what is causing these youngsters to engage in this type of work? | What is the cause of fresh graduates engaging in freelance activities rather than going for full-time employment? What are the advantages and disadvantages of the gig economy for young people? How do age, gender, and academic qualification relate to people’s perception of freelancing? |
Types of Research Questions
There are two main types of research; quantitative and qualitative research . Both types of research require research questions. What research question you will answer is dependent on the type of research you wish to employ.
The first part of designing research is to find a gap and create a fully focused research question.
The following table shows common research questions for a dissertation project. However, it is important to note that these examples of dissertation research questions are straightforward, and the actual research questions may be more complicated than these examples.
| Research question type | Formulation |
|---|---|
| Descriptive approach | What will be the properties of A? |
| Comparative approach | What are the similarities and differences between A and B? |
| Correlational approach | How can you correlate variables A and B? |
| Exploratory approach | Factors affecting the rate of C? Does A and B also influence C? |
| Explanatory approach | What are the causes of C? How does B impact A? What is causing D? |
| Evaluation approach | How useful and influential is C? What role does B play? What are the advantages and disadvantages of A? |
| Action research | How can you improve X with different interventions? |
What data collection method best suits your research?
- Find out by hiring an expert from ResearchProspect today!
- Despite how challenging the subject may be, we are here to help you.
Steps to Write Research Questions
The research question provides you with a path and focuses on the real problem and the research gap you aim to fill. These are steps you need to take if you are unsure about how to write a research question:
Choose an Interesting Topic
Choose a topic of research according to your interest. The selected topic should be neither too broad nor too narrow.
Do Preliminary Research on the Topic
Find articles, books, journals, and theses relevant to your chosen topic. Understand what research problem each scholar addressed as part of their research project.
Consider your Audience
It is necessary to know your audience to develop focused research questions for your essay or dissertation. You can find aspects of your topic that could be interesting to your audience when narrowing your topic.
Start Asking Questions
What, why, when, how, and other open-ended questions will provide in-depth knowledge about the topic.
Evaluate your Question
After formulating a research question, evaluate to check its effectiveness and how it can serve the purpose. Revise and refine the dissertation research question.
- Do you have a clear research question?
It would help if you formed the research question after finding a research gap. This approach will enable the research to solve part of the problem.
- Do you have a focused research question?
It is necessary that the research question is specific and relating to the central aim of your research.
- Do you have a complex research question?
The research question cannot be answered by yes or no but requires in-depth analysis. It often begins with “How” or “Why.”
Begin your Research
After you have prepared dissertation research questions, you should research the existing literature on similar topics to find various perspectives.
Also See: Formulation of Research Question
If you have been struggling to devise research questions for your dissertation or are unsure about which topic would be suitable for your needs, then you might be interested in taking advantage of our dissertation topic and outline service, which includes several topic ideas in your preferred area of study and a 500/1000 words plan on your chosen topic. Our topic and outline service will help you jump-start your dissertation project.
Find out How Our Topics & Outline Service Can Help You!
Tips on How to Write a Strong Research Question
A research question is the foundation of the entire research. Therefore, you should spend as much time as required to refine the research question.
If you have good research questions for the dissertation, research paper , or essay, you can perform the research and analyse your results more effectively. You can evaluate the strength of the research question with the help of the following criteria. Your research question should be;
Intensive and Researchable
- It should cover a single issue
- The question shouldn’t include a subjective judgment
- It can be answerable with the data analysis or research=
Practical and Specific
- It should not include a course of action, policy, or solution
- It should be well-defined
- Answerable within research limits
Complicated and Arguable
- It should not be simple to answer
- Need in-depth knowledge to find facts
- Provides scope for debate and deliberation
Unique and Relevant
- It should lie in your field of study
- Its results should be contributable
- It should be unique
Conclusion – How to Write Research Questions
A research question provides a clear direction for research work. A bigger project, such as a dissertation, may have more than one research question, but every question should focus on one issue only.
Your research questions should be researchable, feasible to answer, specific to find results, complex (for Masters and PhD projects), and relevant to your field of study. Dissertation research questions depend upon the research type you are basing your paper on.
Start creating a research question by choosing an interesting topic, do some preliminary research, consider your audience, start asking questions, evaluating your question, and begin your research.
At ResearchProspect, we have dissertation experts for all academic subjects. Whether you need help with the individual chapters or the whole dissertation paper, you can be confident that your paper competed to the highest academic standard. There is a reason why our clients keep returning to us over and over. You can also look at our essay services if you are struggling to draft a first-class academic paper.
At ResearchProspect, we have dissertation experts for all academic subjects. Whether you need help with the individual chapters or the whole dissertation paper, you can be confident that your paper competed to the highest academic standard. There is a reason why our clients keep returning to us over and over.
You can also look at our essay services if you are struggling to draft a first-class academic paper.
Place Order
Frequently Asked Questions
How are research questions written.
Research questions are written by:
- Identifying your topic.
- Considering what you want to explore.
- Making questions clear and concise.
- Ensuring they’re researchable.
- Avoiding bias or leading language.
- Focusing on one main idea per question.
What are examples of research questions?
- Does regular exercise improve mental well-being in adults over 50?
- How do online courses impact student engagement compared to traditional classes?
- What are the economic effects of prolonged pandemic lockdowns?
- How does early childhood nutrition influence academic performance in later life?
- Does urban green space reduce stress levels?
How to write a research question?
- Identify a specific topic or issue of interest.
- Conduct preliminary research to understand existing knowledge.
- Narrow the focus to address gaps or unresolved issues.
- Phrase the question to be clear, concise, and researchable.
- Ensure it is specific enough for systematic investigation.
How to formulate my research questions for my geography dissertation?
- Identify a geographical topic or phenomenon of interest.
- Review existing literature to find gaps.
- Consider spatial, temporal, environmental, or societal aspects.
- Ensure questions are specific, feasible, and significant.
- Frame questions to guide methodology: quantitative, qualitative, or mixed.
- Seek feedback from peers/advisors.
You May Also Like
Let’s briefly examine the concept of research paradigms, their pillars, purposes, types, examples, and how they can be combined.
Repository of ten perfect research question examples will provide you a better perspective about how to create research questions.
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works
What is Perimenopause?
Menopause is the umbrella term used for the time in which your body begins to naturally stop having periods, up to the time you no longer menstruate at all. As the ovaries begin to slow down, it causes a decline in progesterone and oestrogen which are the hormones in charge of your menstrual cycle. Frequently, when people say they’re “going through the menopause”, they’re actually referring to the stage that is known as ‘perimenopause’. So, what is perimenopause ?
When does perimenopause start?
Studies show that reproductive hormone changes can be seen 8 to 10 years ahead of menopause during ‘premenopause’, however in premenopause you experience no noticeable changes in your body yet. 1
Following premenopause comes the perimenopause stage. This is marked by a significant drop in the hormones in charge of reproduction and is the transitional phase that indicates an end to your reproductive years. During this time, you will have symptoms of menopause but your periods will not yet have fully stopped. It’s often referred to as a ‘second puberty’, and can last anywhere from two to 12 years until you have not had a period for 12 months.
Unfortunately, perimenopause often sets in motion a whole host of uncomfortable symptoms.
Our 12-week programme is an online course to help you lose weight, and keep it off long-term. While many members join to lose weight and improve blood sugars, they continue on this way of life with better sleep, more energy and ongoing confidence.

What are the common symptoms?
If the questions “what is perimenopause? ” and “how will it affect me?” are on your mind, then a good place to start is looking at its common symptoms. Perimenopause is associated with symptoms such as:
- Irregular periods, often heavier or lighter than normal
- Hot flashes
- Night sweats
- Difficulty sleeping 2
- Heart palpitations
- Forgetfulness and concentration difficulties
- Mood swings and/or depression and anxiety 3
- Changes in libido and vaginal dryness
- Weight changes
As well as these common physical symptoms, perimenopause is also associated with an increased risk of developing more concerning health conditions such as:
- Osteoporosis 4
- Heart disease 5
- Breast cancer 6
How to prepare for perimenopause
While the symptoms of perimenopause may seem concerning, there are several steps you can take to lessen the impact of symptoms and prepare for perimenopause. But what is perimenopause prep, and how can you best prepare?
- Start making lifestyle changes now : It’s never too early to start preparing for a positive perimenopause journey. By making a few key lifestyle changes now, you’ll ensure your body has longer to reap the benefits. Improving your diet, daily activity, and reducing stress can have huge effects on your perimenopause experience. 7 If you need a little guidance, head to The Fast 800 Programme where you’ll find recipes designed by our team of nutritionists, exercise videos led by our fitness experts, and even mindfulness videos to help keep you motivated and more calm during this time of change.
- Eat a Mediterranean-style diet : A Mediterranean-style diet has been shown time and time again to be the healthiest way of eating, but it’s particularly effective for preparing for menopause . It helps maintain a healthy weight, combating the natural weight gain that often occurs during perimenopause, and it protects against the conditions you’re put at higher risk of developing, like cardiovascular diseases. What’s more, a Mediterranean-style diet is naturally high in protein and fibre, supporting brain health, sleep, mood, and joint, bone and skin health, all of which are important to take extra care of in the run up to perimenopause. 8
- Up your exercise : Studies have shown that exercise improves menopause symptoms like insomnia, weight gain and anxiety. In the run up to perimenopause some exercises are better than others. HIIT (High intensity interval training) can help with limiting menopause weight gain as it burns 25%-30% more calories than regular cardio, and similarly weight training is particularly effective at strengthening bones and joints, thereby reducing your risk of developing osteoporosis post-menopause. 9 Furthermore, for generally decreasing menopause symptoms, Pilates three times a week has been shown to significantly decrease unwanted symptoms. 10 For exercise guidance including beginner videos on all of these key exercises, head to The Fast 800 Programme .
- Lower your alcohol intake: You may wonder what is perimenopause to do with alcohol? Studies have found that regularly consuming alcohol negatively impacts several uncomfortable perimenopause symptoms, like night sweats and hot flashes. 11 Reducing your alcohol intake has also been associated with a reduced risk of developing breast cancer. 12 We recommend drinking mindfully both before and during perimenopause to help reduce symptom severity.
- Join a community: Perimenopause can feel like a lonely time. Evidence shows that oestrogen fluctuations place you at an increased vulnerability to depression and anxiety, so it’s important to have a community in place in the lead up to perimenopause so you can get to know others who are going through a similar thing, and know that you’re not alone in the journey you’re about to be on. This is why The Fast 800 Programme has a whole dedicated menopause Community, so our members always feel supported, and have a judgement-free space to ask questions like ‘ what is perimenopause? ’ to others who have gone through it.
We often get questions like ‘what is perimenopause?’ and how can you prepare for it, so hopefully this article has given you the answers you need to go forward into this life stage with a little more clarity. For exercise videos, healthy recipes, communities and on-hand support from our team of health experts, sign up to your 7-day free trial of The Fast 800 Programme today.
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/21837-postmenopause
Baker FC, Lampio L, Saaresranta T, Polo-Kantola P. Sleep and Sleep Disorders in the Menopausal Transition. Sleep Med Clin. 2018 Sep;13(3):443-456. doi: 10.1016/j.jsmc.2018.04.011. PMID: 30098758; PMCID: PMC6092036.
Kulkarni J. Perimenopausal depression – an under-recognised entity. Aust Prescr. 2018 Dec;41(6):183-185. doi: 10.18773/austprescr.2018.060. Epub 2018 Dec 3. PMID: 30670885; PMCID: PMC6299176
Lo JC, Burnett-Bowie SA, Finkelstein JS. Bone and the perimenopause. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am. 2011 Sep;38(3):503-17. doi: 10.1016/j.ogc.2011.07.001. PMID: 21961717; PMCID: PMC3920744.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10074318/
Surakasula A, Nagarjunapu GC, Raghavaiah KV. A comparative study of pre- and post-menopausal breast cancer: Risk factors, presentation, characteristics and management. J Res Pharm Pract. 2014 Jan;3(1):12-8. doi: 10.4103/2279-042X.132704. PMID: 24991630; PMCID: PMC4078652.
Kuck MJ, Hogervorst E. Stress, depression, and anxiety: psychological complaints across menopausal stages. Front Psychiatry. 2024 Feb 22;15:1323743. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1323743. PMID: 38455517; PMCID: PMC10917984.
Al-Anazi AF, Qureshi VF, Javaid K, Qureshi S. Preventive effects of phytoestrogens against postmenopausal osteoporosis as compared to the available therapeutic choices: An overview. J Nat Sci Biol Med. 2011 Jul;2(2):154-63. doi: 10.4103/0976-9668.92322. PMID: 22346228; PMCID: PMC3276006.
Falcone PH, Tai CY, Carson LR, Joy JM, Mosman MM, McCann TR, Crona KP, Kim MP, Moon JR. Caloric expenditure of aerobic, resistance, or combined high-intensity interval training using a hydraulic resistance system in healthy men. J Strength Cond Res. 2015 Mar;29(3):779-85. doi: 10.1519/JSC.0000000000000661. PMID: 25162652.
Lee H, Caguicla JM, Park S, Kwak DJ, Won DY, Park Y, Kim J, Kim M. Effects of 8-week Pilates exercise program on menopausal symptoms and lumbar strength and flexibility in postmenopausal women. J Exerc Rehabil. 2016 Jun 30;12(3):247-51. doi: 10.12965/jer.1632630.315. PMID: 27419122; PMCID: PMC4934971.
Leidy Sievert, L., Makhlouf Obermeyer, C., & Price, K. (2006). Determinants of hot flashes and night sweats. Annals of Human Biology, 33(1), 4–16. https://doi.org/10.1080/03014460500421338
Naomi E. Allen, Valerie Beral, Delphine Casabonne, Sau Wan Kan, Gillian K. Reeves, Anna Brown, Jane Green, on behalf of the Million Women Study Collaborators, Moderate Alcohol Intake and Cancer Incidence in Women, JNCI: Journal of the National Cancer Institute, Volume 101, Issue 5, 4 March 2009, Pages 296–305, https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/djn514
Related Articles
High fibre recipes (under 500 calories), keto pumpkin pie recipe, what to eat during menopause, never miss an update, sign up to our newsletter.
- Email (Required)
Lose weight for better health with science-based methods and real, delicious food
Weight loss for better health is easier than ever. try our programme for free today.

Nutritious products for busy days

Subscribe to our Newsletter

COMMENTS
The first question asks for a ready-made solution, and is not focused or researchable. The second question is a clearer comparative question, but note that it may not be practically feasible. For a smaller research project or thesis, it could be narrowed down further to focus on the effectiveness of drunk driving laws in just one or two countries.
A good research question is essential to guide your research paper, dissertation, or thesis. All research questions should be: Focused on a single problem or issue. Researchable using primary and/or secondary sources. Feasible to answer within the timeframe and practical constraints. Specific enough to answer thoroughly.
Descriptive research questions usually start with the word 'what' and aim to measure how a population will respond to one or more variables. Qualitative research questions. Like quantitative research questions, these questions are linked to the research design. However, qualitative research questions may deal with a specific or broad study area.
3. Narrow down your topic and determine potential research questions. Once you have gathered enough knowledge on the topic you want to pursue, you can start focusing on a more specific area of study and narrowing down a research question. One option is to focus on gaps in existing knowledge or recent literature.
Choose a broad topic, such as "learner support" or "social media influence" for your study. Select topics of interest to make research more enjoyable and stay motivated. Preliminary research. The goal is to refine and focus your research question. The following strategies can help: Skim various scholarly articles.
Most professional researchers focus on topics they are genuinely interested in studying. Writers should choose a broad topic about which they genuinely would like to know more. An example of a general topic might be "Slavery in the American South" or "Films of the 1930s.". Do some preliminary research on your general topic.
Step 4: Create a research design. The research design is a practical framework for answering your research questions. It involves making decisions about the type of data you need, the methods you'll use to collect and analyze it, and the location and timescale of your research.
Insights on Creating a Good Research Question. Junichi Tokuda, PhD, focuses on how to start successfully, and divulges the unique approach he has as a basic scientist when developing a good research question. Play Junichi Tokuda video. Ursula Kaiser, MD, encourages drawing on an already established interest in your subject matter to showcase ...
As the name suggests, the research question is the core question (or set of questions) that your study will (attempt to) answer. In many ways, a research question is akin to a target in archery. Without a clear target, you won't know where to concentrate your efforts and focus. Essentially, your research question acts as the guiding light ...
Assess your chosen research question using the FINER criteria that helps you evaluate whether the research is Feasible, Interesting, Novel, Ethical, and Relevant. 1. Formulate the final research question, while ensuring it is clear, well-written, and addresses all the key elements of a strong research question.
5. Make Every Word Count. The final step is to formulate the precise wording of your question. You may need to follow a defined format (e.g., PICO or PEO), or you can phrase the question in your own way. In either case, your research question must clearly state what the paper is about.
In a research paper, the emphasis is on generating a unique question and then synthesizing diverse sources into a coherent essay that supports your argument about the topic. In other words, you integrate information from publications with your own thoughts in order to formulate an argument. Your topic is your starting place: from here, you will ...
1. Choose an interesting general topic: Start with a broad topic about which you're genuinely interested.An example of a general topic might be "the Underground Railroad" or "Films of the 1930s." 2. Do some preliminary research on that general topic: Conduct quick searches in current periodicals or journals, reference books like encyclopedias (which can be found in the library's first floor ...
A good research question is essential to guide your research paper, project, or thesis. It pinpoints exactly what you want to find out and gives your work a ...
A good research question or problem is a vital part of the research process. It directs the project and helps the writer to build a solid argument. A well-developed research question helps an individual to develop a practical thesis. Thus, it is crucial to understand its purpose and features. Purpose of a Research Problem/Question
A good research question is essential to guide your research paper, dissertation, or thesis. All research questions should be: Focused on a single problem or issue. Researchable using primary and/or secondary sources. Feasible to answer within the timeframe and practical constraints. Specific enough to answer thoroughly.
To practice how to write a research question, we suggest the following steps: Find a nice place where you can be alone and connected with nature. Bring nothing else but a journal and a pencil. Take a few moments to breath and observe everything that surrounds you. Use all of your senses to obtain information from your surroundings: smell the ...
Table of contents. Step 1: Introduce your topic. Step 2: Describe the background. Step 3: Establish your research problem. Step 4: Specify your objective (s) Step 5: Map out your paper. Research paper introduction examples. Frequently asked questions about the research paper introduction.
Visualize narrowing a topic as starting with all possible topics and choosing narrower and narrower subsets until you have a specific enough topic to form a research question. All Possible Topics - You'll need to narrow your topic in order to do research effectively. Without specific areas of focus, it will be hard to even know where to begin.
Example Research Question (s) Here are examples of research problems and research questions to help you understand how to create a research question for a given research problem. Example Research Problem. Example Research Question (s) A small-scale company, 'A' in the UK, cannot allocate a marketing budget for next year due to their poor ...
Begin the research and writing process using the following tips: Research your question: Now that you have a research question, you can begin exploring possible answers to it. Your research question allows you to begin researching in a clear direction. Create a thesis statement: Once you have a clear understanding of your research question and ...
Format: In person on the Statesboro Campus or the Armstrong Campus in Savannah Credit Hours: 124. STARTING FALL 2025! Why major in Biomedical Science? Majoring in Biomedical Sciences at Georgia Southern University offers students a comprehensive education in the biological and health sciences, preparing them for a wide range of careers in healthcare, research, and biotechnology.
When does perimenopause start? Studies show that reproductive hormone changes can be seen 8 to 10 years ahead of menopause during 'premenopause', however in premenopause you experience no noticeable changes in your body yet. 1. Following premenopause comes the perimenopause stage.