Science Experiments On The Osmosis Of A Potato
Osmosis, the process in which solvent molecules move from an area of lower solute concentration to an area of higher solute concentration, can easily be demonstrated with potato experiments. Potatoes are full of both water and starch, and will gain water when immersed in watery solutions. Conversely, they will lose water when in concentrated solutions, such as those containing a great deal of starch. You can use potatoes to set up osmosis experiments for students of all ages and levels.

Potatoes in Saltwater
Cut a potato in two, and immerse one of the halves in a very salty solution of water — one containing a quarter cup of salt in a cup of water. Immerse the other piece in tap water containing no added salt. Leave both in their respective solutions for half an hour, then remove the potato halves from their solutions and observe their differences. The one in the salty solution will have shrunk, indicating that water is diffusing from a less concentrated solution to a more concentrated solution. The one in the tap water solution, in contrast, will actually swell slightly, indicating that it is taking in water.
Salt, Sugar and Pure Water
This experiment helps students to differentiate between different degrees of concentration gradients. Make one salt water solution, one sugar water solution, and for the third solution, simply use tap water. Make three thin potato slices — 1/2 cm thick. Place each potato slice into each of the solutions, and leave the slices in the solutions for a half hour.
Observe that the slice placed in salt is very flexible, while the slice placed in sugar is flexible, but less so. Since potatoes already contain sugar, less water will diffuse out of the potato placed in sugar water. The slice placed in water will be rigid, since it will absorb water.
Potato Lengths in Saline Solutions
Give your students potato "cylinders" that are uniform in length and size: for instance, you could cut them to be 70 mm in length and 7 mm in diameter. Make solutions of saline in three different concentrations, 20 percent, 0.9 percent and 0.1 percent. Have the students measure the lengths and diameters of the potato cylinders before and after soaking them in the saline solutions for half an hour. Then, have them calculate the changes in the lengths and diameters of the cylinders, and plot the saline concentrations versus the changes.
Potato Cube Weights
Cut potatoes into four groups of small, uniform cubes measuring 1/2 cm by 1/2 cm. Make four different solutions of sucrose: 10 percent, 5 percent, 1 percent and 0.01 percent. Weigh each group, on a mass balance, before immersing it in the appropriate sucrose solution for half an hour. After immersion, weigh each group again and have your students calculate the changes in the potato masses. Ask them to comment on why a group gained mass, lost mass or retained the same mass.
- The Teachers Corner: Science Experiment–Osmosis
Cite This Article
Lobo, Tricia. "Science Experiments On The Osmosis Of A Potato" sciencing.com , https://www.sciencing.com/science-experiments-osmosis-potato-8360195/. 26 April 2018.
Lobo, Tricia. (2018, April 26). Science Experiments On The Osmosis Of A Potato. sciencing.com . Retrieved from https://www.sciencing.com/science-experiments-osmosis-potato-8360195/
Lobo, Tricia. Science Experiments On The Osmosis Of A Potato last modified August 30, 2022. https://www.sciencing.com/science-experiments-osmosis-potato-8360195/
Recommended
Study of Osmosis by Potato Osmometer
A study of osmosis can be done using a potato osmometer. Osmosis is a phenomenon in which water moves from high solvent to low solvent concentration. The movement of water occurs between two compartments, separated by a semipermeable membrane .
The cell membrane of living organisms behaves as a semipermeable or selective membrane. The permeability of a selective membrane differs based on the size, charge and mass of different molecules.
Biological membranes are impermeable to large biomolecules and polar molecules like ions. But, non-polar molecules (lipids) and small molecules (oxygen, carbon dioxide etc.) can cross the selective barrier.
Water is the solvent that travels down or up the cell concentration gradient through osmosis. We can study water diffusion by creating two compartments and a semipermeable membrane in between.
The difference in the concentration of solutes or solvents between two compartments is the driving force responsible for water movement. Here, we need to note that only solvents can pass the selective barrier, not solutes.
Thus, the diffusion or distribution of water is related to osmosis . This post describes the meaning, requirements, procedure and results of the potato osmometer experiment.
Content: Study of Osmosis by Potato Osmometer
Potato osmometer, materials required, precautions.
It is a common experiment to demonstrate both endosmosis and exosmosis using a potato. Using a potato Osmoscope, we can study osmosis in a living system.
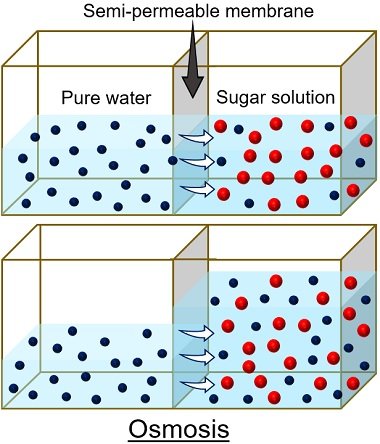
Here, a potato is used because the porous outer surface of the potato acts as a selective membrane .
- The contents within the cell form one compartment.
- The solution surrounding the cell forms another compartment.
Thus, a selective membrane separates two compartments and allows the process of osmosis .
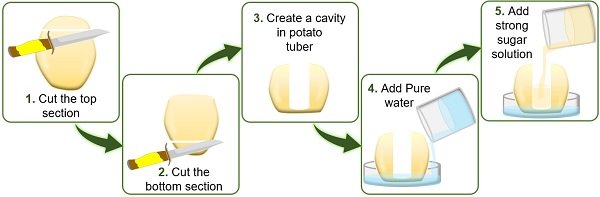
- High solvent concentration in the cell surrounding.
- Low solvent concentration in the cavity of potato tuber.
Following the rule of osmosis, water in the cell surrounding enters the tuber cavity via the cell membrane.
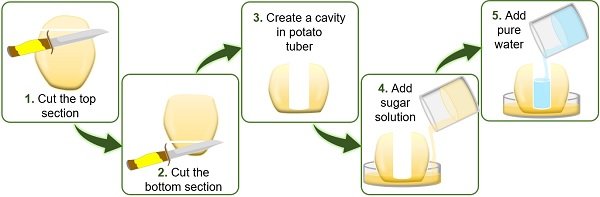
- High solvent concentration in the cavity of potato tuber.
- Low solvent concentration in the cell surrounding.
Following the rule of osmosis, water in the potato cavity enters the surrounding solution via the cell membrane.
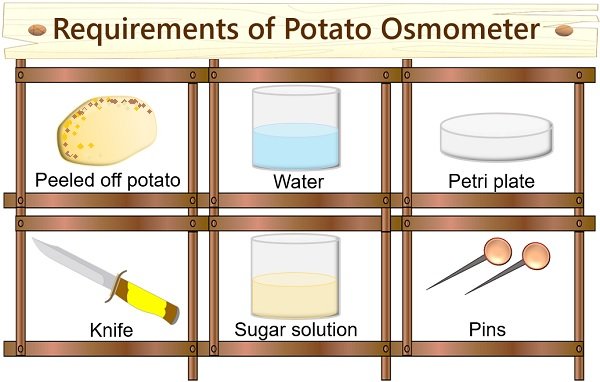
- Peeled off potato
- Concentrated sugar solution
- Petri plate
Video: Study of Osmosis
To perform the potato osmometer experiment, we need to follow the given procedure:
- First, peel off the large-sized potato using a peeler or knife.
- Then cut the upper and lower portions of the peeled potato using a knife. Through this step, we can easily place the potato on the Petri plate.
- Using a knife, make a cavity from the centre of the potato deep into the bottom, leaving some space. Here, the bottom of the potato will function as a selective membrane.
- Then, keep the potato on the Petri plate.
- To study endosmosis , pour water into half of the Petri plate. Next, pour the concentrated sugar solution into half of the cavity created in the potato.
- To study exosmosis , add concentrated sugar solution on the Petri plate and water into the cavity of the potato tuber.
- Then, fix a pin into the potato tuber-A and B to mark the level of sugar solution and water added into the cavity.
- Leave the plate undisturbed for some time until you notice any change.
Observation
- Observe the level of sugar solution in the cavity of potato tuber-A.
- Notice the level of water in the cavity of the potato tuber-B.
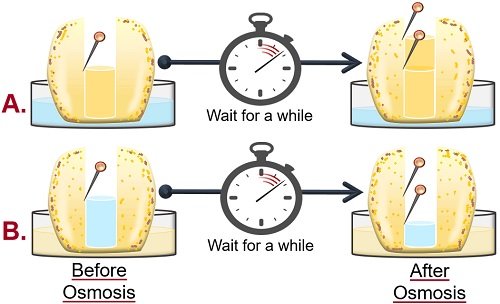
Potato Osmosis Experiment Results
- The level of sugar solution in the cavity of potato tuber-A increases . It occurs because the water in the Petri plate will move towards the cell with a high solute or low solvent concentration. This experiment shows endosmosis , as water goes into the cell or potato tuber.
- In contrast, the level of water in the cavity of potato tuber-B decreases . Here, water in the cavity moves toward the solution in the Petri plate due to the high solute concentration in the surrounding. This experiment shows exosmosis as water leaves the cell or potato tuber.
- The cavity should be deep enough by leaving a minimum thickness at the bottom.
- The sugar solution should have a high osmotic concentration.
The water movement from the Petri plate to the potato cavity or vice versa is due to the difference in the solvent or solute concentration between the two compartments.
Related Topics:
- Germination of Plant
- Difference Between Root and Stem
- Nerve Impulse
- Ozone Formation
- Examples of Adsorption in Daily Life
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Start typing and press enter to search
- Biology Article
- Study Of Osmosis By Potato Osmometer
Understanding Osmosis Using Potato Osmometer
To study by demonstrating the osmosis process by potato osmometer.
What is Osmosis?
Osmosis is the phenomena in which solvent molecules pass through a semi-permeable membrane from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. The process continues until the quantity of fluid is balanced or equalized in both regions, the region of higher concentration and the region of lower concentration of the semipermeable membrane. In other words, osmosis is the diffusion or movement of water from a region of higher water potential to a region of lower water potential.
In osmosis, what are solvent and solute?
The fluid that permeates through the semipermeable membrane is called the solvent, whereas the solute is the dissolved particles in the fluid.
What is the solution?
The mixture of solute and solvent form the solution.
List the different types of solutions.
The following are the types of solutions:
- Hypertonic solution – It is a solution with a high solute level. If living cells are placed in a hypertonic solution, because of lower concentration water moves out of the cell causing it to shrink and becomes plasmolyzed.
- Hypotonic solution – It is a solution with low concentration levels of solute. If living cells are placed in this solution, water passes into the cells because of higher water concentration in comparison to the cell causing the cells to swell and turn turgid.
- Isotonic solution – A solution is said to be isotonic if both solutions have an equal concentration of solute. If living cells are placed in an isotonic solution, no change is shown as there is the equal concentration on both the regions hence the cell retains its original shape.
Material Required
- A fresh large-sized potato tuber
- 20% sucrose solution
- Scalpel/blade
- A Bell pin needle that is labelled with a waterproof ink
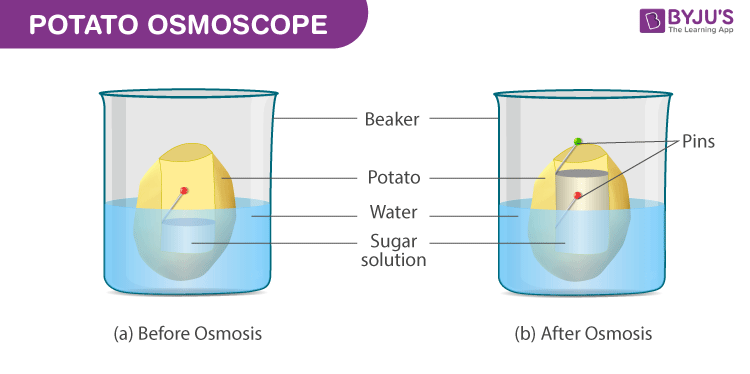
- Slice the potato tuber into two equal halves with the help of a scalpel or a blade. The outer skin is to be peeled off. Since the tuber shape is irregular, slice the halves into squares
- From the mid-region of the tuber, scoop from the soft parenchyma, so as to form a tiny cavity of a square or a circular shape. At the base, the cavity prepared should have a minimum thickness.
- Fill up half the cavity with the freshly prepared 20% sugar solution. Into the cavity, fix a pin in a way that the mark is in the same line with the layer of the sucrose solution.
- Set up the osmometer in a Petri dish/beaker that is filled with water in a way such that 75% of the potato osmometer is immersed in water
- The set up should remain uninterrupted for close to 1 hour.
- Notice the sugar solution in the osmometer towards the end of the experiment
- Carry out the experiment with the help of water in the cavity and the sucrose solution in the petri dish/beaker.
Observation
After a period of time, within the osmoscope, the sugar solution rises and is seen coloured.
- An increase in the level of sucrose solution is observed in the osmometer. It is because of the entrance of water due to endosmosis from the beaker.
- Also, a water potential gradient is built between the sucrose solution in the external water and the osmometer.
- Though both the liquids are divided by living cells of the potato tuber, they allow the entrance of water into the sugar solution.
- This demonstrates the entrance of water into the sugar solution through the tissues of potato serving as a selectively permeable membrane.
Viva Questions
Q.1. What is plasmolysis?
A.1. It is a process, wherein the protoplasm of the plant cell turns round as a result of contraction when placed in a hypertonic solution due to exosmosis resulting in the decline in the tension of the cell wall.
Q.2. What is the significance of osmosis?
A.2. Osmosis maintains cell turgidity. It causes the transportation of nutrients and discharge of metabolic waste products. It preserves the interior environment of a living entity to maintain an equilibrium between the intracellular fluid levels and water.
Q.3. What is diffusion?
A.3. The movement of molecules from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. Osmosis is a type of diffusion.
For more information on related biological concepts and experiments, please register at BYJU’S.
Related Links:

Put your understanding of this concept to test by answering a few MCQs. Click ‘Start Quiz’ to begin!
Select the correct answer and click on the “Finish” button Check your score and answers at the end of the quiz
Visit BYJU’S for all Biology related queries and study materials
Your result is as below
Request OTP on Voice Call

Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Post My Comment
Good Thank you BYJU’S!!
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
The Osmosis Lab

Introduction: The Osmosis Lab

The project idea is to apply an experiment that circulates around diffusion which is the diffusion of water molecules through a membrane which is the potato cores in this experiment. The aim of this project is to find the effect of the sucrose concentration on the mass of the potato. It's considered an essential project because it demonstrates new ideas about a lesson in science which is diffusion.
Step 1: Problem or Question

The experiment was about measuring the mass of potato cores before and after placing them inside a tube of distilled water, and 5 tubes that consist of differently concentrated solutions of sucrose in water. The research question that this experiment circulates around is how the increase in the concentration of sucrose in water affects the mass of the potato ?. Accordingly, the goal of this experiment is to discover the effect of differently concentrated solutions on the mass of the potato cores.
Step 2: Hypothesis

If the concentration of sucrose increases, then the mass of the potato cores will increase accordingly and this can be proved in the process of osmosis. In which osmosis occurs to balance between the concentration of water in a substance and in the air which adds water to air and this makes the air denser. Moreover, the potato cores mass will increase due to adding more amounts of sucrose, because when adding more amounts of sucrose the potato will swallow more sucrose which has a certain mass that will be added to the potato.
Step 3: Variables

Variables are the factors in an experiment that can be controlled, changed (affected), or measured in an experiment. The variables are divided into three different types which are the controlled variable, dependent variable, and the independent variable.
Dependent variable:
The mass of the potato cores is the dependent variable because it gets affected due to the change in the concentration of sucrose. The mass of the potato cores can be found using the weight balance which gives the mass of the potato cores in grams.
Independent variable: The concentration of sucrose is the independent variable in the experiment because the higher concentration of sucrose increases the mass of the potato cores. Moreover, the concentration of sucrose changes as the potato cores get exposed to different concentrations of sucrose which are 0.2, 0.4,0.6, 0.8, and 1.0 in order to determine the relationship between the concentration of sucrose and the potato cores mass.
Controlled variable: The water is the controlled variable because it stays constant and can be controlled by adding more amounts of water or fewer amounts of water into the testing tubes.
Step 4: Background Research

The mass is one of the factors that can be recognized from the background research because it's an essential part of many experiments. Mass is defined as a unit that measures the size of an object as weight in grams (for low weight objects), in kilograms for heavy objects, and in ton for superheavy objects such as machines. In addition, is an essential part of this experiment which is considered as a type of diffusion that can be defined as the movement of water molecules from areas of higher concentration to areas of lower concentration through a membrane. Osmosis is very similar to the other types of diffusion, in which there is only one factor that makes it different or special which is the fact that it's applied only for water molecules.
Step 5: Materials

Potato coring device
6 testing tubes
Distilled water
Weight balance
0.2 ml of the solution in water
0.4 ml of the solution in water
0.6 ml of the solution in water
0.8 ml of the solution in water
1.0 ml of the solution in water
Safety equipment: safety goggles and the lab coat
Step 6: Procedure

Before starting the experiment there were tools that were required for safety precautions which are the safety goggles the lab coat, and gloves.
-First, prepare the materials that are required for the experiment.
-Second, pour distilled water in a beaker then pour it into the testing tube until it's filled up and name it as distilled water.
-Third, pour water into the beaker then pour the water with a concentration of 0.2 ml of sucrose into the second testing tube and name it as s1.
-Fourth, pour water into the beaker then pour the water with a concentration of 0.4 ml of sucrose into the third testing tube and name it as s2.
-Fifth, pour water into the beaker then pour the water with a concentration of 0.6 ml of sucrose into the fourth testing tube and name it as s3.
-Sixth, pour water into the beaker then pour the water with a concentration of 0.8 ml of sucrose into the fifth testing tube and name it as s4.
-Seventh, pour water into the beaker then pour the water with a concentration of 1.0 ml of sucrose into the sixth testing tube and name it as s5.
-Eighth, Use the coring device to cut the potato into 12 small pieces, then remove the potato skin using the razor blade.
-Ninth, measure the mass of two potato cores using the weight balance.
-Tenth, place 2 potato cores in each testing tube and check them after 24 hours.
-Eleventh, remove the potato cores from the testing tubes and measure the weight of each two.
-Finally, record the observations and take notes.
Step 7: Data Table

Step 8: Graph

Step 9: Data Analysis

It's clearly noticeable that there is a positive relationship between the solution's concentration and the mass of the potato in which as the solution's concentration increases, the mass of the potato cores increases. In other words, the mass of the potato cores (dependent variable) depends on the solution's concentration (Independent variable) to change (positively because it increases) and throw out the experiment. For instance, when the potato cores were exposed to the first solution (0.2 g/l) the potato cores had a mass of 10.68, while when the potato cores were exposed to another solution of 0.4 g/l it had a mass of 10.72.
Step 10: Results

The results of the experiment were as the following, the potato cores which were exposed to the first solution with a concentration of 0.2 g/l had a mass of 10.68, the potato cores which were exposed to the second solution with a concentration of 0.4 g/l had a mass of 10.72, while the potato cores which were exposed to the third solution with a concentration of 0.6 g/l had a mass of 10.76. Furthermore, the potato cores which were exposed to the fourth solution with a concentration of 0.8 had a mass of 10.80, finally, the potato core that were exposed to the fifth and lastsolution with a concentration of 1.0 had a mass of 10.84.
Step 11: Conclusion

Since the data shows that the potato cores which were exposed to solution 1 which has a concentration of 0.2 g/l had a new mass of 10.68 g, the potato cores which were exposed to solution 2 which has a concentration of 0.4g/l had a new mass of 10.72 g, and the potato cores which were exposed to the solution 3 which has a concentration of 0.6 g/l had a new mass of 10.76g, the potato cores which were exposed to the solution 4 which has a concentration of 0.8 g/l had a new mass of 10.80 and the potato core which were exposed to the solution 5 which has a concentration of 1.0 had a new mass of 10.84. For that reason, the hypothesis is correct, In which each time the concentration increases, the mass of the potato cores increases accordingly as it has been noticed in the data.
Step 12: Application

This type of research is essential for humanity because it plays an essential role in plant's lives which are an essential factor for human's lives as well, as they provide the necessities for breathing (oxygen) and food. In which osmosis occurs in plants to balance between the amount of water in the air and in the plant in which the plants have higher amounts of water than air, so water diffuses into the air until the amount of water in both the plant and air is equal. But if the plant is not watered to replace the lost amount of water, it wouldn't survive so obviously it will die. This topic could be practiced in various experiments such as gummy bears and sugar cubes by exposing them to solutions with different concentrations.
Step 13: Evaluation

I utilized Communication skills by giving an introductory video that includes the necessary means to present my idea in the project clearly which included a background related to the topic. In addition, I added some photos that clearly showcase the part of the project that I am discussing (in the instructable).
Step 14: List of Refrences

Images used:
https://www.google.com/search?q=problem&safe=stric...
https://www.google.com/search?q=hypothesis&safe=st...
https://www.google.com/search?q=variables&safe=str...
https://www.google.com/search?q=background+researc...
https://www.google.com/search?q=materials+in+exper...
https://www.google.com/search?q=procedure&safe=str...
https://www.google.com/search?q=data+analysis&safe...
https://www.google.com/search?q=osmosis+lab+&tbm=i...
https://www.google.com/search?q=real+life+applicat...
https://www.google.com/search?q=evaluation&tbm=isc...
https://www.google.com/search?q=results&safe=stric...
https://www.google.com/search?q=references&safe=st...
The experiments data:
Due to the current situation and Covid-19, I couldn't collect the required materials to perform the experiment for that reason, I relied on data derived from another person's experiment.

Potato Osmosis
(Chemistry for ages 10+)
I bet you’ve heard before that the roots of a plant are responsible for absorbing water, but how exactly does that happen? It all has to do with chemistry and a process called osmosis, which means the movement of water.
The video above shows one fun way to experiment with some potato and salt water to see how osmosis works on a larger scale. Here’s how it’s done:
1 large potato or 2 small- to medium-sized potatoes Salt Water Graduated cylinder Core borer Knife Ruler 6 cups Food scale Timer Paper towels Adult supervision (Adult supervision at all times please)
- Start by coring the potato. You want at least 2-3 potato strips per cup, so be sure to create 15-20 strips so you have a couple extras just in case any don’t work out.
- After you have created all of the potato cores, you will need to “clean” them up by cutting off any skin or brown spots you see.
- Use the ruler to make each potato strip the same length. The video shows each potato strip being cut to 6 centimeters, though any length is fine as long as all pieces are the same length.
- Now it’s time to make some saltwater. Each cup will have a different concentration of salt, the first of which will be 100 mL of water and have no salt. The remaining cups will each have 100 mL of water with 1 gram of salt, 2 grams, 3 grams, 4 grams, and 5 grams, respectively. Use the graduated cylinder to accurately measure the water you add to each cup, use the food scale to weigh out the proper amount of salt, and be sure to dissolve the salt in the water. Label each cup so you can easily keep track of them.
- Once you have all of your saltwater solutions ready, add 2-3 potato strips (depending on how many you prepared) in each cup. Set a timer for 20 minutes and leave your cups undisturbed during this time.
- When 20 minutes are up, pull the potato strips out of the saltwater and lay them on a paper towel. Be sure to keep track of which potatoes came out of each solution. Using the ruler, measure the length of each potato strip and record their length. The video shows a great example of how to set up a table for recording your results. What do you notice as you measure the potato strips? Have they gotten longer? Shorter? Stay the same?
- The video shows how you can take these findings even further and chart your results into a graph. This is a great way to visualize your results and see how the different solutions impacted the size of potato pieces. Graphs are a very useful tool in the sciences, so try it out and see what you come up with!
Osmosis is the movement of water, but more specifically, it is the movement of water across a semipermeable membrane (like a cell membrane), from high concentration to low. When salt is added to your water, there is a lower concentration of water (because of the salt) than in just plain water.
Potatoes are made up of plant cells that also have water inside them, but they also have their own salts and minerals. Water will move into the potato if there are more salts within it than in the solution the potato is in (likely what you saw with the plain water), which will make the potato grow larger (it swells up with water).
This means the potato is in a hypotonic solution. You can also think of this as more water outside of the potato than in, so it moves from a higher concentration of water to a lower one. On the other hand, we have a cases where the potato is in a hypertonic solution, which means there is more salt in the solution (less water) than in the potato (more water).
In this case, water will move from its higher concentration in the potato to the lower concentration in the saltwater. This will result in the potato pieces shrinking because they are losing water to the environment they are in. There is also the possibility of an isotonic solution, which means the concentrations of salts and water are the same in both the potato and the water it’s in.
When these concentrations are the same, water doesn’t have to move one way or the other so the potato pieces will stay the same size. You might have seen this in some of your potato strips.
This can all seem pretty complicated but osmosis is an important chemical property that makes life possible. For example, the plant cells that make up the roots of a plant will have a hypertonic environment within their cells (they have more salts and less water present) so water from the ground (a hypotonic environment) will move from the dirt into the cells, giving the plant the water it needs to survive.

COMMENTS
This experiment helps students to differentiate between different degrees of concentration gradients. Make one salt water solution, one sugar water solution, and for the third solution, simply use tap water. Make three thin potato slices — 1/2 cm thick.
In this activity, we are going to explore osmosis by looking at a dataset produced with a classic classroom experiment. The experiment uses pieces of potato that are placed in six different solutions of water each with a different solute concentration. The solute is sucrose and the concentrations are measured in units of molarity.
Once the salt concentration in the cup gets higher than inside the potato cells, water moves out of the potato into the cup. This leads to shrinking of the potato cells which explains why the potato strips get smaller in length and diameter. ... Repeat the experiment with different salt concentrations. Test 1, 3, or 5 grams of salt. How do ...
Potato Osmosis Experiment Results. The level of sugar solution in the cavity of potato tuber-A increases. It occurs because the water in the Petri plate will move towards the cell with a high solute or low solvent concentration. This experiment shows endosmosis, as water goes into the cell or potato tuber. In contrast, the level of water in the ...
distilled water compared to inside the potato. Therefore water moves INTO the potato. • Because the salt water contains a lot of salt then there is less water in the salt solution compared with the concentration of water in the potato. This means that water from the potato will pass out of the potato in effort to achieve a balance.
Notice the sugar solution in the osmometer towards the end of the experiment; Carry out the experiment with the help of water in the cavity and the sucrose solution in the petri dish/beaker. Observation. After a period of time, within the osmoscope, the sugar solution rises and is seen coloured. Conclusion
Other Way to Perform Osmosis Potato Experiment for Kids . Another cool way to see osmosis in action is to perform this experiment using grapes and raisins. What You'll Need? 2 - 3 raisins; 2 - 3 fresh grapes; 3 - 4 tablespoons of sugar; 2 glasses of plain water Step-by-Step Guide on How to Perform Osmosis Potato Experiment
In this experiment the semi-permeable membrane is the cell (surface) membrane. Account for the changes - if any - in the mass and length of the strips in water, salt solution and air. Strips in water. Description - Turgid; Mass - The increase in mass of the potato strip in water is due to the movement of water molecules into the plant cells via ...
In other words, the mass of the potato cores (dependent variable) depends on the solution's concentration (Independent variable) to change (positively because it increases) and throw out the experiment. For instance, when the potato cores were exposed to the first solution (0.2 g/l) the potato cores had a mass of 10.68, while when the potato ...
In this case, water will move from its higher concentration in the potato to the lower concentration in the saltwater. This will result in the potato pieces shrinking because they are losing water to the environment they are in. There is also the possibility of an isotonic solution, which means the concentrations of salts and water are the same ...