Crafting Your Developmental Interview Essay: A Guide for Psychology Students
The field of psychology is vast and diverse, with numerous areas of study and research. One such area is developmental psychology, which focuses on understanding how people grow and change over time. A key tool used in this field is the developmental interview, a method of gathering information about an individual's experiences and perceptions at different stages of their life. This essay will delve into the intricacies of crafting a developmental interview essay, a task often assigned to psychology students to help them apply theoretical knowledge in a practical context.
<h2 style="font-weight: bold; margin: 12px 0;">What is a developmental interview essay in psychology?</h2>A developmental interview essay in psychology is a comprehensive paper that involves interviewing an individual and analyzing their responses based on developmental psychology theories. The primary objective of this type of essay is to gain a deeper understanding of the person's developmental stages and how they have influenced their current behaviors, attitudes, and beliefs. The interviewee could be a child, an adolescent, or an adult, depending on the specific focus of the study. The interviewer uses a set of predetermined questions that are designed to elicit responses related to various developmental aspects such as cognitive, emotional, social, and moral development. The responses are then analyzed and interpreted using relevant psychological theories and concepts.
<h2 style="font-weight: bold; margin: 12px 0;">How to conduct a developmental interview in psychology?</h2>Conducting a developmental interview in psychology involves several steps. First, you need to select an appropriate interviewee and obtain their consent. Next, prepare a list of questions that are relevant to the developmental stages you are interested in studying. The questions should be open-ended to encourage the interviewee to share their experiences and perceptions freely. During the interview, ensure to create a comfortable environment for the interviewee and be patient, empathetic, and non-judgmental. After the interview, transcribe the responses and analyze them using appropriate psychological theories and concepts. Finally, write your essay, presenting your findings and interpretations in a clear, logical, and coherent manner.
<h2 style="font-weight: bold; margin: 12px 0;">Which theories are commonly used in a developmental interview essay?</h2>Several theories are commonly used in a developmental interview essay, depending on the specific focus of the study. These include Piaget's cognitive development theory, Erikson's psychosocial development theory, Kohlberg's moral development theory, and Vygotsky's sociocultural theory, among others. These theories provide a framework for understanding the interviewee's developmental stages and how they have influenced their current behaviors, attitudes, and beliefs. They also guide the formulation of the interview questions and the analysis and interpretation of the responses.
<h2 style="font-weight: bold; margin: 12px 0;">Why is a developmental interview essay important in psychology studies?</h2>A developmental interview essay is important in psychology studies for several reasons. First, it provides a practical way of applying theoretical knowledge in a real-world context. Second, it offers valuable insights into the individual's developmental stages and how they have shaped their current behaviors, attitudes, and beliefs. This can help in understanding and addressing various psychological issues. Third, it enhances the researcher's interviewing, analytical, and writing skills, which are crucial in the field of psychology.
<h2 style="font-weight: bold; margin: 12px 0;">What are the challenges in writing a developmental interview essay and how to overcome them?</h2>Writing a developmental interview essay can be challenging due to several reasons. These include difficulties in selecting an appropriate interviewee, formulating relevant interview questions, creating a comfortable environment for the interview, transcribing and analyzing the responses, and writing the essay in a clear, logical, and coherent manner. To overcome these challenges, it is important to plan ahead, do thorough research, practice good interviewing skills, be patient and empathetic during the interview, and seek guidance from experienced individuals or resources.
In conclusion, crafting a developmental interview essay is a complex yet rewarding task that requires a deep understanding of developmental psychology theories, excellent interviewing skills, and proficient writing abilities. Despite the challenges involved, it offers invaluable insights into the human developmental process and enhances the researcher's practical skills. With careful planning, thorough research, and continuous practice, psychology students can master the art of writing a compelling developmental interview essay.


Related Essays
Developmental milestones and memories: how to document interviews in your essay.
The Importance of Documenting Developmental Milestones and MemoriesThe journey of life is marked by numerous developmental milestones and memories that shape our identities and personalities. These milestones, ranging from the first steps to the first words, are not just significant for the individual but also for the family and society at large. They serve as a testament to the growth and evolution of a person. Similarly, memories, both good and bad, play a crucial role in our lives. They influence our decisions, shape our perceptions, and often serve as a source of learning. Documenting these milestones and memories can provide a rich and detailed account of a person's life journey. The Art of Interviewing for Documenting Milestones and MemoriesInterviewing is a powerful tool for documenting developmental milestones and memories. It allows for a direct and personal exploration of an individual's experiences. The key to a successful interview lies in the preparation. It involves understanding the purpose of the interview, researching the subject, and formulating open-ended questions that encourage detailed responses. It's also important to create a comfortable environment for the interviewee, ensuring they feel at ease to share their experiences. Techniques for Effective Documentation in Your EssayOnce the interview is conducted, the next step is to effectively document the information in your essay. Start by organizing the information in a logical manner. This could be chronological, thematic, or based on the significance of the milestones and memories. Use direct quotes from the interviewee to maintain authenticity and add a personal touch to the essay. It's also crucial to provide context for the information, explaining why a particular milestone or memory is significant. The Role of Reflection in Documenting Milestones and MemoriesReflection is an integral part of documenting developmental milestones and memories. It involves analyzing the information gathered from the interview and interpreting it in the context of the individual's life journey. Reflection allows for a deeper understanding of the milestones and memories, revealing patterns, themes, and insights that might not be immediately apparent. It also adds depth to the essay, making it more engaging and meaningful for the reader. The Impact of Documenting Developmental Milestones and MemoriesDocumenting developmental milestones and memories has a profound impact. It not only provides a detailed account of an individual's life journey but also serves as a source of learning and inspiration for others. It can help in understanding human behavior, societal norms, and cultural practices. Moreover, it can serve as a therapeutic tool, allowing individuals to reflect on their experiences, make sense of their past, and gain a better understanding of themselves.In conclusion, documenting developmental milestones and memories through interviews is a powerful way to capture the essence of an individual's life journey. It involves careful preparation, effective interviewing techniques, thoughtful reflection, and skillful documentation. The process, while demanding, is incredibly rewarding, offering a unique insight into the human experience.
From Theory to Practice: Integrating Developmental Psychology Concepts into Your Interview Essay
The integration of developmental psychology concepts into interviews is a fascinating and complex process. It involves understanding the interviewee's developmental stage and tailoring the interview approach accordingly. This essay explores the role of developmental psychology in interviews, how these concepts can be integrated, why it's important to consider these concepts, some examples of these concepts, and who can benefit from this integration. What is the role of developmental psychology in an interview?Developmental psychology plays a significant role in interviews, particularly in understanding the interviewee's behavior, responses, and overall interaction. It provides a framework for interpreting the interviewee's responses in the context of their developmental stage. For instance, an individual in their early adulthood may exhibit different attitudes and perspectives compared to someone in their middle or late adulthood. Understanding these differences can help the interviewer tailor their questions and approach to suit the interviewee's developmental stage, thereby facilitating a more effective and insightful interview. How can developmental psychology concepts be integrated into an interview?Integrating developmental psychology concepts into an interview involves understanding the interviewee's developmental stage and tailoring the interview approach accordingly. This could involve adjusting the complexity of the questions, the level of empathy shown, or the type of feedback given. For instance, an interview with a teenager might require a more empathetic and supportive approach, while an interview with an adult might require a more direct and challenging approach. The key is to understand the interviewee's developmental needs and adjust the interview strategy to meet these needs. Why is it important to consider developmental psychology in an interview?Considering developmental psychology in an interview is important because it helps the interviewer understand the interviewee's perspective and behavior. It provides a framework for interpreting the interviewee's responses and reactions, which can lead to more insightful and meaningful conclusions. Moreover, it can help the interviewer build rapport with the interviewee, as they can tailor their approach to suit the interviewee's developmental needs. This can lead to a more effective and productive interview. What are some examples of developmental psychology concepts that can be applied in an interview?Some examples of developmental psychology concepts that can be applied in an interview include Erikson's stages of psychosocial development, Piaget's stages of cognitive development, and Kohlberg's stages of moral development. These theories provide a framework for understanding the interviewee's developmental stage and tailoring the interview approach accordingly. For instance, an understanding of Erikson's stages can help the interviewer understand the interviewee's struggles and achievements, while an understanding of Piaget's stages can help the interviewer gauge the interviewee's cognitive abilities. Who can benefit from integrating developmental psychology concepts into an interview?Both the interviewer and the interviewee can benefit from integrating developmental psychology concepts into an interview. The interviewer can gain a deeper understanding of the interviewee's perspective and behavior, leading to more insightful and meaningful conclusions. The interviewee, on the other hand, can feel more understood and supported, leading to a more positive and productive interview experience.In conclusion, integrating developmental psychology concepts into interviews can provide numerous benefits. It can help the interviewer understand the interviewee's perspective and behavior, leading to more insightful and meaningful conclusions. It can also help the interviewee feel more understood and supported, leading to a more positive and productive interview experience. As such, it is a valuable tool for anyone involved in the interview process.
The Art of the Developmental Interview: Structuring Your Essay in Early Education Studies
The art of the developmental interview is a crucial aspect of early education studies. It is a tool that allows educators and psychologists to delve into the intricate details of a child's development, providing a comprehensive understanding of their cognitive, emotional, social, and physical growth. This essay explores the purpose, structure, importance, conduct, and timing of developmental interviews in early education studies. What is the purpose of a developmental interview in early education studies?The purpose of a developmental interview in early education studies is to gather comprehensive information about a child's developmental history and current functioning. It is a tool used by educators and psychologists to understand the child's cognitive, emotional, social, and physical development. The information gathered from these interviews can help in identifying any developmental delays or issues, understanding the child's strengths and weaknesses, and planning appropriate educational interventions. It also provides insights into the child's home environment, family dynamics, and other factors that may influence their development. How is a developmental interview structured in early education studies?A developmental interview in early education studies is structured in a systematic and comprehensive manner. It typically begins with gathering background information about the child, including their family history, medical history, and developmental milestones. The interviewer then delves into specific areas of development such as cognitive, language, social, emotional, and physical development. The questions are open-ended to encourage detailed responses. The interviewer also observes the child's behavior and interactions during the interview to gather additional information. Why is a developmental interview important in early education studies?A developmental interview is crucial in early education studies as it provides a holistic view of a child's development. It helps in identifying any developmental delays or issues at an early stage, allowing for timely intervention. It also helps in understanding the child's strengths and areas of interest, which can be used to tailor their educational experiences. Furthermore, it provides insights into the child's home environment and family dynamics, which are critical factors in their development. Who conducts a developmental interview in early education studies?A developmental interview in early education studies is typically conducted by a trained professional such as a psychologist, special education teacher, or early childhood educator. These professionals have the knowledge and skills to ask appropriate questions, interpret the responses, and make accurate assessments. They also have the ability to create a comfortable and supportive environment for the child and their family during the interview. When should a developmental interview be conducted in early education studies?A developmental interview should ideally be conducted at regular intervals during a child's early years. This allows for ongoing monitoring of their development and timely identification of any issues. However, it may also be conducted if there are specific concerns about the child's development or behavior. It is also typically conducted when a child is transitioning to a new educational setting, such as starting preschool or kindergarten.In conclusion, the developmental interview is a powerful tool in early education studies. It provides a holistic view of a child's development, helping to identify any developmental delays or issues, understand the child's strengths and areas of interest, and plan appropriate educational interventions. It is conducted by trained professionals and should ideally be carried out at regular intervals during a child's early years. Understanding the art of the developmental interview is crucial for anyone involved in early education studies.
Exploring Childhood Through Words: Techniques for Writing Developmental Interview Essays
Exploring childhood through words is a fascinating journey that unveils the intricate layers of a child's development. Developmental interview essays serve as a powerful tool in this exploration, providing a window into the child's world. These essays, crafted with care and understanding, can reveal the nuances of a child's cognitive, emotional, social, and physical growth. This essay delves into the techniques for writing developmental interview essays, the importance of understanding childhood development, the beneficiaries of these essays, and the challenges encountered in the process. What are the techniques for writing developmental interview essays?The techniques for writing developmental interview essays involve a combination of research, observation, and effective communication. Firstly, it's essential to understand the developmental stages of childhood, which can be achieved through extensive research. This knowledge will guide the interview process, helping to formulate relevant questions and interpret the responses accurately. Secondly, observation plays a crucial role. Observing the child's behavior, interactions, and reactions can provide valuable insights into their developmental stage. Lastly, effective communication is key. The interviewer must establish a comfortable and trusting environment for the child to express themselves freely. Using age-appropriate language and showing empathy can help in achieving this. How does understanding childhood development aid in writing interview essays?Understanding childhood development is fundamental in writing developmental interview essays. It provides a framework to interpret the child's behaviors, emotions, and responses during the interview. By understanding the typical developmental milestones, the writer can identify any deviations, which could indicate potential issues or exceptional abilities. Moreover, it helps in formulating appropriate questions that are relevant to the child's age and developmental stage. This understanding also aids in presenting the findings in a comprehensive and insightful manner, contributing to the overall quality of the essay. Why are developmental interview essays important in exploring childhood?Developmental interview essays are important in exploring childhood as they provide a detailed insight into a child's growth and development. They help in understanding the child's cognitive, emotional, social, and physical development. These essays can reveal patterns, identify strengths and weaknesses, and highlight any developmental delays or advancements. Furthermore, they can provide valuable information for parents, educators, and psychologists, aiding in the formulation of strategies for the child's future development. Who can benefit from developmental interview essays?Developmental interview essays can benefit a wide range of individuals. Parents can gain a deeper understanding of their child's development, helping them to support their child effectively. Educators can use these essays to tailor their teaching methods to suit the developmental needs of their students. Psychologists can use the information to identify any developmental issues and devise appropriate interventions. Moreover, these essays can also benefit the children themselves by ensuring they receive the necessary support and guidance for their development. What are the challenges in writing developmental interview essays?Writing developmental interview essays can present several challenges. One of the main challenges is ensuring the child feels comfortable and safe during the interview process. The interviewer must establish a rapport with the child and use age-appropriate language. Another challenge is interpreting the child's responses accurately. Children may not express themselves as clearly as adults, and their responses may be influenced by their mood or environment. Furthermore, the writer must have a thorough understanding of childhood development to interpret the findings accurately and present them in a meaningful way.In conclusion, developmental interview essays are a valuable resource in the exploration of childhood. They require a blend of research, observation, and effective communication, underpinned by a thorough understanding of childhood development. Despite the challenges, these essays can provide profound insights into a child's world, benefiting parents, educators, psychologists, and the children themselves. As we continue to explore childhood through words, we contribute to a deeper understanding of human development, paving the way for more effective support and guidance for our future generations.
Popular Essays
Examples of Emergent Properties in Biology
The Impact of Technology on Education
The Humanistic Approach to Personality
Biblical Principles of Leadership
The Impact of Technology on Society
The New Mecca
Advantages of Autocratic Leadership
Advantages of Learning a Foreign Language
Easter Traditions in Mexico
The Tyranny of the Majority: How Long Ballots Can Lead to Unintended Consequences
Minimally Invasive and Remote: A Comprehensive Guide to Telerobotic Surgery
The Benefits of Cheerleading: Beyond the Physical - Exploring the Mental and Social Aspects
Writing a Powerful Personal Statement for the Push Group: A Step-by-Step Approach
The Rise and Fall of Carthage: A Comprehensive History
Epilogue Writing 101: A Guide for Students
My Journey to Becoming American: An Immigrant's Perspective
Gender Roles and Masculinity: A Sociological Perspective
The Role of Empathy in Conducting Successful Patient Interviews: A Guide for Medical Students
Predatory Selection in Action: Case Studies from the Animal Kingdom
Innovations in Water Taxi Technology: Enhancing Efficiency and Accessibility
The Impact of E-Commerce on Tax Laws: A Comprehensive Analysis
The Psychology of Comfort Objects: Why We Love Stuffed Animals
The Psychology of Fonts: Understanding the Impact of Typefaces on Perception and Emotion
Bilingualism and Cognitive Flexibility: The Power of Switching Between Languages
The Four Pillars of a Market Economy: A Comprehensive Essay Guide
Pet Peeves and Relationships: Navigating the Minefield
The Art of Self-Reflection: Using My Typology Essay to Navigate Life's Challenges
The Economic Benefits of Preserving National Parks: A Call to Action
Case Studies in Mandatory Corporate Censorship: Lessons Learned
Essential Anatomy of the Urinary System: From Kidneys to Bladder
Healthcare Access and Equity: Addressing the Disparities in Patient Care
The Relationship Between Minimum Wage and Inflation
St. Kateri Tekakwitha: Embodying Faith and Environmental Stewardship
From 'Stupidity' to Strength: Embracing Our Flaws and Finding Our True Potential
Mastering the Art of Level I Evidence Papers: Tips and Tricks
The Second Law of Thermodynamics: Understanding Entropy in Closed Systems
Challenging the Status Quo: A Call to Action Against Oppression
The Impact of Accountability on Army Unit Performance
Reflecting on My Growth: A Personal Essay on Learning and Transformation
Native American Housing Crisis: A Critical Examination of Solutions
The NSA Spying Scandal: A Case Study in German Privacy Law
The Significance of the Author Audience Purpose Triangle in Literary Criticism
The Urban Divide: Gentrification's Impact on Communities
Understanding the Physics Behind Surfing: A Biomechanical Analysis
Michael Phelps: A Controversial Figure: Examining the Athlete's Public Image and Impact
The Health Hazards of Bed Bugs: A Deep Dive
Ethical Dilemmas in the Real World: How Codes Can Help Students Navigate Difficult Situations
From Faith to Verse: Understanding the Significance of Prayer in Poetry
The Aging Boomer Generation: A Looming Crisis in Long-Term Care
Why do you want to be a Psychologist? 5 Sample Answers
If you are considering a career in psychology, it is essential to understand why you want to pursue this field. Whether you are preparing for a job interview or just exploring your options, “Why do you want to be a psychologist?” question is likely to come up. In this article, we will discuss how to answer this question confidently and effectively with some sample answers.
Table of Contents
What does a Psychologist do?
A psychologist is a mental health professional who studies human behavior and cognitive processes. They use various techniques and methods to assess, diagnose, and treat various psychological and emotional disorders. They also research to understand better how people think, feel, and behave. Psychologists may work in various settings, such as clinics, hospitals, schools, or private practices, specializing in clinical psychology, counseling psychology, or neuropsychology. Overall, they aim to improve people’s mental health and well-being.
🚨 Don’t Miss These🚨
Healthcare Management Interview Questions and Answers
Interview Question: Why do you want to be a nurse? Best Answers
Why do you want to work in healthcare? 7 Best Answers
Why Do You Want to Be a CNA? 5 Sample Answers
Best Nursing Interview Questions and Answers
Why do you want to be a doctor? 8 Sample Answers
How to Answer the Interview Question
To answer this question thoughtfully and confidently. Here are some tips for answering this question effectively:
Express your genuine interest in psychology.
When answering this question, showing a genuine interest in psychology is important. Express how you are passionate about understanding the human mind and behavior and believe studying psychology will help you better understand yourself and others. You can also talk about what sparked your interest in psychology, such as a favorite book, class, or research paper. Emphasize how this field aligns with your personal values and life goals.
Connect your past experiences and achievements
Another way to demonstrate your motivation and commitment to psychology is by connecting your past experiences and achievements to the field. Share experiences that demonstrate your curiosity and proactive approach to learning about psychology. You can also mention any relevant courses or extracurricular activities you participated in, such as a psychology club or volunteer work at a mental health clinic. Highlight your achievements, like research projects, papers you’ve written, or papers you’ve presented about psychology. This will show the interviewer that you have some basic knowledge about the field and can be a dedicated psychology researcher, academic, or practitioner.
Explain your career goals
If you already have career aspirations in psychology, sharing them can showcase your long-term dedication and commitment to the field. For instance, you may aspire to be a clinical psychologist, researcher, counselor, or professor of psychology. You can explain how you see the field evolving and your interest in contributing to its growth. This will illustrate your motivation and dedication to psychology and show that you’ve thought through your prospects and have a clear vision of what you want to achieve.
Highlight the values your chosen psychology school or organization represents
When applying to a specific psychology school or organization, it’s important to research its values, mission, and goals since many psychology departments have particular research or practice commitments. When answering this question, reflecting on these commitments and values will demonstrate your enthusiasm and connection to the school or organization. Perhaps you are impressed by the school’s research on a particular mental health issue, for example. Talk about why that research is important and how you would contribute.
Practice and be brief
Finally, practice with a friend or family when answering this question, and aim to be brief and to the point. Be sure to stay on topic, avoid getting sidetracked, and adopt a confident tone, expressing your desire to contribute to the field of psychology. Being concise will show you are professional and serious about being a psychologist. Start with a clear, concise statement that captures your inspiration to study psychology, and use the rest of your time to explain a few points on what you’ve learned and why psychology is important to you.
5 Good Sample Answers to “Why do you want to be a psychologist?”
- I want to be a psychologist because I am passionate about understanding human behavior and helping people improve their lives. Psychology is a fascinating field that allows us to explore the depths of the human mind and behavior. As a psychologist, I could apply this knowledge to help individuals overcome various challenges, such as anxiety, depression, trauma, and relationship issues. For instance, I have always been interested in cognitive-behavioral therapy, which helps people change negative thinking patterns contributing to emotional distress. By becoming a psychologist, I could use this approach to help clients achieve greater happiness and well-being.
- I want to be a psychologist because I believe mental health is crucial to overall well-being. Unfortunately, many people suffer from mental health problems, and there is still a great deal of stigma surrounding these issues. As a psychologist, I would be able to contribute to reducing this stigma and promoting greater awareness of the importance of mental health. Moreover, I would be able to help people struggling with mental health issues get the support and treatment they need. For example, I could work with individuals who have experienced trauma to help them process their emotions and heal from their experiences.
- I want to be a psychologist because I am fascinated by how our past experiences shape who we are and how we interact with the world around us. As a psychologist, I would have the opportunity to explore this topic in-depth and help people understand how their past experiences may affect their current behaviors and attitudes. For instance, I could work with individuals who have experienced childhood trauma to help them understand how their early experiences may impact their relationships and their ability to trust others.
- I want to be a psychologist because I am interested in the intersection between psychology and technology. As technology advances, psychologists have many exciting new opportunities to use technology to improve mental health outcomes. For example, virtual reality therapy is a new approach that shows great promise in treating anxiety and PTSD. By becoming a psychologist, I would be able to contribute to the development of these new technologies and to help ensure that they are effective and accessible to everyone who needs them.
- I want to be a psychologist because I believe psychology can make a real difference in people’s lives. By helping individuals to understand their thoughts, feelings, and behaviors, we can empower them to make positive changes and achieve their goals. Moreover, psychology has the potential to contribute to broader social and cultural changes, such as reducing prejudice and promoting greater acceptance and understanding of diverse individuals and communities. As a psychologist, I would be able to play a role in these important efforts and to help create a more just and equitable society.
Answering “Why do you want to be a psychologist?” is a great opportunity to express your passion for psychology and how it can make a real difference in people’s lives. Whether you are interested in helping individuals overcome mental health issues, exploring the intersection between psychology and technology, or contributing to broader social change, becoming a psychologist could be the perfect way to pursue your goals. By expressing your passion for psychology, you can demonstrate your commitment to the field and show that you are prepared to use your knowledge and skills to make a positive impact.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply

Interviewing, Part 2: Doing the Talking
What to say and ask during a graduate school interview..
Posted May 18, 2011 | Reviewed by Ekua Hagan
- What Is Motivation?
- Take our Burnout Test
- Find a therapist near me
In this post, we will cover the specifics of what to discuss — and not discuss — during a psychology graduate school interview. Before delving into this topic, candidates should be aware that when programs interview for admission, they can do so with different goals in mind. Allow me to explain.
During some interviews, candidates' paper applications have already been deemed "acceptable." If these candidates pass the "in-person check" by performing with no glaring problems during the interview, they will surely be accepted into the program (what I call "check mode").
In other cases, however, the interview is not merely a check, but a major factor in the decision-making process. Candidates are being compared to others and the quality of their interview performance matters a lot ("interview mode").
Finally, in a few, very select cases, a candidate might have such excellent qualifications that the program is actively trying to recruit them during the interview. That is to say, the faculty believes the individual will improve the program and its reputation and, therefore, they really want him or her to choose to attend that program ("recruit mode").
Unfortunately, it's impossible to know which goal interviewers have in mind in advance, so all candidates should play it safe and assume that their interview performance will be a major factor in their final admittance or rejection.
Talking to Faculty/Staff
Interviewing for a Ph.D. program
As discussed in the previous post about interview formats , candidates who are interviewing for Ph.D. programs in psychology will meet with one or more faculty members. During these meetings, candidates should expect to talk primarily about research. Be prepared to answer questions regarding the research you have been involved with, the research ideas you have, and the previous findings of the faculty members' research. It is imperative to be familiar with each faculty members' research before you meet them. To prepare, read some of their journal articles or book chapters and visit their labs' websites before your interview.
In these meetings, faculty members may also be interested in discussing the skills you have acquired through your previous educational and/or professional experience. This is your chance to assure a potential advisor that you are ready to hit the ground running with research if admitted. Convince him or her that you have learned many skills from your previous experience and you can start working in the lab with relatively little instruction. Be prepared to describe your skills whether they include collecting data from research participants, data analyses, experimental software programming, preparing poster presentations, or writing research reports.
Finally, faculty members will probably want to get a sense of what your personality , work-style, level of motivation , and career goals are like in general to determine if you are a good match for the way they work and train students. They might also inquire about how interested you are in coming to that program if accepted by asking, for example, which other programs you have applied to and/or heard back from, and whether or not you would like to live in the place the university is located.
Questions to Prepare For
- What experience do you have with research?
- Tell me more about (specific research project you have worked on).
- What are you interesting in doing research about as a graduate student?
- How did you become interested in research?
- What draws you to this program?
- Why do you want to be an academic?
During meetings with the faculty, you will also have the opportunity to ask questions. You should ask questions. If you do not, you will appear underprepared and uninterested in the program.
This is a very important opportunity to learn more about your potential dissertation advisor. Asking this faculty member questions and thinking over the responses should help you to understand his or her personality, expectations of graduate students, and whether or not this is someone with who you can work closely for the next four to eight years.
It is also important to ask other faculty members questions. Even if they will not be your advisor, you will still likely interact with them a good deal — they will teach classes you take, possibly serve on your exam and/or dissertation committees, and oftentimes Ph.D. students are encouraged to do research with more than one faculty member.
Questions to Ask
- What lines of research do you envision working on for the next five years?
- What could my role be like in those research projects?
- What should I expect to work on during my first year?
- How do you prefer students to propose a new research project idea?
- Do you have regular lab meetings or one-on-one meetings with your graduate students?
- Where have your students gotten jobs post-graduation?
- Are there specific hurdles that you want your students to achieve (e.g., a first-authored paper within the first three years, a conference presentation, etc.)
- What I should do to be successful in grad school?

Don't ask faculty members too much about coursework. It shows that you are more concerned with getting good grades than producing excellent research. Ask current graduate students instead.
Interviewing for a Master's program
Masters degree interviews are either one-on-one or group interviews. In one-on-one situations, interviews are conducted by a faculty member or a staff member (usually one who oversees graduate studies). He or she will likely ask you a set of questions that are more or less the same questions used in all candidate interviews.
In the beginning, the questions are usually straightforward. Expect to talk about your goals, the experiences that have prepared you to pursue your goals and be a graduate student, and the factors that drew you to the program.
The purpose of these questions is to determine how motivated and well-prepared you are to attend the program and earn a degree, but also to gain a sense of whether or not you come across as professional.
As the interview progresses, the questions might become increasingly difficult to answer. Questions might tap into your thoughts on sensitive topics (e.g., how you address difficult situations, ethical dilemmas, or politically charged topics such as race). These questions are asked to see how you react under stress.
Remember, Master's degree programs hope graduates will become polished professionals who represent the program well in the workplace and practitioner community. Putting candidates in a stressful situation during interviews is an initial way to determine if they either completely crumbling under stress or if they can handle it with composure and poise.
Masters degree interviews can also be group interviews with multiple candidates and interviewers present. Similar to one-on-one interviews, the session might begin with typical questions about your goals and experiences.
As the interview progresses, however, discussion topics might be brought up to the group of candidates. These topics might deal with questions that have no right answer, ethical dilemmas, "what would you do if" scenarios, or performing a group exercise.
This type of discussion simulates a classroom. Interviewers are interested to see how the candidates interact with other "students." Do they contribute to or dominate the conversation? Do they listen to others or ignore what they are saying?
Furthermore, oftentimes these discussions test whether candidates can view difficult questions from multiple perspectives. It is very important that future practitioners of psychology respect the ideas and beliefs of those who are very different from themselves and refrain from imposing their personal belief system on clients.
- What drew you to this program?
- What made you want to go into this field?
- What are your career goals?
- What experiences do you have that have prepared you to pursue this degree/career?
- What would you do if you were faced with (an ethical dilemma related to the field you are pursuing)?
- Tell me about a time you were faced with a difficult decision.
- Is there a particular group of people you feel more comfortable working with less?
During Master's degree program interviews, there will also be a chance for candidates to ask questions. This is an important opportunity to learn more about the program. Have a list of questions prepared. Here are some that you might want to include:
- Will I be expected to/have the option to complete a thesis?
- If I complete this degree, what additional steps will I have to take to become a licensed practitioner?
- What support is available for helping me find an internship/practicum placement?
- Where are recent alumni employed? What do most students do after graduation?
- How will this program prepare me for a Ph.D. program if I decide to pursue a Ph.D.?
- What types of financial aid are offered? What criteria are used for choosing recipients?
Another great resource on interviewing with other questions to prepare for and ask: APA Observer article .
Laura E. Buffardi, Ph.D. is a graduate school admission consultant in psychology and related fields. Visit her website to learn more about improving your graduate school application.

Laura E. Buffardi, Ph.D. , is a post-doctoral researcher in the iScience Group at Universidad de Deusto in Bilbao, Spain.
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Online Therapy
- United States
- Brooklyn, NY
- Chicago, IL
- Houston, TX
- Los Angeles, CA
- New York, NY
- Portland, OR
- San Diego, CA
- San Francisco, CA
- Seattle, WA
- Washington, DC
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Self Tests NEW
- Therapy Center
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

When we fall prey to perfectionism, we think we’re honorably aspiring to be our very best, but often we’re really just setting ourselves up for failure, as perfection is impossible and its pursuit inevitably backfires.
- Emotional Intelligence
- Gaslighting
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience

How to Write a Psychology Essay
Saul McLeod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul McLeod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
On This Page:
Before you write your essay, it’s important to analyse the task and understand exactly what the essay question is asking. Your lecturer may give you some advice – pay attention to this as it will help you plan your answer.
Next conduct preliminary reading based on your lecture notes. At this stage, it’s not crucial to have a robust understanding of key theories or studies, but you should at least have a general “gist” of the literature.
After reading, plan a response to the task. This plan could be in the form of a mind map, a summary table, or by writing a core statement (which encompasses the entire argument of your essay in just a few sentences).
After writing your plan, conduct supplementary reading, refine your plan, and make it more detailed.
It is tempting to skip these preliminary steps and write the first draft while reading at the same time. However, reading and planning will make the essay writing process easier, quicker, and ensure a higher quality essay is produced.
Components of a Good Essay
Now, let us look at what constitutes a good essay in psychology. There are a number of important features.
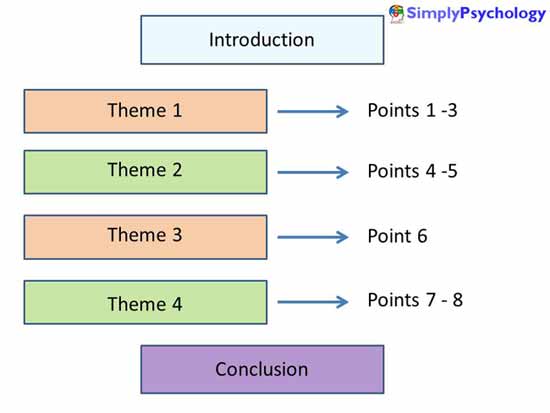
- Global Structure – structure the material to allow for a logical sequence of ideas. Each paragraph / statement should follow sensibly from its predecessor. The essay should “flow”. The introduction, main body and conclusion should all be linked.
- Each paragraph should comprise a main theme, which is illustrated and developed through a number of points (supported by evidence).
- Knowledge and Understanding – recognize, recall, and show understanding of a range of scientific material that accurately reflects the main theoretical perspectives.
- Critical Evaluation – arguments should be supported by appropriate evidence and/or theory from the literature. Evidence of independent thinking, insight, and evaluation of the evidence.
- Quality of Written Communication – writing clearly and succinctly with appropriate use of paragraphs, spelling, and grammar. All sources are referenced accurately and in line with APA guidelines.
In the main body of the essay, every paragraph should demonstrate both knowledge and critical evaluation.
There should also be an appropriate balance between these two essay components. Try to aim for about a 60/40 split if possible.
Most students make the mistake of writing too much knowledge and not enough evaluation (which is the difficult bit).
It is best to structure your essay according to key themes. Themes are illustrated and developed through a number of points (supported by evidence).
Choose relevant points only, ones that most reveal the theme or help to make a convincing and interesting argument.
Knowledge and Understanding
Remember that an essay is simply a discussion / argument on paper. Don’t make the mistake of writing all the information you know regarding a particular topic.
You need to be concise, and clearly articulate your argument. A sentence should contain no unnecessary words, a paragraph no unnecessary sentences.
Each paragraph should have a purpose / theme, and make a number of points – which need to be support by high quality evidence. Be clear why each point is is relevant to the argument. It would be useful at the beginning of each paragraph if you explicitly outlined the theme being discussed (.e.g. cognitive development, social development etc.).
Try not to overuse quotations in your essays. It is more appropriate to use original content to demonstrate your understanding.
Psychology is a science so you must support your ideas with evidence (not your own personal opinion). If you are discussing a theory or research study make sure you cite the source of the information.
Note this is not the author of a textbook you have read – but the original source / author(s) of the theory or research study.
For example:
Bowlby (1951) claimed that mothering is almost useless if delayed until after two and a half to three years and, for most children, if delayed till after 12 months, i.e. there is a critical period.
Maslow (1943) stated that people are motivated to achieve certain needs. When one need is fulfilled a person seeks to fullfil the next one, and so on.
As a general rule, make sure there is at least one citation (i.e. name of psychologist and date of publication) in each paragraph.
Remember to answer the essay question. Underline the keywords in the essay title. Don’t make the mistake of simply writing everything you know of a particular topic, be selective. Each paragraph in your essay should contribute to answering the essay question.
Critical Evaluation
In simple terms, this means outlining the strengths and limitations of a theory or research study.
There are many ways you can critically evaluate:
Methodological evaluation of research
Is the study valid / reliable ? Is the sample biased, or can we generalize the findings to other populations? What are the strengths and limitations of the method used and data obtained?
Be careful to ensure that any methodological criticisms are justified and not trite.
Rather than hunting for weaknesses in every study; only highlight limitations that make you doubt the conclusions that the authors have drawn – e.g., where an alternative explanation might be equally likely because something hasn’t been adequately controlled.
Compare or contrast different theories
Outline how the theories are similar and how they differ. This could be two (or more) theories of personality / memory / child development etc. Also try to communicate the value of the theory / study.
Debates or perspectives
Refer to debates such as nature or nurture, reductionism vs. holism, or the perspectives in psychology . For example, would they agree or disagree with a theory or the findings of the study?
What are the ethical issues of the research?
Does a study involve ethical issues such as deception, privacy, psychological or physical harm?
Gender bias
If research is biased towards men or women it does not provide a clear view of the behavior that has been studied. A dominantly male perspective is known as an androcentric bias.
Cultural bias
Is the theory / study ethnocentric? Psychology is predominantly a white, Euro-American enterprise. In some texts, over 90% of studies have US participants, who are predominantly white and middle class.
Does the theory or study being discussed judge other cultures by Western standards?
Animal Research
This raises the issue of whether it’s morally and/or scientifically right to use animals. The main criterion is that benefits must outweigh costs. But benefits are almost always to humans and costs to animals.
Animal research also raises the issue of extrapolation. Can we generalize from studies on animals to humans as their anatomy & physiology is different from humans?
The PEC System
It is very important to elaborate on your evaluation. Don’t just write a shopping list of brief (one or two sentence) evaluation points.
Instead, make sure you expand on your points, remember, quality of evaluation is most important than quantity.
When you are writing an evaluation paragraph, use the PEC system.
- Make your P oint.
- E xplain how and why the point is relevant.
- Discuss the C onsequences / implications of the theory or study. Are they positive or negative?
For Example
- Point: It is argued that psychoanalytic therapy is only of benefit to an articulate, intelligent, affluent minority.
- Explain: Because psychoanalytic therapy involves talking and gaining insight, and is costly and time-consuming, it is argued that it is only of benefit to an articulate, intelligent, affluent minority. Evidence suggests psychoanalytic therapy works best if the client is motivated and has a positive attitude.
- Consequences: A depressed client’s apathy, flat emotional state, and lack of motivation limit the appropriateness of psychoanalytic therapy for depression.
Furthermore, the levels of dependency of depressed clients mean that transference is more likely to develop.
Using Research Studies in your Essays
Research studies can either be knowledge or evaluation.
- If you refer to the procedures and findings of a study, this shows knowledge and understanding.
- If you comment on what the studies shows, and what it supports and challenges about the theory in question, this shows evaluation.
Writing an Introduction
It is often best to write your introduction when you have finished the main body of the essay, so that you have a good understanding of the topic area.
If there is a word count for your essay try to devote 10% of this to your introduction.
Ideally, the introduction should;
Identify the subject of the essay and define the key terms. Highlight the major issues which “lie behind” the question. Let the reader know how you will focus your essay by identifying the main themes to be discussed. “Signpost” the essay’s key argument, (and, if possible, how this argument is structured).
Introductions are very important as first impressions count and they can create a h alo effect in the mind of the lecturer grading your essay. If you start off well then you are more likely to be forgiven for the odd mistake later one.
Writing a Conclusion
So many students either forget to write a conclusion or fail to give it the attention it deserves.
If there is a word count for your essay try to devote 10% of this to your conclusion.
Ideally the conclusion should summarize the key themes / arguments of your essay. State the take home message – don’t sit on the fence, instead weigh up the evidence presented in the essay and make a decision which side of the argument has more support.
Also, you might like to suggest what future research may need to be conducted and why (read the discussion section of journal articles for this).
Don”t include new information / arguments (only information discussed in the main body of the essay).
If you are unsure of what to write read the essay question and answer it in one paragraph.
Points that unite or embrace several themes can be used to great effect as part of your conclusion.
The Importance of Flow
Obviously, what you write is important, but how you communicate your ideas / arguments has a significant influence on your overall grade. Most students may have similar information / content in their essays, but the better students communicate this information concisely and articulately.
When you have finished the first draft of your essay you must check if it “flows”. This is an important feature of quality of communication (along with spelling and grammar).
This means that the paragraphs follow a logical order (like the chapters in a novel). Have a global structure with themes arranged in a way that allows for a logical sequence of ideas. You might want to rearrange (cut and paste) paragraphs to a different position in your essay if they don”t appear to fit in with the essay structure.
To improve the flow of your essay make sure the last sentence of one paragraph links to first sentence of the next paragraph. This will help the essay flow and make it easier to read.
Finally, only repeat citations when it is unclear which study / theory you are discussing. Repeating citations unnecessarily disrupts the flow of an essay.
Referencing
The reference section is the list of all the sources cited in the essay (in alphabetical order). It is not a bibliography (a list of the books you used).
In simple terms every time you cite/refer to a name (and date) of a psychologist you need to reference the original source of the information.
If you have been using textbooks this is easy as the references are usually at the back of the book and you can just copy them down. If you have been using websites, then you may have a problem as they might not provide a reference section for you to copy.
References need to be set out APA style :
Author, A. A. (year). Title of work . Location: Publisher.
Journal Articles
Author, A. A., Author, B. B., & Author, C. C. (year). Article title. Journal Title, volume number (issue number), page numbers
A simple way to write your reference section is use Google scholar . Just type the name and date of the psychologist in the search box and click on the “cite” link.
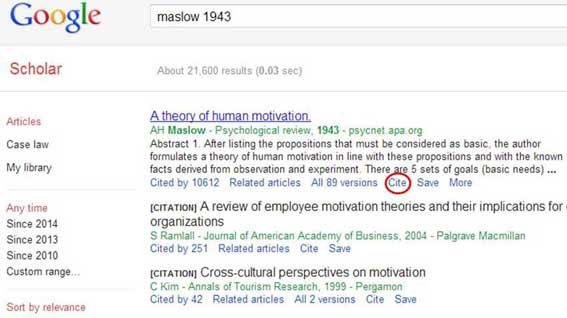
Next, copy and paste the APA reference into the reference section of your essay.

Once again, remember that references need to be in alphabetical order according to surname.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
An interview paper is a research-based essay based on information gathered in interviews with various people. While other research papers primarily cite published print sources, interview papers draw their evidence from unpublished conversations—in person, by phone or by email.
The interview method in psychology is a data collection technique where a researcher engages in direct conversation with individuals to gather information about their thoughts, experiences, and behaviors.
The methods they use are in-depth interview, together with informal interview, observation and visual method plus documents. The unique visual method used by this research compared with the above two, has certain benefits.
This essay will delve into the intricacies of crafting a developmental interview essay, a task often assigned to psychology students to help them apply theoretical knowledge in a practical context.
I decided to interview someone in the Psychology field. Psychology is in the College of Arts and Sciences. I am attracted to this major because I am currently taking an Introduction to Psychology course, and so far it is very interesting to me so far.
Express how you are passionate about understanding the human mind and behavior and believe studying psychology will help you better understand yourself and others. You can also talk about what sparked your interest in psychology, such as a favorite book, class, or research paper.
Here's how to write an interview essay, with example questions and outline ideas. Interview essays allow you to use people as your sources rather than books.
In this post, we will cover the specifics of what to discuss — and not discuss — during a psychology graduate school interview.
Now, let us look at what constitutes a good essay in psychology. There are a number of important features. Global Structure – structure the material to allow for a logical sequence of ideas. Each paragraph / statement should follow sensibly from its predecessor. The essay should “flow”.
Psychology is the study of the overall human brain and mind. There are many types of Psychology, but this quote relates to Behavioral Psychology which is studying observable behaviors rather than mental processes.